AVL koks:
AVL koks ir pašbalansējošs binārās meklēšanas koks ( BST ), kur kreisā un labā apakškoku augstumu starpība nevar būt lielāka par viens visiem mezgliem.
AVL koka piemērs:
Iepriekš minētais koks ir AVL, jo atšķirības starp kreisā un labā apakškoku augstumu katram mezglam ir mazākas vai vienādas ar 1.
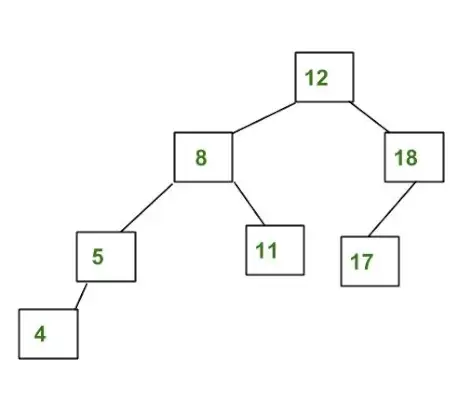
Koka piemērs, kas NAV AVL koks:

Iepriekš minētais koks nav AVL, jo 8 un 12 kreisā un labā apakškoka augstuma atšķirības ir lielākas par 1.
Kāpēc AVL koki?
Lielākā daļa BST darbību (piemēram, meklēšana, maks., min., ievietošana, dzēšana utt.) tiek veiktas O(h) laiks kur h ir BST augstums. Šo operāciju izmaksas var kļūt O(n) priekš šķībs Binārais koks . Ja pārliecināsimies, ka kokam saglabājas augstums O(log(n)) pēc katras ievietošanas un dzēšanas mēs varam garantēt augšējo robežu O(log(n)) visām šīm operācijām. AVL koka augstums vienmēr ir O(log(n)) kur n ir mezglu skaits kokā.
Ievietošana AVL kokā:
Lai pārliecinātos, ka noteiktais koks paliek AVL pēc katras ievietošanas, mums ir jāpaplašina standarta BST ievietošanas darbība, lai veiktu balansēšanu.
Tālāk ir norādītas divas pamata darbības, kuras var veikt, lai līdzsvarotu BST, nepārkāpjot BST rekvizītu (taustiņi (pa kreisi)
- Rotācija pa kreisi
- Pareiza rotācija
T1, T2 and T3 are subtrees of the tree, rooted with y (on the left side) or x (on the right side) y x / Right Rotation / x T3 - - - - - - ->T1 un / <- - - - - - - / T1 T2 Left Rotation T2 T3 Keys in both of the above trees follow the following order keys(T1) < key(x) < keys(T2) < key(y) < keys(T3) So BST property is not violated anywhere.>Ieteicamā prakse AVL koka ievietošana Izmēģiniet to!
Soļi, kas jāievēro ievietošanai:
Ļaujiet tikko ievietotajam mezglam būt In
- Izpildi standartu BST ievietot priekš In .
- Sākot no In , ceļojiet un atrodiet pirmo nesabalansēts mezgls . Ļaujiet Ar būt pirmais nelīdzsvarotais mezgls, un esi bērns no Ar kas nāk ceļā no In uz Ar un x esi mazbērns no Ar kas nāk ceļā no In uz Ar .
- Atkārtoti līdzsvarojiet koku, veicot atbilstošas rotācijas apakškokam, kas sakņojas ar Ar. Var būt 4 iespējamie gadījumi, kas jārisina kā x, y un Ar var sakārtot 4 veidos.
- Tālāk ir norādīti 4 iespējamie izkārtojumi:
- y ir z kreisais bērns un x ir y kreisais atvasinātais (kreisais kreisais burts)
- y ir z kreisais bērns, un x ir y labais atvasinātais (kreisais labais reģistrs)
- y ir z pareizais bērns, un x ir y pareizais bērns (labais labais gadījums)
- y ir z labais atbērns un x ir kreisais y atvasinātais (labais kreisais burts)
Tālāk ir norādītas operācijas, kas jāveic iepriekš minētajos 4 gadījumos. Visos gadījumos mums tikai vajag no jauna līdzsvarot apakškoks sakņojas ar Ar un viss koks kļūst līdzsvarots, jo apakškoka augstums (Pēc atbilstošām rotācijām) sakņojas ar Ar kļūst tāds pats, kāds tas bija pirms ievietošanas.
