Ņemot vērā divas stīgas, S1 un S2 , uzdevums ir atrast garākās kopīgās apakšsecības garumu, t.i., garākās apakšsecības abās virknēs.
A garākā kopīgā apakšsecība (LCS) ir definēta kā garākā apakšsecība, kas ir izplatīta visās dotajās ievades secībās.
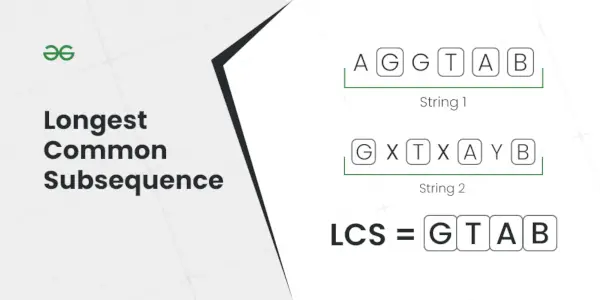
Garākā kopējā secība
Piemēri:
Ieteicamā prakse Garākā kopējā secība Izmēģiniet to!Ievade: S1 = ABC, S2 = ACD
Izvade: 2
Paskaidrojums: Garākā apakšsecība, kas atrodas abās virknēs, ir AC.Ievade: S1 = AGGTAB, S2 = GXTXAYB
Izvade: 4
Paskaidrojums: Garākā kopīgā apakšsecība ir GTAB.Ievade: S1 = ABC, S2 = CBA
Izvade: 1
Paskaidrojums: Ir trīs kopīgas apakšsecības, kuru garums ir 1, A, B un C, un nav kopīgas apakšsecības, kuru garums ir lielāks par 1.Ievade: S1 = XYZW, S2 = XYWZ
Izvade: 3
Paskaidrojums: Ir divas kopīgas apakšsecības, kuru garums ir 3 XYZ un XYW, un nav kopīgas apakšsecības. kura garums pārsniedz 3.
Garākā kopējā secība (LCS), izmantojot rekursiju:
Ģenerējiet visas iespējamās apakšsecības un atrodiet no tām garāko, kas atrodas abās virknēs, izmantojot Lai īstenotu ideju, veiciet tālāk norādītās darbības.
virkne aizstāj visu java
- Izveidojiet rekursīvu funkciju [teiksim lcs() ].
- Pārbaudiet saistību starp vēl neapstrādāto virkņu pirmajām rakstzīmēm.
- Atkarībā no attiecības izsauciet nākamo rekursīvo funkciju, kā minēts iepriekš.
- Atgrieziet kā atbildi saņemtā LCS garumu.
Tālāk ir sniegta rekursīvās pieejas ieviešana:
C++C// A Naive recursive implementation of LCS problem #include using namespace std; // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] int lcs(string X, string Y, int m, int n) // Driver code int main() { string S1 = 'AGGTAB'; string S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = S1.size(); int n = S2.size(); cout << 'Length of LCS is ' << lcs(S1, S2, m, n); return 0; } // This code is contributed by rathbhupendra>Java// A Naive recursive implementation // of LCS problem #include int max(int a, int b); // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], // Y[0..n-1] int lcs(char* X, char* Y, int i, int j) // Utility function to get max of // 2 integers int max(int a, int b) { return (a>b)? a : b; } // Draivera kods int main() { char S1[] = 'BD'; char S2[] = 'ABCD'; int m = strlen(S1); int n = strlen(S2); int i = 0, j = 0; // Funkcijas izsaukums printf('LCS garums ir %d', lcs(S1, S2, i, j)); atgriezties 0; }>Python// A Naive recursive implementation of LCS problem in java import java.io.*; import java.util.