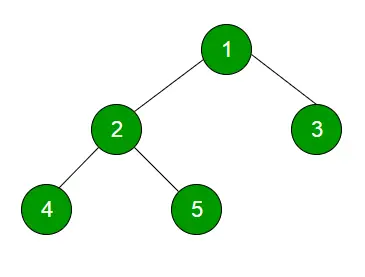
Līmeņa pasūtījumu izbraukšana tehnika ir definēta kā metode koka šķērsošanai, lai visi vienā līmenī esošie mezgli tiktu pilnībā šķērsoti pirms nākamā līmeņa šķērsošanas.
Piemērs:
Ieteicamā prakses līmeņa pasūtījuma šķērsošana Izmēģiniet to!Ievade:
Izvade:
1
23
Četri
Kā darbojas līmeņa pasūtījumu iziešana?
Līmeņu secības šķērsošanas galvenā ideja ir šķērsot visus zemāka līmeņa mezglus, pirms pāriet uz kādu no augstāka līmeņa mezgliem. To var izdarīt jebkurā no šiem veidiem:
- naivais (koka augstuma atrašana un katra līmeņa šķērsošana un šī līmeņa mezglu drukāšana)
- efektīvi izmantojot rindu.
Līmeņa secības iziešana (naiva pieeja):
Atrast augstums no koka. Pēc tam katram līmenim izpildiet rekursīvo funkciju, saglabājot pašreizējo augstumu. Ikreiz, kad sakrīt mezgla līmenis, izdrukājiet šo mezglu.
Tālāk ir aprakstīta iepriekš minētās pieejas īstenošana.
C++ // Recursive CPP program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree #include using namespace std; // A binary tree node has data, // pointer to left child // and a pointer to right child class node { public: int data; node *left, *right; }; // Function prototypes void printCurrentLevel(node* root, int level); int height(node* node); node* newNode(int data); // Function to print level order traversal a tree void printLevelOrder(node* root) { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Print nodes at a current level void printCurrentLevel(node* root, int level) { if (root == NULL) return; if (level == 1) cout << root->datus<< ' '; else if (level>1) { printCurrentLevel(sakne->pa kreisi, līmenis - 1); printCurrentLevel(sakne->pa labi, līmenis - 1); } } // Aprēķiniet koka 'augstumu' — // mezglu skaitu garākajā ceļā no saknes mezgla // uz leju līdz tālākajam lapas mezglam. int augstums(mezgls* mezgls) { if (mezgls == NULL) return 0; else { // Aprēķināt katra apakškoka augstumu int lheight = augstums(mezgls->pa kreisi); int rheight = augstums(mezgls->pa labi); // Izmantot lielāko if (lheight> rheight) { return (lheight + 1); } else { return (pa labi + 1); } } } // Palīdzības funkcija, kas piešķir // jaunu mezglu ar dotajiem datiem un // NULL kreiso un labo rādītāju. mezgls* jaunsMezgls(int dati) { mezgls* Mezgls = jauns mezgls(); Mezgls->dati = dati; Mezgls->pa kreisi = NULL; Mezgls->pa labi = NULL; atgriešanās (Node); } // Draivera kods int main() { node* root = newNode(1); sakne->pa kreisi = newNode(2); sakne->pa labi = newNode(3); sakne->pa kreisi->pa kreisi = newNode(4); sakne->pa kreisi->pa labi = newNode(5); cout<< 'Level Order traversal of binary tree is
'; printLevelOrder(root); return 0; } // This code is contributed by rathbhupendra> C // Recursive C program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree #include #include // A binary tree node has data, // pointer to left child // and a pointer to right child struct node { int data; struct node *left, *right; }; // Function prototypes void printCurrentLevel(struct node* root, int level); int height(struct node* node); struct node* newNode(int data); // Function to print level order traversal a tree void printLevelOrder(struct node* root) { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Print nodes at a current level void printCurrentLevel(struct node* root, int level) { if (root == NULL) return; if (level == 1) printf('%d ', root->dati); else if (līmenis> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root->left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(sakne->pa labi, līmenis - 1); } } // Aprēķiniet koka 'augstumu' -- mezglu // skaitu garākajā ceļā no saknes mezgla // uz leju līdz tālākajam lapas mezglam int augstums(struct node* node) { if (node == NULL) atgriež 0; else { // Aprēķināt