1. Kreisais kreisais korpuss
T1, T2, T3 and T4 are subtrees. z y / / y T4 Right Rotate (z) x z / - - - - - - - - ->/ / x T3 T1 T2 T3 T4 / T1 T2>
2. Kreisais labais korpuss
z z x / / / y T4 Left Rotate (y) x T4 Right Rotate(z) y z / - - - - - - - - ->/ - - - - - - - -> / / T1 x y T3 T1 T2 T3 T4 / / T2 T3 T1 T2>
3. Labais labais gadījums
z y / / T1 y Left Rotate(z) z x / - - - - - - - ->/ / T2 x T1 T2 T3 T4 / T3 T4>
4. Labais kreisais korpuss
z z x / / / T1 y Right Rotate (y) T1 x Left Rotate(z) z y / - - - - - - - - ->/ - - - - - - - -> / / x T4 T2 y T1 T2 T3 T4 / / T2 T3 T3 T4>
Ilustrācija par ievietošanu pie AVL koka





Pieeja:
Ideja ir izmantot rekursīvo BST ievietojumu, pēc ievietošanas mēs iegūstam norādes uz visiem senčiem pa vienam augšupvērstā veidā. Tāpēc mums nav nepieciešams vecāku rādītājs, lai ceļotu augšup. Pats rekursīvais kods ceļo uz augšu un apmeklē visus tikko ievietotā mezgla senčus.
Lai īstenotu ideju, veiciet tālāk norādītās darbības.
- Izpildiet parasto BST ievietošana.
- Pašreizējam mezglam ir jābūt vienam no tikko ievietotā mezgla priekštečiem. Atjauniniet augstums no pašreizējā mezgla.
- Iegūstiet līdzsvara koeficientu (kreisā apakškoka augstums – labais apakškoka augstums) no pašreizējā mezgla.
- Ja līdzsvara koeficients ir lielāks par 1, tad pašreizējais mezgls ir nelīdzsvarots, un mēs atrodamies vai nu Kreisais Kreisais korpuss vai pa kreisi Labais korpuss . Lai pārbaudītu, vai tā ir kreisais kreisais korpuss vai ne, salīdziniet tikko ievietoto atslēgu ar atslēgu kreisā apakškoka sakne .
- Ja līdzsvara koeficients ir mazāks par -1 , tad pašreizējais mezgls ir nelīdzsvarots, un mēs esam vai nu labajā labajā vai labā-kreisajā reģistrā. Lai pārbaudītu, vai tas ir pareizais reģistrs vai nē, salīdziniet tikko ievietoto atslēgu ar atslēgu labajā apakškoka saknē.
Tālāk ir aprakstīta iepriekš minētās pieejas īstenošana.
C++14
// C++ program to insert a node in AVL tree> #include> using> namespace> std;> > // An AVL tree node> class> Node> {> >public>:> >int> key;> >Node *left;> >Node *right;> >int> height;> };> > // A utility function to get the> // height of the tree> int> height(Node *N)> {> >if> (N == NULL)> >return> 0;> >return> N->augstums;>> // A utility function to get maximum> // of two integers> int> max(>int> a,>int> b)> {> >return> (a>b)? a : b;>> /* Helper function that allocates a> >new node with the given key and> >NULL left and right pointers. */> Node* newNode(>int> key)> {> >Node* node =>new> Node();> >node->atslēga = atslēga;>> // added at leaf> >return>(node);> }> > // A utility function to right> // rotate subtree rooted with y> // See the diagram given above.> Node *rightRotate(Node *y)> {> >Node *x = y->pa kreisi;>> // Perform rotation> >x->pa labi = y;>> // Update heights> >y->augstums = max(augstums(y->pa kreisi),> >height(y->pa labi)) + 1;>> >height(x->pa labi)) + 1;>> // Return new root> >return> x;> }> > // A utility function to left> // rotate subtree rooted with x> // See the diagram given above.> Node *leftRotate(Node *x)> {> >Node *y = x->pa labi;>> // Perform rotation> >y->pa kreisi = x;>> // Update heights> >x->augstums = max(augstums(x->pa kreisi),> >height(x->pa labi)) + 1;>> >height(y->pa labi)) + 1;>> // Return new root> >return> y;> }> > // Get Balance factor of node N> int> getBalance(Node *N)> {> >if> (N == NULL)> >return> 0;> >return> height(N->pa kreisi) - augstums(N->pa labi);>> // Recursive function to insert a key> // in the subtree rooted with node and> // returns the new root of the subtree.