Eilera ceļš ir ceļš grafikā, kas katru malu apmeklē tieši vienu reizi. Eilera ķēde ir Eilera ceļš, kas sākas un beidzas vienā virsotnē.
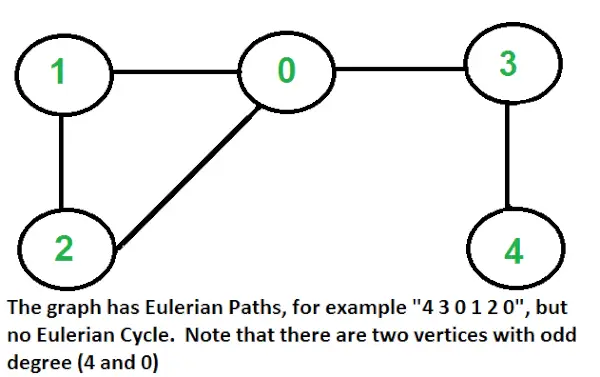


Kā uzzināt, vai dotais grafiks ir eilera grafiks vai nav?
Problēma ir tāda pati kā nākamajā jautājumā. Vai ir iespējams uzzīmēt doto grafiku, nepaceļot zīmuli no papīra un neizsekojot nevienai no malām vairāk nekā vienu reizi.
Grafu sauc par Eilerianu, ja tam ir Eilera cikls, un par puseileriānu, ja tam ir Eilera ceļš. Šķiet, ka problēma ir līdzīga Hamiltona ceļam, kas ir NP pilnīga problēma vispārīgam grafikam. Par laimi, mēs varam noskaidrot, vai dotajam grafikam ir Eilera ceļš vai nav polinoma laikā. Faktiski mēs to varam atrast O(V+E) laikā.
Tālāk ir norādītas dažas interesantas nevirzītu grafiku īpašības ar Eilera ceļu un ciklu. Mēs varam izmantot šos rekvizītus, lai noskaidrotu, vai grafiks ir Eilerians vai nav.
Eilera cikls: Nevirzītam grafikam ir Eilera cikls, ja ir patiesi šādi divi nosacījumi.
ctc pilna forma
- Visas virsotnes, kuru grāds nav nulle, ir savienotas. Mums nerūp virsotnes ar nulles pakāpi, jo tās nepieder pie Eilera cikla vai ceļa (mēs ņemam vērā tikai visas malas).
- Visām virsotnēm ir pāra pakāpe.
Eilera ceļš: Nevirzītam grafikam ir Eilera ceļš, ja ir patiesi šādi divi nosacījumi.
- Tas pats, kas nosacījums (a) Eilerija ciklam.
- Ja nullei vai divām virsotnēm ir nepāra pakāpe un visām pārējām virsotnēm ir pāra pakāpe. Ņemiet vērā, ka nevirzītā grafā nav iespējama tikai viena virsotne ar nepāra pakāpi (nevirzītā grafā visu pakāpju summa vienmēr ir pāra)
Ņemiet vērā, ka grafs bez malām tiek uzskatīts par Eileri, jo nav malu, ko šķērsot.
Kā tas darbojas?
Eilera ceļā katru reizi, kad mēs apmeklējam virsotni v, mēs ejam cauri divām neapmeklētām malām ar vienu gala punktu kā v. Tāpēc visām Eilera ceļa vidus virsotnēm ir jābūt pāra pakāpei. Eilerija ciklam jebkura virsotne var būt vidējā virsotne, tāpēc visām virsotnēm jābūt pāra pakāpei.