*; public class LongestCommonSubsequence { // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] int lcs(String X, String Y, int m, int n) n == 0) return 0; if (X.charAt(m - 1) == Y.charAt(n - 1)) return 1 + lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n - 1); else return max(lcs(X, Y, m, n - 1), lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n)); // Utility function to get max of 2 integers int max(int a, int b) { return (a>b)? a : b; } // Draivera kods public static void main(String[] args) { LongestCommonSubsequence lcs = new LongestCommonSubsequence(); Virkne S1 = 'AGGTAB'; Virkne S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = S1.garums(); int n = S2.garums(); System.out.println('LCS garums ir' + ' ' + lcs.lcs(S1, S2, m, n)); } } // Šī koda autors ir Saket Kumar>C## A Naive recursive Python implementation of LCS problem def lcs(X, Y, m, n): if m == 0 or n == 0: return 0 elif X[m-1] == Y[n-1]: return 1 + lcs(X, Y, m-1, n-1) else: return max(lcs(X, Y, m, n-1), lcs(X, Y, m-1, n)) # Driver code if __name__ == '__main__': S1 = 'AGGTAB' S2 = 'GXTXAYB' print('Length of LCS is', lcs(S1, S2, len(S1), len(S2)))>// C# Naive recursive implementation of LCS problem using System; class GFG { // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] static int lcs(String X, String Y, int m, int n) if (m == 0 // Utility function to get max of 2 integers static int max(int a, int b) { return (a>b)? a : b; } // Draivera kods public static void Main() { String S1 = 'AGGTAB'; Virkne S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = S1.Garums; int n = S2.Garums; Console.Write('LCS garums ir' + ' ' + lcs(S1, S2, m, n)); } } // Šī koda autors ir Sam007>>Javascript>> PHP>>
IzvadeLength of LCS is 4>Laika sarežģītība: O(2m+n)
Palīgtelpa: O(1)Garākā kopējā secība (LCS), izmantojot Memoizācija :
1. Optimāla apakšstruktūra:
Skatiet, lai atrisinātu L(X[0, 1, . . ., m-1], Y[0, 1, . . . , n-1]) struktūru, mēs izmantojam X[0 apakšstruktūras , 1, …, m-2], Y[0, 1,…, n-2], atkarībā no situācijas (t.i., tos optimāli izmantojot), lai atrastu kopuma risinājumu.
2. Apakšproblēmas, kas pārklājas:
Ja mēs izmantojam iepriekš minēto rekursīvo pieeju virknēm BD un ABCD , mēs iegūsim daļēju rekursijas koku, kā parādīts zemāk. Šeit redzams, ka apakšproblēma L(BD, ABCD) tiek aprēķināta vairāk nekā vienu reizi. Ja ņem vērā kopējo koku, būs vairākas šādas pārklājošas apakšproblēmas.
binārā meklēšanas koks]L(AXYT, AYZX)
/
L(AXY, AYZX) L(AXYT, AYZ)
/ /
L(AX, AYZX) L(AXY, AYZ) L(AXY, AYZ) L(AXYT, AY)Pieeja: Šo divu īpašību klātbūtnes dēļ problēmas risināšanai varam izmantot dinamisko programmēšanu vai memoizāciju. Tālāk ir sniegta pieeja risinājumam, izmantojot rekursiju.
- Izveidojiet rekursīvu funkciju. Izveidojiet arī 2D masīvu, lai saglabātu unikāla stāvokļa rezultātu.
- Rekursijas izsaukuma laikā, ja viens un tas pats stāvoklis tiek izsaukts vairāk nekā vienu reizi, mēs varam tieši atgriezt šim stāvoklim saglabāto atbildi, nevis veikt atkārtotu aprēķinu.
Tālāk ir aprakstīta iepriekš minētās pieejas īstenošana.