> Node* insert(Node* node,>int> key)> {> >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node == NULL)> >return>(newNode(key));> > >if> (key key)> >node->pa kreisi = ievietot(mezgls->pa kreisi, atslēga);>> if> (key>mezgls->atslēga)>> // Equal keys are not allowed in BST> >return> node;> > >/* 2. Update height of this ancestor node */> >node->augstums = 1 + max(augstums(mezgls->pa kreisi),> >height(node->pa labi));>> /* 3. Get the balance factor of this ancestor> >node to check whether this node became> >unbalanced */> >int> balance = getBalance(node);> > >// If this node becomes unbalanced, then> >// there are 4 cases> > >// Left Left Case> >if> (balance>1 && taustiņš kreisais->taustiņš)> >return> rightRotate(node);> > >// Right Right Case> >if> (balance node->labais->taustiņš)>> leftRotate(node);> > >// Left Right Case> >if> (balance>1 && taustiņš> mezgls->kreisais->taustiņš)> >{> >node->pa kreisi = pa kreisiPagriezt(mezgls->pa kreisi);>> rightRotate(node);> >}> > >// Right Left Case> >if> (balance <-1 && key right->atslēga)>> >node->pa labi = pa labiPagriezt(mezgls->pa labi);>> leftRotate(node);> >}> > >/* return the (unchanged) node pointer */> >return> node;> }> > // A utility function to print preorder> // traversal of the tree.> // The function also prints height> // of every node> void> preOrder(Node *root)> {> >if>(root != NULL)> >{> >cout ' '; preOrder(root->pa kreisi); preOrder(root->right); } } // Draivera kods int main() { Mezgls *root = NULL; /* Augšējā attēlā norādītā koka konstruēšana */ sakne = insert(root, 10); sakne = ievietot(sakne, 20); sakne = ievietot(sakne, 30); sakne = ievietot(sakne, 40); sakne = ievietot(sakne, 50); sakne = ievietot(sakne, 25); /* Izbūvētais AVL koks būtu 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50 */ cout<< 'Preorder traversal of the ' 'constructed AVL tree is
'; preOrder(root); return 0; } // This code is contributed by // rathbhupendra> |
>
>
C
// C program to insert a node in AVL tree> #include> #include> > // An AVL tree node> struct> Node> {> >int> key;> >struct> Node *left;> >struct> Node *right;> >int> height;> };> > // A utility function to get the height of the tree> int> height(>struct> Node *N)> {> >if> (N == NULL)> >return> 0;> >return> N->augstums;>> // A utility function to get maximum of two integers> int> max(>int> a,>int> b)> {> >return> (a>b)? a : b;>> /* Helper function that allocates a new node with the given key and> >NULL left and right pointers. */> struct> Node* newNode(>int> key)> {> >struct> Node* node = (>struct> Node*)> >malloc>(>sizeof>(>struct> Node));> >node->atslēga = atslēga;>> return>(node);> }> > // A utility function to right rotate subtree rooted with y> // See the diagram given above.> struct> Node *rightRotate(>struct> Node *y)> {> >struct> Node *x = y->pa kreisi;>> Node *T2 = x->pa labi;>> // Perform rotation> >x->pa labi = y;>> // Update heights> >y->augstums = max(augstums(y->pa kreisi),> >height(y->pa labi)) + 1;>> >height(x->pa labi)) + 1;>> // Return new root> >return> x;> }> > // A utility function to left rotate subtree rooted with x> // See the diagram given above.> struct> Node *leftRotate(>struct> Node *x)> {> >struct> Node *y = x->pa labi;>> Node *T2 = y->pa kreisi;>> // Perform rotation> >y->pa kreisi = x;>> // Update heights> >x->augstums = max(augstums(x->pa kreisi),> >height(x->pa labi)) + 1;>> >height(y->pa labi)) + 1;>> // Return new root> >return> y;> }> > // Get Balance factor of node N> int> getBalance(>struct> Node *N)> {> >if> (N == NULL)> >return> 0;> >return> height(N->pa kreisi) - augstums(N->pa labi);>> // Recursive function to insert a key in the subtree rooted> // with node and returns the new root of the subtree.> struct> Node* insert(>struct> Node* node,>int> key)> {> >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node == NULL)> >return>(newNode(key));> > >if> (key key)> >node->pa kreisi = ievietot(mezgls->pa kreisi, atslēga);>> if> (key>mezgls->atslēga)>> // Equal keys are not allowed in BST> >return> node;> > >/* 2. Update height of this ancestor node */> >node->augstums = 1 + max(augstums(mezgls->pa kreisi),> >height(node->pa labi));>> /* 3. Get the balance factor of this ancestor> >node to check whether this node became> >unbalanced */> >int> balance = getBalance(node);> > >// If this node becomes unbalanced, then> >// there are 4 cases> > >// Left