Īstenošana:
C++
// A C++ program to check if a given graph is Eulerian or not> #include> #include> using> namespace> std;> // A class that represents an undirected graph> class> Graph> {> >int> V;>// No. of vertices> >list<>int>>*adj;>>:> >// Constructor and destructor> >Graph(>int> V) {>this>->V = V; adj =>new> list<>int>>[IN]; }> >~Graph() {>delete> [] adj; }>// To avoid memory leak> >// function to add an edge to graph> >void> addEdge(>int> v,>int> w);> >// Method to check if this graph is Eulerian or not> >int> isEulerian();> >// Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected> >bool> isConnected();> >// Function to do DFS starting from v. Used in isConnected();> >void> DFSUtil(>int> v,>bool> visited[]);> };> void> Graph::addEdge(>int> v,>int> w)> {> >adj[v].push_back(w);> >adj[w].push_back(v);>// Note: the graph is undirected> }> void> Graph::DFSUtil(>int> v,>bool> visited[])> {> >// Mark the current node as visited and print it> >visited[v] =>true>;> >// Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex> >list<>int>>::iterators i;> >for> (i = adj[v].begin(); i != adj[v].end(); ++i)> >if> (!visited[*i])> >DFSUtil(*i, visited);> }> // Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected.> // It mainly does DFS traversal starting from> bool> Graph::isConnected()> {> >// Mark all the vertices as not visited> >bool> visited[V];> >int> i;> >for> (i = 0; i visited[i] = false; // Find a vertex with non-zero degree for (i = 0; i if (adj[i].size() != 0) break; // If there are no edges in the graph, return true if (i == V) return true; // Start DFS traversal from a vertex with non-zero degree DFSUtil(i, visited); // Check if all non-zero degree vertices are visited for (i = 0; i if (visited[i] == false && adj[i].size()>0) return false; atgriezt patiesu; } /* Funkcija atgriež vienu no šādām vērtībām 0 --> Ja grafs nav Eilera 1 --> Ja grafam ir Eilera ceļš (puseilerāns) 2 --> Ja grafam ir Eilera ķēde (Eilera shēma) */ int Graph::isEulerian() { // Pārbaudiet, vai visas virsotnes, kas nav nulles pakāpes, ir savienotas if (isConnected() == false) return 0; // Skaitīt virsotnes ar nepāra pakāpi int nepāra = 0; for (int i = 0; i if (adj[i].size() & 1) odd++; // Ja skaits ir lielāks par 2, tad grafiks nav Eilerija if (nepāra> 2) atgriež 0; // Ja nepāra skaits ir 2, tad pus-eilerian // Ja nepāra skaits ir 0, tad eulerian // Ņemiet vērā, ka nepāra skaitlis nekad nevar būt 1 nevirzītai grafa atgriešanai 1 : 2 } // Funkcija, lai palaistu testa gadījumus test(Grafs &g) { int res = g.isEulerian(); ja (res == 0) cout<< 'graph is not Eulerian
'; else if (res == 1) cout << 'graph has a Euler path
'; else cout << 'graph has a Euler cycle
'; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { // Let us create and test graphs shown in above figures Graph g1(5); g1.addEdge(1, 0); g1.addEdge(0, 2); g1.addEdge(2, 1); g1.addEdge(0, 3); g1.addEdge(3, 4); test(g1); Graph g2(5); g2.addEdge(1, 0); g2.addEdge(0, 2); g2.addEdge(2, 1); g2.addEdge(0, 3); g2.addEdge(3, 4); g2.addEdge(4, 0); test(g2); Graph g3(5); g3.addEdge(1, 0); g3.addEdge(0, 2); g3.addEdge(2, 1); g3.addEdge(0, 3); g3.addEdge(3, 4); g3.addEdge(1, 3); test(g3); // Let us create a graph with 3 vertices // connected in the form of cycle Graph g4(3); g4.addEdge(0, 1); g4.addEdge(1, 2); g4.addEdge(2, 0); test(g4); // Let us create a graph with all vertices // with zero degree Graph g5(3); test(g5); return 0; }> |
>
>
Java
alfa-beta atzarošana
