Iestatītais interfeiss atrodas java.util pakotnē un paplašina Kolekcijas saskarne . Tā ir nesakārtota objektu kolekcija, kurā nevar saglabāt dublētās vērtības. Tā ir saskarne, kas ievieš matemātisko kopu. Šajā interfeisā ir ietvertas no kolekcijas saskarnes mantotās metodes un pievienota funkcija, kas ierobežo dublēto elementu ievietošanu. Ir divas saskarnes, kas paplašina kopas ieviešanu, proti, SortedSet un NavigableSet.
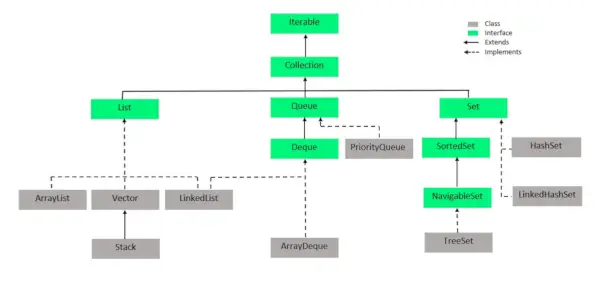
Iepriekš redzamajā attēlā navigējamā kopa paplašina sakārtotās kopas saskarni. Tā kā kopa nesaglabā ievietošanas secību, navigējamās kopas saskarne nodrošina ieviešanu, lai pārvietotos pa komplektu. Klase, kas ievieš navigējamo kopu, ir TreeSet, kas ir pašbalansējoša koka ieviešana. Tāpēc šī saskarne nodrošina veidu, kā pārvietoties pa šo koku.
Deklarācija: Iestatīšanas saskarne tiek deklarēta šādi:
public interface Set extends Collection>
Komplektu objektu izveide
Tā kā Set ir an saskarne , objektus nevar izveidot no veida kopas. Mums vienmēr ir nepieciešama klase, kas paplašina šo sarakstu, lai izveidotu objektu. Un arī pēc ieviešanas Generics Java 1.5 versijā ir iespējams ierobežot komplektā glabājamo objektu veidu. Šo tipa drošo komplektu var definēt šādi:
// Obj is the type of the object to be stored in Set Set set = new HashSet ();>
Apspriedīsim tālāk sniegtajā Set saskarnē esošās metodes tabulas formātā:
| Metode | Apraksts |
|---|---|
| pievienot (elements) | Šo metodi izmanto, lai komplektam pievienotu noteiktu elementu. Funkcija pievieno elementu tikai tad, ja norādītais elements jau nav iekļauts kopā, pretējā gadījumā funkcija atgriež False, ja elements jau atrodas kopā. |
| pievienot visu (kolekcija) | Šo metodi izmanto, lai esošajai kopai pievienotu visus elementus no minētās kolekcijas. Elementi tiek pievienoti nejauši, neievērojot īpašu secību. |
| skaidrs () | Šo metodi izmanto, lai noņemtu visus elementus no kopas, bet ne izdzēstu kopu. Atsauce uz komplektu joprojām pastāv. |
| satur (elementu) | Šo metodi izmanto, lai pārbaudītu, vai komplektā ir vai nav noteikts elements. |
| satur visu (kolekcija) | Šo metodi izmanto, lai pārbaudītu, vai komplektā ir visi dotajā kolekcijā esošie elementi. Šī metode atgriež vērtību “true”, ja komplektā ir visi elementi, un atgriež vērtību “false”, ja trūkst kāda no elementiem. |
| hashCode() | Šī metode tiek izmantota, lai iegūtu hashCode vērtību šai kopas instancei. Tas atgriež vesela skaitļa vērtību, kas ir hashCode vērtība šai kopas instancei. |
| ir tukšs() | Šo metodi izmanto, lai pārbaudītu, vai komplekts ir tukšs. |
| iterators () | Šo metodi izmanto, lai atgrieztu iterators no komplekta. Elementi no komplekta tiek atgriezti nejaušā secībā. |
| noņemt (elements) | Šo metodi izmanto, lai noņemtu doto elementu no kopas. Šī metode atgriež vērtību True, ja norādītais elements atrodas komplektā, pretējā gadījumā tā atgriež vērtību False. |
| noņemt visu (kolekcija) | Šo metodi izmanto, lai no kolekcijas noņemtu visus komplektā esošos elementus. Šī metode atgriež patieso vērtību, ja šī kopa ir mainīta izsaukuma rezultātā. |