Left Case> >if> (balance>1 && taustiņš kreisais->taustiņš)> >return> rightRotate(node);> > >// Right Right Case> >if> (balance node->labais->taustiņš)>> leftRotate(node);> > >// Left Right Case> >if> (balance>1 && taustiņš> mezgls->kreisais->taustiņš)> >{> >node->pa kreisi = pa kreisiPagriezt(mezgls->pa kreisi);>> rightRotate(node);> >}> > >// Right Left Case> >if> (balance <-1 && key right->atslēga)>> >node->pa labi = pa labiPagriezt(mezgls->pa labi);>> leftRotate(node);> >}> > >/* return the (unchanged) node pointer */> >return> node;> }> > // A utility function to print preorder traversal> // of the tree.> // The function also prints height of every node> void> preOrder(>struct> Node *root)> {> >if>(root != NULL)> >{> >printf>(>'%d '>, root->atslēga);>> }> > /* Driver program to test above function*/> int> main()> {> >struct> Node *root = NULL;> > >/* Constructing tree given in the above figure */> >root = insert(root, 10);> >root = insert(root, 20);> >root = insert(root, 30);> >root = insert(root, 40);> >root = insert(root, 50);> >root = insert(root, 25);> > >/* The constructed AVL Tree would be> >30> >/> >20 40> >/> >10 25 50> >*/> > >printf>(>'Preorder traversal of the constructed AVL'> >' tree is
'>);> >preOrder(root);> > >return> 0;> }> |
>
>
Java
// Java program for insertion in AVL Tree> class> Node {> >int> key, height;> >Node left, right;> > >Node(>int> d) {> >key = d;> >height =>1>;> >}> }> > class> AVLTree {> > >Node root;> > >// A utility function to get the height of the tree> >int> height(Node N) {> >if> (N ==>null>)> >return> 0>;> > >return> N.height;> >}> > >// A utility function to get maximum of two integers> >int> max(>int> a,>int> b) {> >return> (a>b)? a : b;>> > >// A utility function to right rotate subtree rooted with y> >// See the diagram given above.> >Node rightRotate(Node y) {> >Node x = y.left;> >Node T2 = x.right;> > >// Perform rotation> >x.right = y;> >y.left = T2;> > >// Update heights> >y.height = max(height(y.left), height(y.right)) +>1>;> >x.height = max(height(x.left), height(x.right)) +>1>;> > >// Return new root> >return> x;> >}> > >// A utility function to left rotate subtree rooted with x> >// See the diagram given above.> >Node leftRotate(Node x) {> >Node y = x.right;> >Node T2 = y.left;> > >// Perform rotation> >y.left = x;> >x.right = T2;> > >// Update heights> >x.height = max(height(x.left), height(x.right)) +>1>;> >y.height = max(height(y.left), height(y.right)) +>1>;> > >// Return new root> >return> y;> >}> > >// Get Balance factor of node N> >int> getBalance(Node N) {> >if> (N ==>null>)> >return> 0>;> > >return> height(N.left) - height(N.right);> >}> > >Node insert(Node node,>int> key) {> > >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node ==>null>)> >return> (>new> Node(key));> > >if> (key node.left = insert(node.left, key); else if (key>mezgls.atslēga) node.right = insert(mezgls.labais, atslēga); else // Dublētas atslēgas nav atļautas atgriešanas mezgls; /* 2. Atjaunināt šī priekšteča mezgla augstumu */ node.height = 1 + max(height(node.left), height(node.right)); /* 3. Iegūstiet šī priekšteča mezgla līdzsvara koeficientu, lai pārbaudītu, vai šis mezgls nav bijis nelīdzsvarots */ int balance = getBalance(node); // Ja šis mezgls kļūst nelīdzsvarots, tad ir // 4 gadījumi Left Left Case if (bilance> 1 && key return rightRotate(node); // Right Right Case if (balance<-1 && key>node.right.key) return leftRotate(node); // Left Right Case if (bilance> 1 && key> node.left.key) { node.left = leftRotate(node.left); atgriezties pa labiPagriezt(mezgls); } // Labais kreisais burts if (balanss<-1 && key node.right = rightRotate(node.right); return leftRotate(node); } /* return the (unchanged) node pointer */ return node; } // A utility function to print preorder traversal // of the tree. // The function also prints height of every node void preOrder(Node node) { if (node != null) { System.out.print(node.key + ' '); preOrder(node.left); preOrder(node.right); } } public static void main(String[] args) { AVLTree tree = new AVLTree(); /* Constructing tree given in the above figure */ tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 10); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 20); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 30); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 40); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 50); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 25); /* The constructed AVL Tree would be 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50 */ System.out.println('Preorder traversal' + ' of constructed tree is : '); tree.preOrder(tree.root); } } // This code has been contributed by Mayank Jaiswal> |
>
>
Python3
# Python code to insert a node in AVL tree> > # Generic tree node class> class> TreeNode(>object>):> >def> __init__(>self>, val):> >self>.val>=> val> >self>.left>=> None> >self>.right>=> None> >self>.height>=> 1> > # AVL tree class which supports the> # Insert operation> class> AVL_Tree(>object>):> > ># Recursive function to insert key in> ># subtree rooted with node and returns> ># new root of subtree.> >def> insert(>self>, root, key):> > ># Step 1 - Perform normal BST> >if> not> root:> >return> TreeNode(key)> >elif> key root.left = self.insert(root.left, key) else: root.right = self.insert(root.right, key) # Step 2 - Update the height of the # ancestor node root.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(root.left), self.getHeight(root.right)) # Step 3 - Get the balance factor balance = self.getBalance(root) # Step 4 - If the node is unbalanced, # then try out the 4 cases # Case 1 - Left Left if balance>1 un atslēga atgriež self.rightRotate(root) # 2. gadījums — pa labi, ja līdzsvars<-1 and key>root.right.val: return self.leftRotate(root) # 3. gadījums — pa kreisi pa labi, ja līdzsvars> 1 un taustiņš> root.left.val: root.left = self.leftRotate(root.left) atgriezties self.rightRotate(root) ) # 4. gadījums — pa labi pa kreisi, ja līdzsvars<-1 and key root.right = self.rightRotate(root.right) return self.leftRotate(root) return root def leftRotate(self, z): y = z.right T2 = y.left # Perform rotation y.left = z z.right = T2 # Update heights z.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(z.left), self.getHeight(z.right)) y.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(y.left), self.getHeight(y.right)) # Return the new root return y def rightRotate(self, z): y = z.left T3 = y.right # Perform rotation y.right = z z.left = T3 # Update heights z.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(z.left), self.getHeight(z.right)) y.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(y.left), self.getHeight(y.right)) # Return the new root return y def getHeight(self, root): if not root: return 0 return root.height def getBalance(self, root): if not root: return 0 return self.getHeight(root.left) - self.getHeight(root.right) def preOrder(self, root): if not root: return print('{0} '.format(root.val), end='') self.preOrder(root.left) self.preOrder(root.right) # Driver program to test above function myTree = AVL_Tree() root = None root = myTree.insert(root, 10) root = myTree.insert(root, 20) root = myTree.insert(root, 30) root = myTree.insert(root, 40) root = myTree.insert(root, 50) root = myTree.insert(root, 25) '''The constructed AVL Tree would be 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50''' # Preorder Traversal print('Preorder traversal of the', 'constructed AVL tree is') myTree.preOrder(root) print() # This code is contributed by Ajitesh Pathak> |
>
>
C#