// A Java program to check if a given graph is Eulerian or not> import> java.io.*;> import> java.util.*;> import> java.util.LinkedList;> // This class represents an undirected graph using adjacency list> // representation> class> Graph> {> >private> int> V;>// No. of vertices> >// Array of lists for Adjacency List Representation> >private> LinkedList adj[];> >// Constructor> >Graph(>int> v)> >{> >V = v;> >adj =>new> LinkedList[v];> >for> (>int> i=>0>; i adj[i] = new LinkedList(); } //Function to add an edge into the graph void addEdge(int v, int w) { adj[v].add(w);// Add w to v's list. adj[w].add(v); //The graph is undirected } // A function used by DFS void DFSUtil(int v,boolean visited[]) { // Mark the current node as visited visited[v] = true; // Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex Iterator i = adj[v].listIterator(); while (i.hasNext()) { int n = i.next(); if (!visited[n]) DFSUtil(n, visited); } } // Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are // connected. It mainly does DFS traversal starting from boolean isConnected() { // Mark all the vertices as not visited boolean visited[] = new boolean[V]; int i; for (i = 0; i visited[i] = false; // Find a vertex with non-zero degree for (i = 0; i if (adj[i].size() != 0) break; // If there are no edges in the graph, return true if (i == V) return true; // Start DFS traversal from a vertex with non-zero degree DFSUtil(i, visited); // Check if all non-zero degree vertices are visited for (i = 0; i if (visited[i] == false && adj[i].size()>0) return false; atgriezt patiesu; } /* Funkcija atgriež vienu no šādām vērtībām 0 --> Ja grafs nav Eilera 1 --> Ja grafam ir Eilera ceļš (puseilerāns) 2 --> Ja grafam ir Eilera ķēde (Eilera shēma) */ int isEulerian() { // Pārbaudiet, vai visas virsotnes, kas nav nulles pakāpes, ir savienotas if (isConnected() == false) return 0; // Skaitīt virsotnes ar nepāra pakāpi int nepāra = 0; for (int i = 0; i if (adj[i].size()%2!=0) nepāra++; // Ja skaits ir lielāks par 2, tad grafiks nav Eilerija if (nepāra> 2) atgriež 0; / / Ja nepāra skaitlis ir 2, tad semi-eulerian // Ja nepāra skaits ir 0, tad eulerian // Ņemiet vērā, ka nepāra skaitlis nekad nevar būt 1 nevirzītai grafa atgriešanai (nepāra = 2) } // Funkcija, lai palaistu testa gadījumus void test() { int res = isEulerian() if (res == 0) System.out.println('graph nav Eulerian' else if (res == 1) System). out.println('grafam ir Eilera ceļš'); else System.out.println('grafikā ir Eilera cikls' } // Draiveris: public static void main(String args[]) { / / Izveidosim un pārbaudīsim grafikus, kas parādīti iepriekš attēlos. Graph(5) g1.addEdge(0, 2); (0, 3); addEdge(2, 1) g2.addEdge(4, 0). .addEdge(1, 0); g3.pievienotEdge(0, 2); g3.pievienotEdge(2, 1); g3.pievienotEdge(0, 3); g3.pievienotEdge(3, 4); g3.pievienotEdge(1, 3); g3.test(); // Izveidosim grafiku ar 3 virsotnēm // savienojam cikla formā Graph g4 = new Graph(3); g4.pievienotEdge(0, 1); g4.pievienotEdge(1, 2); g4.pievienotEdge(2, 0); g4.test(); // Izveidosim grafiku ar visām virsotnēm // ar nulles grādu Graph g5 = new Graph(3); g5.test(); } } // Šo kodu ir sagatavojis Aakash Hasija> |
>
>
Python3
propozicionālā loģika
# Python program to check if a given graph is Eulerian or not> #Complexity : O(V+E)> from> collections>import> defaultdict> # This class represents a undirected graph using adjacency list representation> class> Graph:> >def> __init__(>self>, vertices):> >self>.V>=> vertices># No. of vertices> >self>.graph>=> defaultdict(>list>)># default dictionary to store graph> ># function to add an edge to graph> >def> addEdge(>self>, u, v):> >self>.graph[u].append(v)> >self>.graph[v].append(u)> ># A function used by isConnected> >def> DFSUtil(>self>, v, visited):> ># Mark the current node as visited> >visited[v]>=> True> ># Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex> >for> i>in> self>.graph[v]:> >if> visited[i]>=>=> False>:> >self>.DFSUtil(i, visited)> >'''Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are> >connected. It mainly does DFS traversal starting from> >node with non-zero degree'''> >def> isConnected(>self>):> ># Mark all the vertices as not visited> >visited>=> [>False>]>*>(>self>.V)> ># Find a vertex with non-zero degree> >for> i>in> range>(>self>.V):> >if> len>(>self>.graph[i]) !