C++Java// A Top-Down DP implementation // of LCS problem #include using namespace std; // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], // Y[0..n-1] int lcs(char* X, char* Y, int m, int n, vector>& dp) { if (m == 0 || n == 0) atgriež 0; ja (X[m - 1] == Y[n - 1]) atgriešanās dp[m][n] = 1 + lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n - 1, dp); if (dp[m][n] != -1) { return dp[m][n]; } return dp[m][n] = max(lcs(X, Y, m, n - 1, dp), lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n, dp)); } // Draivera kods int main() { char X[] = 'AGGTAB'; char Y[] = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = strlen(X); int n = strlen(Y); vektors > dp(m + 1, vektors (n + 1, -1)); cout<< 'Length of LCS is ' << lcs(X, Y, m, n, dp); return 0; }> Python/*package whatever //do not write package name here */ import java.io.*; class GFG { // A Top-Down DP implementation of LCS problem // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] static int lcs(String X, String Y, int m, int n, int[][] dp) { if (m == 0 || n == 0) return 0; if (dp[m][n] != -1) return dp[m][n]; if (X.charAt(m - 1) == Y.charAt(n - 1)) { dp[m][n] = 1 + lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n - 1, dp); return dp[m][n]; } dp[m][n] = Math.max(lcs(X, Y, m, n - 1, dp), lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n, dp)); return dp[m][n]; } // Drivers code public static void main(String args[]) { String X = 'AGGTAB'; String Y = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = X.length(); int n = Y.length(); int[][] dp = new int[m + 1][n + 1]; for (int i = 0; i < m + 1; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n + 1; j++) { dp[i][j] = -1; } } System.out.println('Length of LCS is ' + lcs(X, Y, m, n, dp)); } } // This code is contributed by shinjanpatra>C## A Top-Down DP implementation of LCS problem # Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] def lcs(X, Y, m, n, dp): if (m == 0 or n == 0): return 0 if (dp[m][n] != -1): return dp[m][n] if X[m - 1] == Y[n - 1]: dp[m][n] = 1 + lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n - 1, dp) return dp[m][n] dp[m][n] = max(lcs(X, Y, m, n - 1, dp), lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n, dp)) return dp[m][n] # Driver code X = 'AGGTAB' Y = 'GXTXAYB' m = len(X) n = len(Y) dp = [[-1 for i in range(n + 1)]for j in range(m + 1)] print(f'Length of LCS is {lcs(X, Y, m, n, dp)}') # This code is contributed by shinjanpatra>Javascript/* C# Naive recursive implementation of LCS problem */ using System; class GFG { /* Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] */ static int lcs(char[] X, char[] Y, int m, int n, int[, ] L) { if (m == 0 || n == 0) return 0; if (L[m, n] != -1) return L[m, n]; if (X[m - 1] == Y[n - 1]) { L[m, n] = 1 + lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n - 1, L); return L[m, n]; } L[m, n] = max(lcs(X, Y, m, n - 1, L), lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n, L)); return L[m, n]; } /* Utility function to get max of 2 integers */ static int max(int a, int b) { return (a>b)? a : b; } public static void Main() { String s1 = 'AGGTAB'; Virkne s2 = 'GXTXAYB'; char[] X = s1.ToCharArray(); char[] Y = s2.ToCharArray(); int m = X. Garums; int n = Y.Length; int[, ] L = jauns int[m + 1, n + 1]; for (int i = 0; i<= m; i++) { for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) { L[i, j] = -1; } } Console.Write('Length of LCS is' + ' ' + lcs(X, Y, m, n, L)); } } // This code is contributed by akshitsaxenaa09>/* A Top-Down DP implementation of LCS problem */ /* Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] */ function lcs(X, Y, m, n, dp) { if (m == 0 || n == 0) return 0; if (X[m - 1] == Y[n - 1]) return dp[m][n] = 1 + lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n - 1, dp); if (dp[m][n] != -1) { return dp[m][n]; } return dp[m][n] = Math.max(lcs(X, Y, m, n - 1, dp), lcs(X, Y, m - 1, n, dp)); } /* Driver code */ let X = 'AGGTAB'; let Y = 'GXTXAYB'; let m = X.length; let n = Y.length; let dp = new Array(m + 1); for(let i = 0; i < m + 1; i++) { dp[i] = new Array(n + 1).fill(-1); } console.log('Length of LCS is ' + lcs(X, Y, m, n, dp)); // This code is contributed by shinjanpatra>
IzvadeLaika sarežģītība: O(m * n), kur m un n ir virknes garums. Javascript
Palīgtelpa: O(m * n) Šeit tiek ignorēta rekursīvā steka telpa.Garākā kopējā secība (LCS), izmantojot augšupvērstu (tabulāciju):
Mēs varam izmantot šādas darbības, lai ieviestu dinamiskās programmēšanas pieeju LCS.
- Izveidojiet 2D masīvu dp[][] ar rindām un kolonnām, kas vienādas ar katras ievades virknes garumu plus 1 [rindu skaits norāda indeksus S1 un kolonnas norāda indeksus S2 ].
- Inicializējiet dp masīva pirmo rindu un kolonnu uz 0.
- Atkārtojiet dp masīva rindas, sākot no 1 (teiksim, izmantojot iteratoru i ).
- Katram i , atkārtojiet visas kolonnas no j = 1 līdz n :
- Ja S1[i-1] ir vienāds ar S2[j-1] , iestatiet pašreizējo dp masīva elementu uz elementa vērtību uz ( dp[i-1][j-1] + 1 ).