// C# program for insertion in AVL Tree> using> System;> > class> Node> {> >public> int> key, height;> >public> Node left, right;> > >public> Node(>int> d)> >{> >key = d;> >height = 1;> >}> }> > public> class> AVLTree> {> > >Node root;> > >// A utility function to get> >// the height of the tree> >int> height(Node N)> >{> >if> (N ==>null>)> >return> 0;> > >return> N.height;> >}> > >// A utility function to get> >// maximum of two integers> >int> max(>int> a,>int> b)> >{> >return> (a>b)? a : b;>> > >// A utility function to right> >// rotate subtree rooted with y> >// See the diagram given above.> >Node rightRotate(Node y)> >{> >Node x = y.left;> >Node T2 = x.right;> > >// Perform rotation> >x.right = y;> >y.left = T2;> > >// Update heights> >y.height = max(height(y.left),> >height(y.right)) + 1;> >x.height = max(height(x.left),> >height(x.right)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> x;> >}> > >// A utility function to left> >// rotate subtree rooted with x> >// See the diagram given above.> >Node leftRotate(Node x)> >{> >Node y = x.right;> >Node T2 = y.left;> > >// Perform rotation> >y.left = x;> >x.right = T2;> > >// Update heights> >x.height = max(height(x.left),> >height(x.right)) + 1;> >y.height = max(height(y.left),> >height(y.right)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> y;> >}> > >// Get Balance factor of node N> >int> getBalance(Node N)> >{> >if> (N ==>null>)> >return> 0;> > >return> height(N.left) - height(N.right);> >}> > >Node insert(Node node,>int> key)> >{> > >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node ==>null>)> >return> (>new> Node(key));> > >if> (key node.left = insert(node.left, key); else if (key>mezgls.atslēga) node.right = insert(mezgls.labais, atslēga); else // Dublētas atslēgas nav atļautas atgriešanas mezgls; /* 2. Atjaunināt šī priekšteča mezgla augstumu */ node.height = 1 + max(height(node.left), height(node.right)); /* 3. Iegūstiet šī priekšteča mezgla līdzsvara koeficientu, lai pārbaudītu, vai šis mezgls nav bijis nelīdzsvarots */ int balance = getBalance(node); // Ja šis mezgls kļūst nelīdzsvarots, tad ir // 4 gadījumi Left Left Case if (bilance> 1 && key return rightRotate(node); // Right Right Case if (balansa mezgls.right.key) return leftRotate(node) // Left Right Case if (balance> 1 && key> node.left.key) { node.left = leftRotate(node.left) // Right Left Case if (balanss);<-1 && key < node.right.key) { node.right = rightRotate(node.right); return leftRotate(node); } /* return the (unchanged) node pointer */ return node; } // A utility function to print preorder traversal // of the tree. // The function also prints height of every node void preOrder(Node node) { if (node != null) { Console.Write(node.key + ' '); preOrder(node.left); preOrder(node.right); } } // Driver code public static void Main(String[] args) { AVLTree tree = new AVLTree(); /* Constructing tree given in the above figure */ tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 10); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 20); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 30); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 40); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 50); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 25); /* The constructed AVL Tree would be 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50 */ Console.Write('Preorder traversal' + ' of constructed tree is : '); tree.preOrder(tree.root); } } // This code has been contributed // by PrinciRaj1992> |
>
>
Javascript
> > >// JavaScript program for insertion in AVL Tree> >class Node {> >constructor(d) {> >this>.key = d;> >this>.height = 1;> >this>.left =>null>;> >this>.right =>null>;> >}> >}> > >class AVLTree {> >constructor() {> >this>.root =>null>;> >}> > >// A utility function to get> >// the height of the tree> >height(N) {> >if> (N ==>null>)>return> 0;> > >return> N.height;> >}> > >// A utility function to get> >// maximum of two integers> >max(a, b) {> >return> a>b ? a : b;>> > >// A utility function to right> >// rotate subtree rooted with y> >// See the diagram given above.