Šajā rakstā mēs redzēsim dažādus veidus, kā ierakstīt failā, izmantojot Java programmēšanas valodu. Java FileWriter klase java tiek izmantota, lai failā ierakstītu uz rakstzīmēm orientētus datus, jo šī klase ir uz rakstzīmēm orientēta klase, jo tā tiek izmantota failu apstrādē Java.
Tur ir daudz veidi, kā rakstīt failā Java jo ir daudzas klases un metodes, kas var sasniegt šādu mērķi:
- Izmantojot writeString() metodi
- Izmantojot FileWriter klasi
- BufferedWriter klases izmantošana
- Izmantojot FileOutputStream klasi
1. metode: rakstīšanas string() metodes izmantošana
Šo metodi atbalsta Java versija 11. Šai metodei var būt nepieciešami četri parametri. Tie ir faila ceļš, rakstzīmju secība, rakstzīmju kopa un opcijas. Pirmie divi parametri ir obligāti, lai šī metode ierakstītu failā. Tas raksta rakstzīmes kā faila saturu. Tas atgriež faila ceļu un var izmantot četru veidu izņēmumus. To labāk izmantot, ja faila saturs ir īss.
Piemērs: Tas parāda, kā tiek izmantots writeString() metode, kas atrodas klasē Faili, lai ierakstītu datus failā. Cita klase — ceļš — tiek izmantota, lai faila nosaukumam piešķirtu ceļu, kurā tiks rakstīts saturs. Failu klasei ir cita metode readString() lai lasītu jebkura esošā faila saturu, kas tiek izmantots kodā, lai pārbaudītu, vai saturs ir pareizi ierakstīts failā.
Java
int uz virkni konvertēšanu
// Java Program to Write Into a File> // using writeString() Method> // Importing required classes> import> java.io.IOException;> import> java.nio.file.Files;> import> java.nio.file.Path;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >throws> IOException> >{> >// Assigning the content of the file> >String text> >=>'Welcome to geekforgeeks
Happy Learning!'>;> >// Defining the file name of the file> >Path fileName = Path.of(> >'/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/demo.docx'>);> >// Writing into the file> >Files.writeString(fileName, text);> >// Reading the content of the file> >String file_content = Files.readString(fileName);> >// Printing the content inside the file> >System.out.println(file_content);> >}> }> |
>
atspējot izstrādātāja režīmu
>Izvade
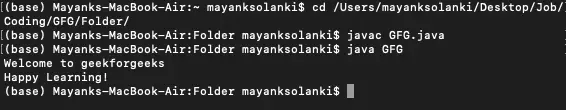
Welcome to geekforgeeks Happy Learning!>
2. metode: FileWriter klases izmantošana
Ja faila saturs ir īss, vēl viena labāka iespēja ir izmantot FileWriter klasi, lai rakstītu failā. Tas arī raksta rakstzīmju straumi kā faila saturu, piemēram, writeString() metodi. Šīs klases konstruktors nosaka noklusējuma rakstzīmju kodējumu un noklusējuma bufera lielumu baitos.
Šis piemērs ilustrē FileWriter klases izmantošanu satura ierakstīšanai failā. Lai rakstītu failā, ir jāizveido FileWriter klases objekts ar faila nosaukumu. Tālāk tiek izmantota metode write(), lai failā ierakstītu teksta mainīgā vērtību. Ja faila rakstīšanas laikā rodas kāda kļūda, tiks izmests IOException un kļūdas ziņojums tiks izdrukāts no uztveršanas bloka.
Piemērs:
Java
// Java Program to Write into a File> // using FileWriterClass> // Importing required classes> import> java.io.FileWriter;> import> java.io.IOException;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Content to be assigned to a file> >// Custom input just for illustration purposes> >String text> >=>'Computer Science Portal techcodeview.com'>;> >// Try block to check if exception occurs> >try> {> >// Create a FileWriter object> >// to write in the file> >FileWriter fWriter =>new> FileWriter(> >'/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/demo.docx'>);> >// Writing into file> >// Note: The content taken above inside the> >// string> >fWriter.write(text);> >// Printing the contents of a file> >System.out.println(text);> >// Closing the file writing connection> >fWriter.close();> >// Display message for successful execution of> >// program on the console> >System.out.println(> >'File is created successfully with the content.'>);> >}> >// Catch block to handle if exception occurs> >catch> (IOException e) {> >// Print the exception> >System.out.print(e.getMessage());> >}> >}> }> |
>
javascript apmācība
>Izvade
File is created successfully with the content.>

3. metode: BufferedWriter klases izmantošana
To izmanto, lai rakstītu tekstu rakstzīmju izvades straumē. Tam ir noklusējuma bufera izmērs, taču var piešķirt lielu bufera izmēru. Tas ir noderīgi rakstzīmju, virkņu un masīvu rakstīšanai. Labāk ir ietīt šo klasi ar jebkuru rakstītāju klasi, lai ierakstītu datus failā, ja nav nepieciešama tūlītēja izvade.