- Pretējā gadījumā iestatiet pašreizējo dp masīva elementu uz maksimālo vērtību dp[i-1][j] un dp[i][j-1] .
- Pēc ligzdotajām cilpām pēdējais dp masīva elements saturēs LCS garumu.
Lai labāk izprastu, skatiet tālāk redzamo ilustrāciju:
Ilustrācija:
Sakiet, ka stīgas ir S1 = AGGTAB un S2 = GXTXAYB .
Pirmais solis: Sākotnēji izveidojiet 2D matricu (piemēram, dp[][]) ar izmēru 8 x 7, kuras pirmā rinda un pirmā kolonna ir aizpildīta ar 0.
Dp tabulas izveide
Otrais solis: Travers, ja i = 1. Kad j kļūst par 5, S1[0] un S2[4] ir vienādi. Tātad dp[][] ir atjaunināts. Pārējiem elementiem ņem maksimālo vērtību dp[i-1][j] un dp[i][j-1]. (Šajā gadījumā, ja abas vērtības ir vienādas, mēs esam izmantojuši bultiņas iepriekšējām rindām).
1. rindas aizpildīšana
Trešais solis: Kamēr šķērso i = 2, S1[1] un S2[0] ir vienādi (abi ir “G”). Tātad dp vērtība šajā šūnā tiek atjaunināta. Pārējie elementi tiek atjaunināti atbilstoši nosacījumiem.
Aizpildot rindu Nr. 2
Ceturtais solis: Ja i = 3, S1[2] un S2[0] atkal ir vienādi. Atjauninājumi ir šādi.
Aizpildīšanas rinda Nr. 3
Piektais solis: Ja i = 4, mēs varam redzēt, ka S1[3] un S2[2] ir vienādi. Tātad dp[4][3] atjaunināts kā dp[3][2] + 1 = 2.
4. rindas aizpildīšana
Sestais solis: Šeit mēs redzam, ka i = 5 un j = 5 S1[4] un S2[4] vērtības ir vienādas (t.i., abas ir “A”). Tātad dp[5][5] tiek attiecīgi atjaunināts un kļūst par 3.
5. rindas aizpildīšana
kā palaist skriptu operētājsistēmā LinuxPēdējais solis: Ja i = 6, skatiet abu virkņu pēdējās rakstzīmes ir vienādas (tās ir “B”). Tāpēc dp[6][7] vērtība kļūst par 4.
Pēdējās rindas aizpildīšana
Tātad mēs iegūstam maksimālo kopējās apakšsecības garumu kā 4 .
Tālāk ir parādīta LCS problēmas ieviešana tabulas veidā.
C++Java// Dynamic Programming C++ implementation // of LCS problem #include using namespace std; // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], // Y[0..n-1] int lcs(string X, string Y, int m, int n) { // Initializing a matrix of size // (m+1)*(n+1) int L[m + 1][n + 1]; // Following steps build L[m+1][n+1] // in bottom up fashion. Note that // L[i][j] contains length of LCS of // X[0..i-1] and Y[0..j-1] for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++) { for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) if (i == 0 } // L[m][n] contains length of LCS // for X[0..n-1] and Y[0..m-1] return L[m][n]; } // Driver code int main() { string S1 = 'AGGTAB'; string S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = S1.size(); int n = S2.size(); // Function call cout << 'Length of LCS is ' << lcs(S1, S2, m, n); return 0; }>Python// Dynamic Programming Java implementation of LCS problem import java.util.*; public class LongestCommonSubsequence { // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] int lcs(String X, String Y, int m, int n) { int L[][] = new int[m + 1][n + 1]; // Following steps build L[m+1][n+1] in bottom up // fashion. Note that L[i][j] contains length of LCS // of X[0..i-1] and Y[0..j-1] for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++) { for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) j == 0) L[i][j] = 0; else if (X.charAt(i - 1) == Y.charAt(j - 1)) L[i][j] = L[i - 1][j - 1] + 1; else L[i][j] = max(L[i - 1][j], L[i][j - 1]); } return L[m][n]; } // Utility function to get max of 2 integers int max(int a, int b) { return (a>b)? a : b; } public static void