| paturēt visu (kolekcija) | Šo metodi izmanto, lai saglabātu visus elementus no kopas, kas ir minēti dotajā kolekcijā. Šī metode atgriež patieso vērtību, ja šī kopa ir mainīta izsaukuma rezultātā. |
| Izmērs() | Šo metodi izmanto, lai iegūtu komplekta izmēru. Tas atgriež vesela skaitļa vērtību, kas apzīmē elementu skaitu. |
| toArray() | Šo metodi izmanto, lai izveidotu masīvu no tādiem pašiem elementiem kā komplektā. |
Ilustrācija: Programmas paraugs kopas interfeisa ilustrēšanai
Java
// Java program Illustrating Set Interface> > // Importing utility classes> import> java.util.*;> > // Main class> public> class> GFG {> > >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Demonstrating Set using HashSet> >// Declaring object of type String> >Set hash_Set =>new> HashSet();> > >// Adding elements to the Set> >// using add() method> >hash_Set.add(>'Geeks'>);> >hash_Set.add(>'For'>);> >hash_Set.add(>'Geeks'>);> >hash_Set.add(>'Example'>);> >hash_Set.add(>'Set'>);> > >// Printing elements of HashSet object> >System.out.println(hash_Set);> >}> }> |
>
>Izvade
[Set, Example, Geeks, For]>
Darbības komplekta interfeisā
Iestatījuma saskarne ļauj lietotājiem veikt pamata matemātisko darbību komplektā. Paņemsim divus masīvus, lai saprastu šīs pamatdarbības. Pieņemsim, ka kopa1 = [1, 3, 2, 4, 8, 9, 0] un kopa2 = [1, 3, 7, 5, 4, 0, 7, 5]. Tad iespējamās operācijas komplektos ir:
1. Krustojums: Šī darbība atgriež visus kopīgos elementus no dotajām divām kopām. Iepriekšminētajām divām kopām krustpunkts būtu:
Intersection = [0, 1, 3, 4]>
2. Savienība: Šī darbība pievieno visus elementus vienā komplektā ar otru. Iepriekšminētajām divām kopām savienība būtu:
Union = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9]>
3. Atšķirība: Šī darbība noņem visas vienā kopā esošās vērtības no otras kopas. Iepriekšminētajām divām kopām atšķirība būtu šāda:
Difference = [2, 8, 9]>
Tagad īstenosim šādas iepriekš definētās darbības šādi:
Piemērs:
Java
python drukā līdz 2 zīmēm aiz komata
// Java Program Demonstrating Operations on the Set> // such as Union, Intersection and Difference operations> > // Importing all utility classes> import> java.util.*;> > // Main class> public> class> SetExample {> > >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String args[])> >{> >// Creating an object of Set class> >// Declaring object of Integer type> >Set a =>new> HashSet();> > >// Adding all elements to List> >a.addAll(Arrays.asList(> >new> Integer[] {>1>,>3>,>2>,>4>,>8>,>9>,>0> }));> > >// Again declaring object of Set class> >// with reference to HashSet> >Set b =>new> HashSet();> > >b.addAll(Arrays.asList(> >new> Integer[] {>1>,>3>,>7>,>5>,>4>,>0>,>7>,>5> }));> > > >// To find union> >Set union =>new> HashSet(a);> >union.addAll(b);> >System.out.print(>'Union of the two Set'>);> >System.out.println(union);> > >// To find intersection> >Set intersection =>new> HashSet(a);> >intersection.retainAll(b);> >System.out.print(>'Intersection of the two Set'>);> >System.out.println(intersection);> > >// To find the symmetric difference> >Set difference =>new> HashSet(a);> >difference.removeAll(b);> >System.out.print(>'Difference of the two Set'>);> >System.out.println(difference);> >}> }> |