katra apakškoka augstumu int lheight = augstums(mezgls->pa kreisi); int rheight = augstums(mezgls->pa labi); // Izmantot lielāko if (lheight> rheight) return (lheight + 1); cits atgriešanās (pa labi + 1); } } // Palīdzības funkcija, kas piešķir jaunu mezglu ar // dotajiem datiem un NULL kreiso un labo rādītāju. struct node* newNode(int data) { struct node* node = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); mezgls->dati = dati; mezgls->pa kreisi = NULL; mezgls->pa labi = NULL; atgriešanās (mezgls); } // Draivera programma, lai pārbaudītu iepriekš minētās funkcijas int main() { struct node* root = newNode(1); sakne->pa kreisi = newNode(2); sakne->pa labi = newNode(3); sakne->pa kreisi->pa kreisi = newNode(4); sakne->pa kreisi->pa labi = newNode(5); printf('Binārā koka līmeņa secība ir
'); printLevelOrder(sakne); atgriezties 0; }> Java // Recursive Java program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree // Class containing left and right child of current // node and key value class Node { int data; Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = null; } } class BinaryTree { // Root of the Binary Tree Node root; public BinaryTree() { root = null; } // Function to print level order traversal of tree void printLevelOrder() { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Compute the 'height' of a tree -- the number of // nodes along the longest path from the root node // down to the farthest leaf node. int height(Node root) { if (root == null) return 0; else { // Compute height of each subtree int lheight = height(root.left); int rheight = height(root.right); // use the larger one if (lheight>pa labi) atgriešanās (lheight + 1); cits atgriešanās (pa labi + 1); } } // Drukāt mezglus pašreizējā līmenī void printCurrentLevel(Node root, int level) { if (root == null) return; if (līmenis == 1) System.out.print(root.data + ' '); else if (līmenis> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root.left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(root.right, level - 1); } } // Draivera programma iepriekš minēto funkciju pārbaudei public static void main(String args[]) { BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree(); koks.sakne = jauns mezgls(1); tree.root.left = jauns mezgls(2); tree.root.right = jauns mezgls(3); tree.root.left.left = jauns mezgls(4); tree.root.left.right = jauns mezgls(5); System.out.println('Līmeņa secības šķērsošana' + 'binārais koks ir '); koks.printLevelOrder(); } }> Python # Recursive Python program for level # order traversal of Binary Tree # A node structure class Node: # A utility function to create a new node def __init__(self, key): self.data = key self.left = None self.right = None # Function to print level order traversal of tree def printLevelOrder(root): h = height(root) for i in range(1, h+1): printCurrentLevel(root, i) # Print nodes at a current level def printCurrentLevel(root, level): if root is None: return if level == 1: print(root.data, end=' ') elif level>1: printCurrentLevel(root.left, level-1) print CurrentLevel(root.right, level-1) # Aprēķiniet koka augstumu — mezglu skaitu # gar garāko ceļu no saknes mezgla līdz # vistālākajai lapai mezgla def augstums(mezgls): ja mezgls ir Nav: atgriezt 0 else: # Aprēķiniet katra apakškoka augstumu lheight = augstums(mezgls.pa kreisi) rheight = augstums(mezgls.labais) # Izmantojiet lielāko, ja lheight> rheight: atgriezties lheight+1 else: return rheight+1 # Draivera programma, lai pārbaudītu iepriekš minēto funkciju, ja __name__ == '__main__': root = Node(1) root.left = Node(2) root.right = Node(3) root. left.left = Mezgls(4) root.left.right = Mezgls(5) print('Binārā koka līmeņa secība ir -') printLevelOrder(root) # Šo kodu ir sagatavojis Nikhils Kumars