Minimax ir sava veida atkāpšanās algoritms, kas tiek izmantots lēmumu pieņemšanā un spēles teorijā, lai atrastu spēlētājam optimālo gājienu, pieņemot, ka arī jūsu pretinieks spēlē optimāli. To plaši izmanto divu spēlētāju gājienu spēlēs, piemēram, Tic-Tac-Toe, Backgammon, Mancala, Chess utt.
Programmā Minimax divus spēlētājus sauc par maksimizatoru un minimizētāju. The maksimizētājs mēģina iegūt pēc iespējas augstāku punktu skaitu minimizētājs cenšas rīkoties pretēji un iegūt pēc iespējas zemāku punktu skaitu.
Katram valdes stāvoklim ir ar to saistīta vērtība. Konkrētajā stāvoklī, ja maksimizētājs ir pārsvars, dēļa rezultāts parasti būs pozitīva. Ja šajā dēļa stāvoklī pārsvars ir minimizētājam, tad tā parasti ir negatīva vērtība. Galda vērtības tiek aprēķinātas, izmantojot dažas heiristikas, kas ir unikālas katram spēles veidam.
Piemērs:
Apsveriet spēli, kurai ir 4 gala stāvokļi un ceļi, lai sasniegtu gala stāvokli, ir no saknes līdz 4 ideāla binārā koka lapām, kā parādīts zemāk. Pieņemsim, ka esat maksimizējošs spēlētājs un jums ir pirmā iespēja pārvietoties, t.i., jūs atrodaties saknē un pretinieks atrodas nākamajā līmenī. Kuru gājienu jūs veiktu kā maksimizējošs spēlētājs, ņemot vērā, ka arī jūsu pretinieks spēlē optimāli?
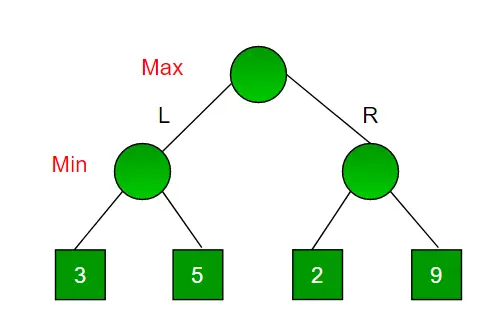
Tā kā šis algoritms ir balstīts uz atkāpšanos, tas izmēģina visas iespējamās kustības, pēc tam atkāpjas un pieņem lēmumu.
- Maksimizators iet pa kreisi: tagad ir minimizētāju kārta. Minimizētājam tagad ir iespēja izvēlēties starp 3 un 5. Tā kā tas ir samazinātājs, tas noteikti izvēlēsies vismazāko no abiem, tas ir, 3
- Maksimizētājs iet pa labi: tagad ir minimizētāju kārta. Minimizētājam tagad ir iespēja izvēlēties starp 2 un 9. Viņš izvēlēsies 2, jo tā ir vismazākā starp divām vērtībām.
Ja esat maksimizētājs, jūs izvēlētos lielāku vērtību, kas ir 3. Tādējādi maksimizatora optimālā kustība ir iet pa kreisi, un optimālā vērtība ir 3.
Tagad spēles koks izskatās šādi:

Augšējais koks parāda divus iespējamos punktus, kad maksimizators veic kustības pa kreisi un pa labi.
Piezīme. Lai gan labajā apakškokā ir vērtība 9, minimizētājs to nekad neizvēlēsies. Vienmēr jāpieņem, ka pretinieks spēlē optimāli.
Zemāk ir tā īstenošana.