> >rightRotate(y) {> >var> x = y.left;> >var> T2 = x.right;> > >// Perform rotation> >x.right = y;> >y.left = T2;> > >// Update heights> >y.height =>this>.max(>this>.height(y.left),> >this>.height(y.right)) + 1;> >x.height =>this>.max(>this>.height(x.left),> >this>.height(x.right)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> x;> >}> > >// A utility function to left> >// rotate subtree rooted with x> >// See the diagram given above.> >leftRotate(x) {> >var> y = x.right;> >var> T2 = y.left;> > >// Perform rotation> >y.left = x;> >x.right = T2;> > >// Update heights> >x.height =>this>.max(>this>.height(x.left),> >this>.height(x.right)) + 1;> >y.height =>this>.max(>this>.height(y.left),> >this>.height(y.right)) + 1;> > >// Return new root> >return> y;> >}> > >// Get Balance factor of node N> >getBalance(N) {> >if> (N ==>null>)>return> 0;> > >return> this>.height(N.left) ->this>.height(N.right);> >}> > >insert(node, key) {> >/* 1. Perform the normal BST insertion */> >if> (node ==>null>)>return> new> Node(key);> > >if> (key node.left = this.insert(node.left, key); else if (key>mezgls.atslēga) node.right = this.insert(mezgls.labais, atslēga); // Dublētas atslēgas nav atļautas, pretējā gadījumā atgriežas mezgls; /* 2. Atjauniniet šī priekšteča mezgla augstumu */ node.height = 1 + this.max(this.height(node.left), this.height(node.right)); /* 3. Iegūstiet šī priekšteča mezgla līdzsvara koeficientu, lai pārbaudītu, vai šis mezgls nav bijis nelīdzsvarots */ var balance = this.getBalance(node); // Ja šis mezgls kļūst nelīdzsvarots, tad ir // 4 gadījumi Left Left Case if (bilance> 1 && key return this.rightRotate(node); // Right Right Case if (balance node.right.key) atgriež šo. leftRotate(node); // Left Right Case if (balance> 1 && key> node.left.key) { node.left = this.leftRotate(node.left) return this.right(node); Kreisais burts, ja (bilance<-1 && key < node.right.key) { node.right = this.rightRotate(node.right); return this.leftRotate(node); } /* return the (unchanged) node pointer */ return node; } // A utility function to print preorder traversal // of the tree. // The function also prints height of every node preOrder(node) { if (node != null) { document.write(node.key + ' '); this.preOrder(node.left); this.preOrder(node.right); } } } // Driver code var tree = new AVLTree(); /* Constructing tree given in the above figure */ tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 10); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 20); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 30); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 40); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 50); tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 25); /* The constructed AVL Tree would be 30 / 20 40 / 10 25 50 */ document.write( 'Preorder traversal of the ' + 'constructed AVL tree is ' ); tree.preOrder(tree.root);> |
>
>Izvade
Preorder traversal of the constructed AVL tree is 30 20 10 25 40 50>
Sarežģītības analīze
Laika sarežģītība: O(log(n)), ievietošanai
Palīgtelpa: O(1)
java uzlabota cilpa
Rotācijas darbības (griešanās pa kreisi un pa labi) aizņem nemainīgu laiku, jo tur tiek mainītas tikai dažas norādes. Arī augstuma atjaunināšana un līdzsvara faktora iegūšana prasa pastāvīgu laiku. Tātad AVL ieliktņa laika sarežģītība paliek tāda pati kā BST ievietojumam, kas ir O (h), kur h ir koka augstums. Tā kā AVL koks ir līdzsvarots, augstums ir O (Logn). Tātad AVL ievietojuma laika sarežģītība ir O (Logn).
Salīdzinājums ar Red Black Tree:
AVL koks un citi pašbalansējošie meklēšanas koki, piemēram, Red Black, ir noderīgi, lai visas pamatdarbības veiktu O(log n) laikā. AVL koki ir līdzsvarotāki salīdzinājumā ar sarkanmelnajiem kokiem, taču tie var izraisīt lielāku rotāciju ievietošanas un dzēšanas laikā. Tātad, ja jūsu lietojumprogrammā ir daudz biežu ievietošanas un dzēšanas, priekšroka jādod sarkanmelnajiem kokiem. Un, ja ievietošana un dzēšana notiek retāk un biežāk tiek veikta meklēšana, tad priekšroka jādod AVL kokam, nevis Red Black Tree .
Šis ir ieraksts dzēšanai AVL kokā:
AVL koks | 2. kopa (dzēšana)