>
>Izvade
Union of the two Set[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9] Intersection of the two Set[0, 1, 3, 4] Difference of the two Set[2, 8, 9]>
Dažādu darbību veikšana SortedSet
Pēc ieviešanas Generics Java 1.5 versijā ir iespējams ierobežot komplektā glabājamo objektu tipu. Tā kā Set ir saskarne, to var izmantot tikai ar klasi, kas ievieš šo saskarni. HashSet ir viena no plaši izmantotajām klasēm, kas ievieš Set saskarni. Tagad apskatīsim, kā ar HashSet veikt dažas bieži izmantotās darbības. Mēs veiksim šādas darbības:
- Elementu pievienošana
- Piekļuve elementiem
- Elementu noņemšana
- Atkārtoti elementi
- Atkārtošana, izmantojot komplektu
Tagad apspriedīsim šīs darbības atsevišķi šādi:
1. darbība: Elementu pievienošana
Lai komplektam pievienotu elementu, mēs varam izmantot add() metode . Tomēr ievietošanas secība komplektā netiek saglabāta. Iekšēji katram elementam tiek ģenerēts jaukums un vērtības tiek saglabātas attiecībā pret ģenerēto jaucējkodu. vērtības tiek salīdzinātas un sakārtotas augošā secībā. Mums ir jāņem vērā, ka elementu dublikāti nav atļauti un visi dublētie elementi tiek ignorēti. Turklāt kopa pieņem Null vērtības.
Piemērs
Java
// Java Program Demonstrating Working of Set by> // Adding elements using add() method> > // Importing all utility classes> import> java.util.*;> > // Main class> class> GFG {> > >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Creating an object of Set and> >// declaring object of type String> >Set hs =>new> HashSet();> > >// Adding elements to above object> >// using add() method> >hs.add(>'B'>);> >hs.add(>'B'>);> >hs.add(>'C'>);> >hs.add(>'A'>);> > >// Printing the elements inside the Set object> >System.out.println(hs);> >}> }> |
>
>Izvade
[A, B, C]>
2. darbība: Piekļuve elementiem
Pēc elementu pievienošanas, ja vēlamies piekļūt elementiem, mēs varam izmantot iebūvētās metodes, piemēram, include() .
Piemērs
Java
binārā koka inorder šķērsošana
// Java code to demonstrate Working of Set by> // Accessing the Elements of the Set object> > // Importing all utility classes> import> java.util.*;> > // Main class> class> GFG {> > >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Creating an object of Set and> >// declaring object of type String> >Set hs =>new> HashSet();> > >// Elements are added using add() method> >// Later onwards we will show accessing the same> > >// Custom input elements> >hs.add(>'A'>);> >hs.add(>'B'>);> >hs.add(>'C'>);> >hs.add(>'A'>);> > >// Print the Set object elements> >System.out.println(>'Set is '> + hs);> > >// Declaring a string> >String check =>'D'>;> > >// Check if the above string exists in> >// the SortedSet or not> >// using contains() method> >System.out.println(>'Contains '> + check +>' '> >+ hs.contains(check));> >}> }> |
>
>Izvade
Set is [A, B, C] Contains D false>
3. darbība: Vērtību noņemšana
Vērtības var noņemt no kopas, izmantojot metodi remove() .