C++
// A simple C++ program to find> // maximum score that> // maximizing player can get.> #include> using> namespace> std;> // Returns the optimal value a maximizer can obtain.> // depth is current depth in game tree.> // nodeIndex is index of current node in scores[].> // isMax is true if current move is> // of maximizer, else false> // scores[] stores leaves of Game tree.> // h is maximum height of Game tree> int> minimax(>int> depth,>int> nodeIndex,>bool> isMax,> >int> scores[],>int> h)> {> >// Terminating condition. i.e> >// leaf node is reached> >if> (depth == h)> >return> scores[nodeIndex];> >// If current move is maximizer,> >// find the maximum attainable> >// value> >if> (isMax)> >return> max(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>false>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>false>, scores, h));> >// Else (If current move is Minimizer), find the minimum> >// attainable value> >else> >return> min(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>true>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>true>, scores, h));> }> // A utility function to find Log n in base 2> int> log2(>int> n)> {> >return> (n==1)? 0 : 1 + log2(n/2);> }> // Driver code> int> main()> {> >// The number of elements in scores must be> >// a power of 2.> >int> scores[] = {3, 5, 2, 9, 12, 5, 23, 23};> >int> n =>sizeof>(scores)/>sizeof>(scores[0]);> >int> h = log2(n);> >int> res = minimax(0, 0,>true>, scores, h);> >cout <<>'The optimal value is : '> << res << endl;> >return> 0;> }> |
>
>
Java
// A simple java program to find maximum score that> // maximizing player can get.> import> java.io.*;> class> GFG {> > // Returns the optimal value a maximizer can obtain.> // depth is current depth in game tree.> // nodeIndex is index of current node in scores[].> // isMax is true if current move is of maximizer, else false> // scores[] stores leaves of Game tree.> // h is maximum height of Game tree> >static> int> minimax(>int> depth,>int> nodeIndex,>boolean> isMax,> >int> scores[],>int> h)> {> >// Terminating condition. i.e leaf node is reached> >if> (depth == h)> >return> scores[nodeIndex];> >// If current move is maximizer, find the maximum attainable> >// value> >if> (isMax)> >return> Math.max(minimax(depth+>1>, nodeIndex*>2>,>false>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+>1>, nodeIndex*>2> +>1>,>false>, scores, h));> >// Else (If current move is Minimizer), find the minimum> >// attainable value> >else> >return> Math.min(minimax(depth+>1>, nodeIndex*>2>,>true>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+>1>, nodeIndex*>2> +>1>,>true>, scores, h));> }> // A utility function to find Log n in base 2> >static> int> log2(>int> n)> {> return> (n==>1>)?>0> :>1> + log2(n/>2>);> }> // Driver code> >public> static> void> main (String[] args) {> >// The number of elements in scores must be> >// a power of 2.> >int> scores[] = {>3>,>5>,>2>,>9>,>12>,>5>,>23>,>23>};> >int> n = scores.length;> >int> h = log2(n);> >int> res = minimax(>0>,>0>,>true>, scores, h);> >System.out.println(>'The optimal value is : '> +res);> > >}> }> // This code is contributed by vt_m> |
>
>
C#
// A simple C# program to find maximum score that> // maximizing player can get.> using> System;> public> class> GFG> {> > // Returns the optimal value a maximizer can obtain.> // depth is current depth in game tree.> // nodeIndex is index of current node in scores[].> // isMax is true if current move is of maximizer, else false> // scores[] stores leaves of Game tree.> // h is maximum height of Game tree> static> int> minimax(>int> depth,>int> nodeIndex,>bool> isMax,> >int> []scores,>int> h)> {> >// Terminating condition. i.e leaf node is reached> >if> (depth == h)> >return> scores[nodeIndex];> >// If current move is maximizer, find the maximum attainable> >// value> >if> (isMax)> >return> Math.Max(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>false>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>false>, scores, h));> >// Else (If current move is Minimizer), find the minimum> >// attainable value> >else> >return> Math.Min(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>true>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>true>, scores, h));> }> // A utility function to find Log n in base 2> static> int> log2(>int> n)> {> >return> (n==1)? 