>=> 0>:> >break> ># If there are no edges in the graph, return true> >if> i>=>=> self>.V>->1>:> >return> True> ># Start DFS traversal from a vertex with non-zero degree> >self>.DFSUtil(i, visited)> ># Check if all non-zero degree vertices are visited> >for> i>in> range>(>self>.V):> >if> visited[i]>=>=> False> and> len>(>self>.graph[i])>>> >return> False> >return> True> >'''The function returns one of the following values> >0 -->Ja grafiks nav Eilerija> >1 -->Ja grafam ir Eilera ceļš (puseilerian)> >2 -->Ja grafikā ir Eilera ķēde (Eulera ķēde) '''> >def> isEulerian(>self>):> ># Check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected> >if> self>.isConnected()>=>=> False>:> >return> 0> >else>:> ># Count vertices with odd degree> >odd>=> 0> >for> i>in> range>(>self>.V):> >if> len>(>self>.graph[i])>%> 2> !>=> 0>:> >odd>+>=> 1> >'''If odd count is 2, then semi-eulerian.> >If odd count is 0, then eulerian> >If count is more than 2, then graph is not Eulerian> >Note that odd count can never be 1 for undirected graph'''> >if> odd>=>=> 0>:> >return> 2> >elif> odd>=>=> 2>:> >return> 1> >elif> odd>>> >return> 0> ># Function to run test cases> >def> test(>self>):> >res>=> self>.isEulerian()> >if> res>=>=> 0>:> >print>(>'graph is not Eulerian'>)> >elif> res>=>=> 1>:> >print>(>'graph has a Euler path'>)> >else>:> >print>(>'graph has a Euler cycle'>)> # Let us create and test graphs shown in above figures> g1>=> Graph(>5>)> g1.addEdge(>1>,>0>)> g1.addEdge(>0>,>2>)> g1.addEdge(>2>,>1>)> g1.addEdge(>0>,>3>)> g1.addEdge(>3>,>4>)> g1.test()> g2>=> Graph(>5>)> g2.addEdge(>1>,>0>)> g2.addEdge(>0>,>2>)> g2.addEdge(>2>,>1>)> g2.addEdge(>0>,>3>)> g2.addEdge(>3>,>4>)> g2.addEdge(>4>,>0>)> g2.test()> g3>=> Graph(>5>)> g3.addEdge(>1>,>0>)> g3.addEdge(>0>,>2>)> g3.addEdge(>2>,>1>)> g3.addEdge(>0>,>3>)> g3.addEdge(>3>,>4>)> g3.addEdge(>1>,>3>)> g3.test()> # Let us create a graph with 3 vertices> # connected in the form of cycle> g4>=> Graph(>3>)> g4.addEdge(>0>,>1>)> g4.addEdge(>1>,>2>)> g4.addEdge(>2>,>0>)> g4.test()> # Let us create a graph with all vertices> # with zero degree> g5>=> Graph(>3>)> g5.test()> # This code is contributed by Neelam Yadav> |
>
labākā automašīna pasaulē
>
C#
// A C# program to check if a given graph is Eulerian or not> using> System;> using> System.Collections.Generic;> > // This class represents an undirected graph using adjacency list> // representation> public> class> Graph> {> >private> int> V;>// No. of vertices> > >// Array of lists for Adjacency List Representation> >private> List<>int>>[]adj;> > >// Constructor> >Graph(>int> v)> >{> >V = v;> >adj =>new> List<>int>>[in];> >for> (>int> i=0; i adj[i] = new List |
>
>
Javascript
> // A Javascript program to check if a given graph is Eulerian or not> // This class represents an undirected graph using adjacency list> // representation> class Graph> {> >// Constructor> >constructor(v)> >{> >this>.V = v;> >this>.adj =>new> Array(v);> >for> (let i = 0; i this.adj[i] = []; } // Function to add an edge into the graph addEdge(v,w) { this.adj[v].push(w);// Add w to v's list. this.adj[w].push(v); //The graph is undirected } // A function used by DFS DFSUtil(v,visited) { // Mark the current node as visited visited[v] = true; // Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex for(let i of this.adj[v]) { let n = i; if (!visited[n]) this.DFSUtil(n, visited); } } // Method to check if all non-zero degree vertices are // connected. It mainly does DFS traversal starting from isConnected() { // Mark all the vertices as not visited let visited = new Array(this.V); let i; for (i = 0; i |
ankita lokhande vecums
>graph has a Euler path graph has a Euler cycle graph is not Eulerian graph has a Euler cycle graph has a Euler cycle>
Laika sarežģītība: O(V+E)
Telpas sarežģītība: O(V+E)
Nākamie raksti:
Eilera ceļš un shēma virzītiem grafikiem.
Flerī algoritms Eilēra ceļa vai ķēdes izdrukāšanai?