Piemērs:
Java
// Java Program to write into a File> // Using BufferedWriter Class> // Importing java input output libraries> import> java.io.BufferedWriter;> import> java.io.FileWriter;> import> java.io.IOException;> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Assigning the file content> >// Note: Custom contents taken as input to> >// illustrate> >String text> >=>'Computer Science Portal techcodeview.com'>;> >// Try block to check for exceptions> >try> {> >// Step 1: Create an object of BufferedWriter> >BufferedWriter f_writer> >=>new> BufferedWriter(>new> FileWriter(> >'/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/demo.docx'>));> >// Step 2: Write text(content) to file> >f_writer.write(text);> >// Step 3: Printing the content inside the file> >// on the terminal/CMD> >System.out.print(text);> >// Step 4: Display message showcasing> >// successful execution of the program> >System.out.print(> >'File is created successfully with the content.'>);> >// Step 5: Close the BufferedWriter object> >f_writer.close();> >}> >// Catch block to handle if exceptions occurs> >catch> (IOException e) {> >// Print the exception on console> >// using getMessage() method> >System.out.print(e.getMessage());> >}> >}> }> |
>
>Izvade
java programmēšanas masīvi
File is created successfully with the content.>

Šis piemērs parāda klases BufferedWriter izmantošanu, lai rakstītu failā. Lai failā ierakstītu saturu, ir jāizveido arī BufferedWriter klases objekts, piemēram, FileWriter. Bet šī klase atbalsta lielu saturu, lai rakstītu failā, izmantojot lielu bufera izmēru.
4. metode: FileOutputStream klases izmantošana
To izmanto, lai failā ierakstītu neapstrādātus straumes datus. Klases FileWriter un BufferedWriter tiek izmantotas, lai failā ierakstītu tikai tekstu, bet bināros datus var ierakstīt, izmantojot klasi FileOutputStream.
Datu ierakstīšana failā, izmantojot FileOutputStream klase ir parādīta nākamajā piemērā. Lai ierakstītu datus failā, ir jāizveido arī klases objekts ar faila nosaukumu. Šeit virknes saturs tiek pārveidots par baitu masīvu, kas tiek ierakstīts failā, izmantojot rakstīt () metodi.
Piemērs:
Java
// Java Program to Write into a File> // using FileOutputStream Class> // Importing java input output classes> import> java.io.FileOutputStream;> import> java.io.IOException;> public> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Assign the file content> >String fileContent =>'Welcome to geeksforgeeks'>;> >FileOutputStream outputStream =>null>;> >// Try block to check if exception occurs> >try> {> >// Step 1: Create an object of FileOutputStream> >outputStream =>new> FileOutputStream(>'file.txt'>);> >// Step 2: Store byte content from string> >byte>[] strToBytes = fileContent.getBytes();> >// Step 3: Write into the file> >outputStream.write(strToBytes);> >// Print the success message (Optional)> >System.out.print(> >'File is created successfully with the content.'>);> >}> >// Catch block to handle the exception> >catch> (IOException e) {> >// Display the exception/s> >System.out.print(e.getMessage());> >}> >// finally keyword is used with in try catch block> >// and this code will always execute whether> >// exception occurred or not> >finally> {> >// Step 4: Close the object> >if> (outputStream !=>null>) {> >// Note: Second try catch block ensures that> >// the file is closed even if an error> >// occurs> >try> {> >// Closing the file connections> >// if no exception has occurred> >outputStream.close();> >}> >catch> (IOException e) {> >// Display exceptions if occurred> >System.out.print(e.getMessage());> >}> >}> >}> >}> }> |
reliģiju saraksts
>
>Izvade
File is created successfully with the content.>