0 : 1 + log2(n/2);> }> // Driver code> static> public> void> Main ()> {> >// The number of elements in scores must be> >// a power of 2.> >int> []scores = {3, 5, 2, 9, 12, 5, 23, 23};> >int> n = scores.Length;> >int> h = log2(n);> >int> res = minimax(0, 0,>true>, scores, h);> >Console.WriteLine(>'The optimal value is : '> +res);> > }> }> // This code is contributed by ajit.> |
tējkarotes lielums
>
>
Python3
# A simple Python3 program to find> # maximum score that> # maximizing player can get> import> math> def> minimax (curDepth, nodeIndex,> >maxTurn, scores,> >targetDepth):> ># base case : targetDepth reached> >if> (curDepth>=>=> targetDepth):> >return> scores[nodeIndex]> > >if> (maxTurn):> >return> max>(minimax(curDepth>+> 1>, nodeIndex>*> 2>,> >False>, scores, targetDepth),> >minimax(curDepth>+> 1>, nodeIndex>*> 2> +> 1>,> >False>, scores, targetDepth))> > >else>:> >return> min>(minimax(curDepth>+> 1>, nodeIndex>*> 2>,> >True>, scores, targetDepth),> >minimax(curDepth>+> 1>, nodeIndex>*> 2> +> 1>,> >True>, scores, targetDepth))> > # Driver code> scores>=> [>3>,>5>,>2>,>9>,>12>,>5>,>23>,>23>]> treeDepth>=> math.log(>len>(scores),>2>)> print>(>'The optimal value is : '>, end>=> '')> print>(minimax(>0>,>0>,>True>, scores, treeDepth))> # This code is contributed> # by rootshadow> |
>
>
Javascript
> // Javascript program to find maximum score that> // maximizing player can get.> // Returns the optimal value a maximizer can obtain.> // depth is current depth in game tree.> // nodeIndex is index of current node in scores[].> // isMax is true if current move is of maximizer, else false> // scores[] stores leaves of Game tree.> // h is maximum height of Game tree> >function> minimax(depth, nodeIndex, isMax,> >scores, h)> {> >// Terminating condition. i.e leaf node is reached> >if> (depth == h)> >return> scores[nodeIndex];> > >// If current move is maximizer, find the maximum attainable> >// value> >if> (isMax)> >return> Math.max(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>false>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>false>, scores, h));> > >// Else (If current move is Minimizer), find the minimum> >// attainable value> >else> >return> Math.min(minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2,>true>, scores, h),> >minimax(depth+1, nodeIndex*2 + 1,>true>, scores, h));> }> > // A utility function to find Log n in base 2> >function> log2(n)> {> return> (n==1)? 0 : 1 + log2(n/2);> }> > // Driver Code> >// The number of elements in scores must be> >// a power of 2.> >let scores = [3, 5, 2, 9, 12, 5, 23, 23];> >let n = scores.length;> >let h = log2(n);> >let res = minimax(0, 0,>true>, scores, h);> >document.write(>'The optimal value is : '> +res);> > > > |
>
>
Izvade:
The optimal value is: 12>
Laika sarežģītība: O(b^d) b ir sazarojuma koeficients, un d ir diagrammas vai koka dziļuma vai kārtas skaits.
Kosmosa sarežģītība: O(bd), kur b ir sazarošanās koeficients d, ir koka maksimālais dziļums, kas līdzīgs DFS.
Šī raksta ideja ir iepazīstināt ar Minimax ar vienkāršu piemēru.
- Iepriekš minētajā piemērā spēlētājam ir tikai divas izvēles iespējas. Kopumā var būt vairāk izvēles iespēju. Tādā gadījumā mums ir jāatkārto visas iespējamās kustības un jāatrod maksimums/minimums. Piemēram, spēlē Tic-Tac-Toe pirmais spēlētājs var veikt 9 iespējamos gājienus.
- Iepriekš minētajā piemērā rezultāti (spēļu koka lapas) ir doti mums. Tipiskai spēlei mums ir jāatvasina šīs vērtības
Mēs drīzumā aptversim Tic Tac Toe ar Minimax algoritmu.
Šī raksta autors ir Akshay L. Aradhya.