Singhs(nickzuck_007)> C# // Recursive c# program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree using System; // Class containing left and right // child of current node and key value public class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = null; } } class GFG { // Root of the Binary Tree public Node root; public void BinaryTree() { root = null; } // Function to print level order // traversal of tree public virtual void printLevelOrder() { int h = height(root); int i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) { printCurrentLevel(root, i); } } // Compute the 'height' of a tree -- // the number of nodes along the longest // path from the root node down to the // farthest leaf node. public virtual int height(Node root) { if (root == null) { return 0; } else { // Compute height of each subtree int lheight = height(root.left); int rheight = height(root.right); // use the larger one if (lheight>pa labi) { atgriešanās (gaisums + 1); } else { return (pa labi + 1); } } } // Drukāt mezglus pašreizējā līmenī public virtual void printCurrentLevel(Node root, int level) { if (root == null) { return; } if (līmenis == 1) { Console.Write(root.data + ' '); } else if (līmenis> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root.left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(root.right, level - 1); } } // Draivera kods public static void Main(string[] args) { GFG koks = new GFG(); koks.sakne = jauns mezgls(1); tree.root.left = jauns mezgls(2); tree.root.right = jauns mezgls(3); tree.root.left.left = jauns mezgls(4); tree.root.left.right = jauns mezgls(5); Console.WriteLine('Līmeņa secības traversal ' + 'binārā koka ir '); koks.printLevelOrder(); } } // Šo kodu ir sagatavojis Shrikant13> Javascript // Recursive javascript program for level // order traversal of Binary Tree // Class containing left and right child of current // node and key value class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Root of the Binary Tree var root= null; // Function to print level order traversal of tree function printLevelOrder() { var h = height(root); var i; for (i = 1; i <= h; i++) printCurrentLevel(root, i); } // Compute the 'height' of a tree -- the number // of nodes along the longest path // from the root node down to the farthest leaf node. function height(root) { if (root == null) return 0; else { // Compute height of each subtree var lheight = height(root.left); var rheight = height(root.right); // Use the larger one if (lheight>pa labi) atgriešanās (lheight + 1); cits atgriešanās (pa labi + 1); } } // Drukāt mezglus pašreizējā līmenī function printCurrentLevel(root , level) { if (root == null) return; if (līmenis == 1) console.log(root.data + ' '); else if (līmenis> 1) { printCurrentLevel(root.left, level - 1); printCurrentLevel(root.right, level - 1); } } // Draivera programma iepriekš minēto funkciju pārbaudei root = new Node(1); root.left = jauns mezgls(2); root.right = jauns mezgls(3); root.left.left = jauns mezgls(4); root.left.right = jauns mezgls(5); console.log('Binārā koka līmeņu secība ir '); printLevelOrder(); // Šo kodu ir izstrādājis umadevi9616> Izvade
Level Order traversal of binary tree is 1 2 3 4 5>
Laika sarežģītība: O(N), kur N ir mezglu skaits šķībajā kokā.
Palīgtelpa: O(1) Ja ņem vērā rekursijas steku, izmantotā vieta ir O(N).
fibonači kods java
Līmeņa pasūtījumu apceļošana, izmantojot Rinda
Mums jāapmeklē zemākā līmeņa mezgli pirms jebkura augstākā līmeņa mezgla, šī ideja ir diezgan līdzīga rindas idejai. Nospiediet rindas zemāka līmeņa mezglus. Kad tiek apmeklēts kāds mezgls, izņemiet šo mezglu no rindas un iespiediet rindā šī mezgla atvasināto.
Tas nodrošina, ka zemāka līmeņa mezgls tiek apmeklēts pirms jebkura augstāka līmeņa mezgla.