main(String[] args) { GarākāCommonSubsequence lcs = new GarākāCommonSubsequence(); Virkne S1 = 'AGGTAB'; Virkne S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = S1.garums(); int n = S2.garums(); System.out.println('LCS garums ir' + ' ' + lcs.lcs(S1, S2, m, n)); } } // Šī koda autors ir Saket Kumar>C## Dynamic Programming implementation of LCS problem def lcs(X, Y, m, n): # Declaring the array for storing the dp values L = [[None]*(n+1) for i in range(m+1)] # Following steps build L[m+1][n+1] in bottom up fashion # Note: L[i][j] contains length of LCS of X[0..i-1] # and Y[0..j-1] for i in range(m+1): for j in range(n+1): if i == 0 or j == 0: L[i][j] = 0 elif X[i-1] == Y[j-1]: L[i][j] = L[i-1][j-1]+1 else: L[i][j] = max(L[i-1][j], L[i][j-1]) # L[m][n] contains the length of LCS of X[0..n-1] & Y[0..m-1] return L[m][n] # Driver code if __name__ == '__main__': S1 = 'AGGTAB' S2 = 'GXTXAYB' m = len(S1) n = len(S2) print('Length of LCS is', lcs(S1, S2, m, n)) # This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)>// Dynamic Programming implementation of LCS problem using System; class GFG { // Returns length of LCS for X[0..m-1], Y[0..n-1] static int lcs(String X, String Y, int m, int n) { int[, ] L = new int[m + 1, n + 1]; // Following steps build L[m+1][n+1] // in bottom up fashion. // Note that L[i][j] contains length of // LCS of X[0..i-1] and Y[0..j-1] for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++) { for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) j == 0) L[i, j] = 0; else if (X[i - 1] == Y[j - 1]) L[i, j] = L[i - 1, j - 1] + 1; else L[i, j] = max(L[i - 1, j], L[i, j - 1]); } return L[m, n]; } // Utility function to get max of 2 integers static int max(int a, int b) { return (a>b)? a : b; } // Draivera kods public static void Main() { String S1 = 'AGGTAB'; Virkne S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; int m = S1.Garums; int n = S2.Garums; Console.Write('LCS garums ir' + ' ' + lcs(S1, S2, m, n)); } } // Šī koda autors ir Sam007>>PHP // Dynamic Programming C# // implementation of LCS problem function lcs($X , $Y, $m, $n) { // Following steps build L[m+1][n+1] // in bottom up fashion . // Note: L[i][j] contains length of // LCS of X[0..i-1] and Y[0..j-1] for ($i = 0; $i <= $m; $i++) { for ($j = 0; $j <= $n; $j++) if ($i == 0 } // L[m][n] contains the length of // LCS of X[0..n-1] & Y[0..m-1] return $L[$m][$n]; } // Driver Code $S1 = 'AGGTAB'; $S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; $m = strlen($S1); $n = strlen($S2) ; echo 'Length of LCS is '; echo lcs($S1, $S2, $m, $n); // This code is contributed // by Shivi_Aggarwal ?>>>
IzvadeLength of LCS is 4>Laika sarežģītība: O(m * n), kas ir daudz labāks par naivās rekursīvās ieviešanas sliktākā gadījuma laika sarežģītību.
Palīgtelpa: O(m * n), jo algoritms izmanto lieluma (m+1)*(n+1) masīvu, lai saglabātu kopējo apakšvirkņu garumu.Garākā kopīgā secība (LCS), izmantojot augšupvērstu (no apakšas uz augšu) (telpas optimizācija):
- Iepriekš minētajā tabulēšanas pieejā mēs izmantojam L[i-1][j] un L[i][j] utt, šeit L[i-1] attiecas uz matricas L iepriekšējo rindu un L[i] attiecas uz pašreizējā rinda.
- Mēs varam veikt telpas optimizāciju, izmantojot divus vektorus, no kuriem viens ir iepriekšējais un otrs ir pašreizējais.
- Kad iekšējā for cilpa iziet, mēs inicializējam iepriekšējo vienādu ar strāvu.