Piemērs
Java
// Java Program Demonstrating Working of Set by> // Removing Element/s from the Set> > // Importing all utility classes> import> java.util.*;> > // Main class> class> GFG {> > >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Declaring object of Set of type String> >Set hs =>new> HashSet();> > >// Elements are added> >// using add() method> > >// Custom input elements> >hs.add(>'A'>);> >hs.add(>'B'>);> >hs.add(>'C'>);> >hs.add(>'B'>);> >hs.add(>'D'>);> >hs.add(>'E'>);> > >// Printing initial Set elements> >System.out.println(>'Initial HashSet '> + hs);> > >// Removing custom element> >// using remove() method> >hs.remove(>'B'>);> > >// Printing Set elements after removing an element> >// and printing updated Set elements> >System.out.println(>'After removing element '> + hs);> >}> }> |
c++ sadalīta virkne
>
>Izvade
Initial HashSet [A, B, C, D, E] After removing element [A, C, D, E]>
4. darbība: Atkārtošana, izmantojot komplektu
Ir dažādi veidi, kā atkārtot komplektu. Slavenākais no tiem ir uzlabotās cilpas izmantošana.
Piemērs
Java
// Java Program to Demonstrate Working of Set by> // Iterating through the Elements> > // Importing utility classes> import> java.util.*;> > // Main class> class> GFG {> > >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Creating object of Set and declaring String type> >Set hs =>new> HashSet();> > >// Adding elements to Set> >// using add() method> > >// Custom input elements> >hs.add(>'A'>);> >hs.add(>'B'>);> >hs.add(>'C'>);> >hs.add(>'B'>);> >hs.add(>'D'>);> >hs.add(>'E'>);> > >// Iterating through the Set> >// via for-each loop> >for> (String value : hs)> > >// Printing all the values inside the object> >System.out.print(value +>', '>);> > >System.out.println();> >}> }> |
>
>Izvade
A, B, C, D, E,>
Klases, kas ievieš saskarni Set Java kolekcijās, var viegli uztvert tālāk redzamajā attēlā, un tās ir norādītas šādi:
- HashSet
- EnumSet
- LinkedHashSet
- TreeSet

1. klase: HashSet
HashSet klase, kas ir ieviesta kolekcijas ietvars ir neatņemama īstenošana Piemērs
Java
// Java program Demonstrating Creation of Set object> // Using the Hashset class> > // Importing utility classes> import> java.util.*;> > // Main class> class> GFG {> > >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Creating object of Set of type String> >Set h =>new> HashSet();> > >// Adding elements into the HashSet> >// using add() method> > >// Custom input elements> >h.add(>'India'>);> >h.add(>'Australia'>);> >h.add(>'South Africa'>);> > >// Adding the duplicate element> >h.add(>'India'>);> > >// Displaying the HashSet> >System.out.println(h);> > >// Removing items from HashSet> >// using remove() method> >h.remove(>'Australia'>);> >System.out.println(>'Set after removing '> >+>'Australia:'> + h);> > >// Iterating over hash set items> >System.out.println(>'Iterating over set:'>);> > >// Iterating through iterators> >Iterator i = h.iterator();> > >// It holds true till there is a single element> >// remaining in the object> >while> (i.hasNext())> > >System.out.println(i.next());> >}> }> |
>
>Izvade
[South Africa, Australia, India] Set after removing Australia:[South Africa, India] Iterating over set: South Africa India>
2. klase: EnumSet
EnumSet klase, kas ir ieviesta kolekciju ietvars ir viena no specializētajām saskarnes Set implementācijām lietošanai ar uzskaites veids . Tā ir augstas veiktspējas komplekta ieviešana, kas ir daudz ātrāka nekā HashSet. Visiem elementiem uzskaitījuma kopā ir jānāk no viena uzskaitījuma veida, kas tiek norādīts, kad kopa tiek tieši vai netieši izveidota. Apskatīsim, kā izveidot kopas objektu, izmantojot šo klasi.
