The free() funkcija C tiek izmantots, lai atbrīvotu vai sadalītu dinamiski piešķirto atmiņu un palīdz samazināt atmiņas zudumu. The C bezmaksas () funkciju nevar izmantot, lai atbrīvotu statiski piešķirto atmiņu (piem., lokālos mainīgos) vai stekā piešķirto atmiņu. To var izmantot tikai, lai noņemtu kaudzes atmiņu, kas iepriekš piešķirta, izmantojot funkcijas malloc (), calloc () un realloc ().
Funkcija free () ir definēta iekšpusē galvenes fails.
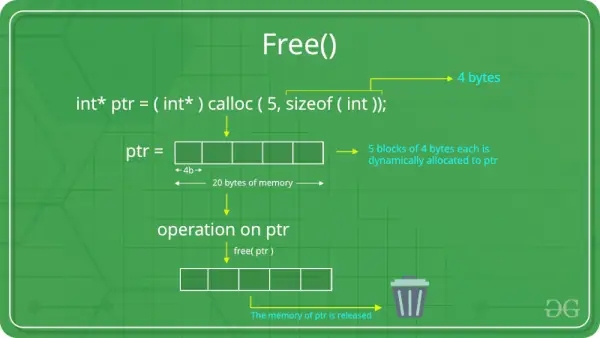
C free() funkcija
Funkcijas free() sintakse valodā C
void free (void * ptr );>
Parametri
- ptr ir rādītājs uz atmiņas bloku, kas ir jāatbrīvo vai jāatdala.
Atdeves vērtība
- Funkcija free () neatgriež nekādu vērtību.
Bezmaksas () piemēri
1. piemērs:
Sekojošā C programma ilustrē izmantošanu calloc() funkcija, lai dinamiski piešķirtu atmiņu un bezmaksas () funkcija, lai atbrīvotu šo atmiņu.
C
mašīnraksta bultiņas funkcija
// C program to demonstrate use of> // free() function using calloc()> #include> #include> int> main()> {> >// This pointer ptr will hold the> >// base address of the block created> >int>* ptr;> >int> n = 5;> >// Get the number of elements for the array> >printf>(>'Enter number of Elements: %d
'>, n);> >scanf>(>'%d'>, &n);> >// Dynamically allocate memory using calloc()> >ptr = (>int>*)>calloc>(n,>sizeof>(>int>));> >// Check if the memory has been successfully> >// allocated by calloc() or not> >if> (ptr == NULL) {> >printf>(>'Memory not allocated
'>);> >exit>(0);> >}> >// Memory has been Successfully allocated using calloc()> >printf>(>'Successfully allocated the memory using '> >'calloc().
'>);> >// Free the memory> >free>(ptr);> >printf>(>'Calloc Memory Successfully freed.'>);> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>Izvade
Enter number of Elements: 5 Successfully allocated the memory using calloc(). Calloc Memory Successfully freed.>
2. piemērs:
Sekojošā C programma ilustrē izmantošanu malloc () funkcija, lai dinamiski piešķirtu atmiņu un bezmaksas () funkcija, lai atbrīvotu šo atmiņu.
C
// C program to demonstrate use of> // free() function using malloc()> #include> #include> int> main()> {> >// This pointer ptr will hold the> >// base address of the block created> >int>* ptr;> >int> n = 5;> >// Get the number of elements for the array> >printf>(>'Enter number of Elements: %d
'>, n);> >scanf>(>'%d'>, &n);> >// Dynamically allocate memory using malloc()> >ptr = (>int>*)>malloc>(n *>sizeof>(>int>));> >// Check if the memory has been successfully> >// allocated by malloc() or not> >if> (ptr == NULL) {> >printf>(>'Memory not allocated
'>);> >exit>(0);> >}> >// Memory has been Successfully allocated using malloc()> >printf>(>'Successfully allocated the memory using '> >'malloc().
'>);> >// Free the memory> >free>(ptr);> >printf>(>'Malloc Memory Successfully freed.'>);> >return> 0;> }> |
>
prologa valoda
>Izvade
Enter number of Elements: 5 Successfully allocated the memory using malloc(). Malloc Memory Successfully freed.>