Zemāk ir aprakstīta iepriekš minētās pieejas īstenošana:
C++ // C++ program to print level order traversal #include using namespace std; // A Binary Tree Node struct Node { int data; struct Node *left, *right; }; // Iterative method to find height of Binary Tree void printLevelOrder(Node* root) { // Base Case if (root == NULL) return; // Create an empty queue for level order traversal queueq; // Iekļauts saknes rindā un inicializēts augstums q.push(root); while (q.empty() == false) { // Izdrukā rindas priekšpusi un noņem to no rindas Node* node = q.front(); cout<< node->datus<< ' '; q.pop(); // Enqueue left child if (node->pa kreisi != NULL) q.push(node->left); // Ierindot labo atvasi if (node->right != NULL) q.push(node->right); } } // Utilīta funkcija jauna koka mezgla izveidei Node* newNode(int data) { Node* temp = new Node; temp->dati = dati; temp->pa kreisi = temp->pa labi = NULL; atgriešanās temperatūra; } // Draivera programma, lai pārbaudītu augstāk minētās funkcijas int main() { // Izveidosim bināro koku, kas parādīts iepriekš diagrammā Node* root = newNode(1); sakne->pa kreisi = newNode(2); sakne->pa labi = newNode(3); sakne->pa kreisi->pa kreisi = newNode(4); sakne->pa kreisi->pa labi = newNode(5); cout<< 'Level Order traversal of binary tree is
'; printLevelOrder(root); return 0; }> C // Iterative Queue based C program // to do level order traversal // of Binary Tree #include #include #define MAX_Q_SIZE 500 // A binary tree node has data, // pointer to left child // and a pointer to right child struct node { int data; struct node* left; struct node* right; }; // Function prototypes struct node** createQueue(int*, int*); void enQueue(struct node**, int*, struct node*); struct node* deQueue(struct node**, int*); // Given a binary tree, print its nodes in level order // using array for implementing queue void printLevelOrder(struct node* root) { int rear, front; struct node** queue = createQueue(&front, &rear); struct node* temp_node = root; while (temp_node) { printf('%d ', temp_node->dati); // Rindā atstāto bērnu if (temp_node->left) enQueue(queue, &rear, temp_node->left); // Rindā labo atvasināto if (temp_node->right) enQueue(queue, &rear, temp_node->right); // Atvienot mezglu un padarīt to temp_node temp_node = deQueue(queue, &front); } } // Utilītas funkcijas struct node** createQueue(int* front, int* rear) { struct node** queue = (struct node**)malloc( sizeof(struct node*) * MAX_Q_SIZE); *priekšpuse = *aizmugure = 0; atgriešanas rinda; } void enQueue(struct node** rinda, int* aizmugure, struct node* new_node) { rinda[*aizmugure] = jauns_mezgls; (*aizmugurē)++; } struct node* deQueue(struct node** rinda, int* front) { (*front)++; atgriešanas rinda[*priekšpuse - 1]; } // Palīdzības funkcija, kas piešķir jaunu mezglu ar // dotajiem datiem un NULL kreiso un labo rādītāju. struct node* newNode(int data) { struct node* node = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); mezgls->dati = dati; mezgls->pa kreisi = NULL; mezgls->pa labi = NULL; atgriešanās (mezgls); } // Draivera programma, lai pārbaudītu iepriekš minētās funkcijas int main() { struct node* root = newNode(1); sakne->pa kreisi = newNode(2); sakne->pa labi = newNode(3); sakne->pa kreisi->pa kreisi = newNode(4); sakne->pa kreisi->pa labi = newNode(5); printf('Binārā koka līmeņa secība ir
'); printLevelOrder(sakne); atgriezties 0; }> Java // Iterative Queue based Java program // to do level order traversal // of Binary Tree import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; // Class to represent Tree node class Node { int data; Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = null; right = null; } } // Class to print Level Order Traversal class BinaryTree { Node root; // Given a binary tree. Print // its nodes in level order // using array for implementing queue void printLevelOrder() { Queuerinda = jauns LinkedList(); queue.add(sakne); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { // poll() noņem pašreizējo galveni. Mezgls tempNode = queue.poll(); System.out.print(tempNode.data + ' '); // Ielikt rindā kreiso bērnu if (tempNode.left != null) { queue.add(tempNode.left); } // Iestatīt pareizo bērnu rindā if (tempNode.right != null) { queue.add(tempNode.right); } } } public static void main(String