Tālāk ir norādīta ieviešana:
C++Java// Dynamic Programming C++ implementation // of LCS problem #include using namespace std; int longestCommonSubsequence(string& text1, string& text2) { int n = text1.size(); int m = text2.size(); // initializing 2 vectors of size m vectorprev(m + 1, 0), cur (m + 1, 0); for (int idx2 = 0; idx2< m + 1; idx2++) cur[idx2] = 0; for (int idx1 = 1; idx1 < n + 1; idx1++) { for (int idx2 = 1; idx2 < m + 1; idx2++) { // if matching if (text1[idx1 - 1] == text2[idx2 - 1]) cur[idx2] = 1 + prev[idx2 - 1]; // not matching else cur[idx2] = 0 + max(cur[idx2 - 1], prev[idx2]); } prev = cur; } return cur[m]; } int main() { string S1 = 'AGGTAB'; string S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; // Function call cout << 'Length of LCS is ' << longestCommonSubsequence(S1, S2); return 0; }> Python// Dynamic Programming Java implementation of LCS problem import java.util.Arrays; public class GFG { public static int longestCommonSubsequence(String text1, String text2) { int n = text1.length(); int m = text2.length(); // Initializing 2 arrays of size m int[] prev = new int[m + 1]; int[] cur = new int[m + 1]; for (int idx1 = 1; idx1 < n + 1; idx1++) { for (int idx2 = 1; idx2 < m + 1; idx2++) { // If matching if (text1.charAt(idx1 - 1) == text2.charAt(idx2 - 1)) cur[idx2] = 1 + prev[idx2 - 1]; // Not matching else cur[idx2] = Math.max(cur[idx2 - 1], prev[idx2]); } prev = Arrays.copyOf(cur, m + 1); } return cur[m]; } public static void main(String[] args) { String S1 = 'AGGTAB'; String S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; // Function call System.out.println('Length of LCS is ' + longestCommonSubsequence(S1, S2)); } }>C#def longestCommonSubsequence(text1, text2): n = len(text1) m = len(text2) # Initializing two lists of size m prev = [0] * (m + 1) cur = [0] * (m + 1) for idx1 in range(1, n + 1): for idx2 in range(1, m + 1): # If characters are matching if text1[idx1 - 1] == text2[idx2 - 1]: cur[idx2] = 1 + prev[idx2 - 1] else: # If characters are not matching cur[idx2] = max(cur[idx2 - 1], prev[idx2]) prev = cur.copy() return cur[m] if __name__ == '__main__': S1 = 'AGGTAB' S2 = 'GXTXAYB' # Function call print('Length of LCS is', longestCommonSubsequence(S1, S2)) # This code is contributed by Rishabh Mathur>Javascriptusing System; class Program { static int LongestCommonSubsequence(string text1, string text2) { int n = text1.Length; int m = text2.Length; // initializing 2 arrays of size m int[] prev = new int[m + 1]; int[] cur = new int[m + 1]; for (int idx2 = 0; idx2 < m + 1; idx2++) cur[idx2] = 0; for (int idx1 = 1; idx1 < n + 1; idx1++) { for (int idx2 = 1; idx2 < m + 1; idx2++) { // if matching if (text1[idx1 - 1] == text2[idx2 - 1]) cur[idx2] = 1 + prev[idx2 - 1]; // not matching else cur[idx2] = 0 + Math.Max(cur[idx2 - 1], prev[idx2]); } prev = cur; } return cur[m]; } static void Main() { string S1 = 'AGGTAB'; string S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; // Function call Console.WriteLine('Length of LCS is ' + LongestCommonSubsequence(S1, S2)); } }>function longestCommonSubsequence(text1, text2) { const n = text1.length; const m = text2.length; // Initializing two arrays of size m let prev = new Array(m + 1).fill(0); let cur = new Array(m + 1).fill(0); for (let idx2 = 0; idx2 < m + 1; idx2++) { cur[idx2] = 0; } for (let idx1 = 1; idx1 < n + 1; idx1++) { for (let idx2 = 1; idx2 < m + 1; idx2++) { // If characters match if (text1[idx1 - 1] === text2[idx2 - 1]) { cur[idx2] = 1 + prev[idx2 - 1]; } // If characters don't match else { cur[idx2] = Math.max(cur[idx2 - 1], prev[idx2]); } } // Update the 'prev' array prev = [...cur]; } return cur[m]; } // Main function function main() { const S1 = 'AGGTAB'; const S2 = 'GXTXAYB'; // Function call console.log('Length of LCS is ' + longestCommonSubsequence(S1, S2)); } // Call the main function main();>
IzvadeLaika sarežģītība: O(m * n), kas paliek nemainīgs.
Palīgtelpa: O(m), jo algoritms izmanto divus m izmēra masīvus.