Piemērs
Java
// Java program to demonstrate the> // creation of the set object> // using the EnumSet class> import> java.util.*;> > enum> Gfg { CODE, LEARN, CONTRIBUTE, QUIZ, MCQ }> ;> > public> class> GFG {> > >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Creating a set> >Set set1;> > >// Adding the elements> >set1 = EnumSet.of(Gfg.QUIZ, Gfg.CONTRIBUTE,> >Gfg.LEARN, Gfg.CODE);> > >System.out.println(>'Set 1: '> + set1);> >}> }> |
>
>Izvade
Set 1: [CODE, LEARN, CONTRIBUTE, QUIZ]>
3. klase: LinkedHashSet
LinkedHashSet klase, kas ir ieviesta kolekciju ietvars ir pasūtīta HashSet versija, kas uztur divkāršu sarakstu visos elementos. Ja iterācijas secība ir jāuztur, tiek izmantota šī klase. Iterējot, izmantojot HashSet, secība ir neparedzama, savukārt LinkedHashSet ļauj mums iterēt elementus tādā secībā, kādā tie tika ievietoti. Apskatīsim, kā izveidot kopas objektu, izmantojot šo klasi.
Piemērs
Java
// Java program to demonstrate the> // creation of Set object using> // the LinkedHashset class> import> java.util.*;> > class> GFG {> > >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >Set lh =>new> LinkedHashSet();> > >// Adding elements into the LinkedHashSet> >// using add()> >lh.add(>'India'>);> >lh.add(>'Australia'>);> >lh.add(>'South Africa'>);> > >// Adding the duplicate> >// element> >lh.add(>'India'>);> > >// Displaying the LinkedHashSet> >System.out.println(lh);> > >// Removing items from LinkedHashSet> >// using remove()> >lh.remove(>'Australia'>);> >System.out.println(>'Set after removing '> >+>'Australia:'> + lh);> > >// Iterating over linked hash set items> >System.out.println(>'Iterating over set:'>);> >Iterator i = lh.iterator();> >while> (i.hasNext())> >System.out.println(i.next());> >}> }> |
>
>
base64 atšifrēt jsIzvade
[India, Australia, South Africa] Set after removing Australia:[India, South Africa] Iterating over set: India South Africa>
4. klase: TreeSet
TreeSet klase, kas ir ieviesta kolekciju ietvars un SortedSet interfeisa ieviešana un SortedSet paplašina kopas interfeisu. Tas darbojas kā vienkāršs komplekts, izņemot to, ka tajā tiek saglabāti elementi sakārtotā formātā. TreeSet glabāšanai izmanto koka datu struktūru. Objekti tiek glabāti sakārtotā, augošā secībā. Bet mēs varam atkārtot dilstošā secībā, izmantojot metodi TreeSet.descendingIterator(). Apskatīsim, kā izveidot kopas objektu, izmantojot šo klasi.
Piemērs
Java
// Java Program Demonstrating Creation of Set object> // Using the TreeSet class> > // Importing utility classes> import> java.util.*;> > // Main class> class> GFG {> > >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Creating a Set object and declaring it of String> >// type> >// with reference to TreeSet> >Set ts =>new> TreeSet();> > >// Adding elements into the TreeSet> >// using add()> >ts.add(>'India'>);> >ts.add(>'Australia'>);> >ts.add(>'South Africa'>);> > >// Adding the duplicate> >// element> >ts.add(>'India'>);> > >// Displaying the TreeSet> >System.out.println(ts);> > >// Removing items from TreeSet> >// using remove()> >ts.remove(>'Australia'>);> >System.out.println(>'Set after removing '> >+>'Australia:'> + ts);> > >// Iterating over Tree set items> >System.out.println(>'Iterating over set:'>);> >Iterator i = ts.iterator();> > >while> (i.hasNext())> >System.out.println(i.next());> >}> }> |
>
>Izvade
[Australia, India, South Africa] Set after removing Australia:[India, South Africa] Iterating over set: India South Africa>