args[]) { // Bināra koka izveide un // mezglu ievadīšana BinaryTree tree_level = new BinaryTree(); tree_level.root = jauns mezgls(1); tree_level.root.left = jauns mezgls(2); tree_level.root.right = jauns mezgls(3); tree_level.root.left.left = jauns mezgls(4); tree_level.root.left.right = jauns mezgls(5); System.out.println('Binārā koka līmeņu secība ir - '); tree_level.printLevelOrder(); } }> Python # Python program to print level # order traversal using Queue # A node structure class Node: # A utility function to create a new node def __init__(self, key): self.data = key self.left = None self.right = None # Iterative Method to print the # height of a binary tree def printLevelOrder(root): # Base Case if root is None: return # Create an empty queue # for level order traversal queue = [] # Enqueue Root and initialize height queue.append(root) while(len(queue)>0): # Izdrukājiet rindas priekšpusi un # noņemiet to no rindas print(queue[0].data, end=' ') node = queue.pop(0) # Ja node.left nav None: queue.append(node.left) # Iekļaut labās rindas atvasinātāju, ja node.right nav Neviens: queue.append(node.right) # Draiverprogramma, lai pārbaudītu iepriekš minēto funkciju, ja __name__ == '__main__': root = Node(1 ) root.left = Mezgls(2) root.right = Mezgls(3) root.left.left = Mezgls(4) root.left.right = Mezgls(5) print('Līmeņa secība Binārā koka šķērsošana ir - ') printLevelOrder(root) # Šo kodu ir sagatavojis Nikhils Kumars Singhs(nickzuck_007)> C# // Iterative Queue based C# program // to do level order traversal // of Binary Tree using System; using System.Collections.Generic; // Class to represent Tree node public class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = null; right = null; } } // Class to print Level Order Traversal public class BinaryTree { Node root; // Given a binary tree. Print // its nodes in level order using // array for implementing queue void printLevelOrder() { Queuerinda = jauna rinda(); rinda.Rinda(sakne); while (rinda.Skaits != 0) { Mezgls tempMezgls = rinda.Dequeue(); Console.Write(tempNode.data + ' '); // Ielikt rindā kreiso bērnu if (tempNode.left != null) { queue.Enqueue(tempNode.left); } // Iestatīt pareizo atvasināto rindu if (tempNode.right != null) { queue.Enqueue(tempNode.right); } } } // Draivera kods public static void Main() { // Bināra koka izveide un // mezglu ievadīšana BinaryTree tree_level = new BinaryTree(); tree_level.root = jauns mezgls(1); tree_level.root.left = jauns mezgls(2); tree_level.root.right = jauns mezgls(3); tree_level.root.left.left = jauns mezgls(4); tree_level.root.left.right = jauns mezgls(5); Console.WriteLine('Binārā koka līmeņa secības traversal ' + 'ir - '); tree_level.printLevelOrder(); } } // Šo kodu sniedza PrinciRaj1992> Javascript class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Class to represent a deque (double-ended queue) class Deque { constructor() { this.queue = []; } // Method to add an element to the end of the queue enqueue(item) { this.queue.push(item); } // Method to remove and return the first element of the queue dequeue() { return this.queue.shift(); } // Method to check if the queue is empty isEmpty() { return this.queue.length === 0; } } // Function to perform level order traversal of a binary tree function printLevelOrder(root) { // Create a deque to store nodes for traversal const queue = new Deque(); // Add the root node to the queue queue.enqueue(root); // Continue traversal until the queue is empty while (!queue.isEmpty()) { // Remove and get the first node from the queue const tempNode = queue.dequeue(); // Print the data of the current node console.log(tempNode.data + ' '); // Enqueue the left child if it exists if (tempNode.left !== null) { queue.enqueue(tempNode.left); } // Enqueue the right child if it exists if (tempNode.right !== null) { queue.enqueue(tempNode.right); } } } // Create a binary tree and enter the nodes const root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); // Print the level order traversal of the binary tree console.log('Level order traversal of binary tree is - '); printLevelOrder(root);> Izvade
Level Order traversal of binary tree is 1 2 3 4 5>
Laika sarežģītība: O(N), kur N ir mezglu skaits binārajā kokā.
Palīgtelpa: O(N), kur N ir mezglu skaits binārajā kokā.