 #practiceLinkDiv { display: none !important; }
#practiceLinkDiv { display: none !important; }Izmantojot bināro koku, atrodiet garākā ceļa garumu, kas sastāv no mezgliem ar secīgām vērtībām augošā secībā. Katrs mezgls tiek uzskatīts par ceļu, kura garums ir 1.
Piemēri:
In below diagram binary tree with longest consecutive path(LCP) are shown :
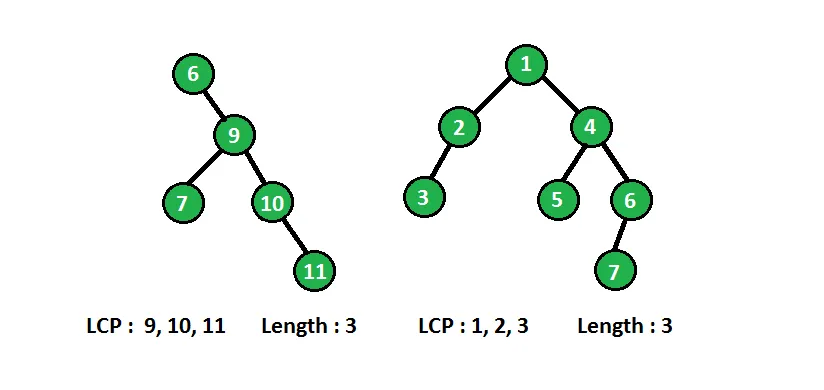
Mēs varam atrisināt iepriekš minēto problēmu rekursīvi. Katrā mezglā mums ir nepieciešama informācija par tā vecākmezglu, ja pašreizējam mezglam ir par vienu vērtību lielāka nekā tā vecākmezglam, tad tas veic secīgu ceļu katrā mezglā, mēs salīdzināsim mezgla vērtību ar tā vecākvērtību un attiecīgi atjaunināsim garāko ceļu pēc kārtas.
Lai iegūtu vecākmezgla vērtību, mēs nodosim (node_value + 1) kā argumentu rekursīvajai metodei un salīdzināsim mezgla vērtību ar šo argumenta vērtību, ja tas atbilst, atjauniniet secīgā ceļa pašreizējo garumu, pretējā gadījumā pašreizējo ceļa garumu no jauna inicializēsim par 1.
Lai labāk izprastu, lūdzu, skatiet tālāk norādīto kodu:
C++// C/C++ program to find longest consecutive // sequence in binary tree #include
// Java program to find longest consecutive // sequence in binary tree class Node { int data; Node left right; Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = null; } } class Result { int res = 0; } class BinaryTree { Node root; // method returns length of longest consecutive // sequence rooted at node root int longestConsecutive(Node root) { if (root == null) return 0; Result res = new Result(); // call utility method with current length 0 longestConsecutiveUtil(root 0 root.data res); return res.res; } // Utility method to return length of longest // consecutive sequence of tree private void longestConsecutiveUtil(Node root int curlength int expected Result res) { if (root == null) return; // if root data has one more than its parent // then increase current length if (root.data == expected) curlength++; else curlength = 1; // update the maximum by current length res.res = Math.max(res.res curlength); // recursively call left and right subtree with // expected value 1 more than root data longestConsecutiveUtil(root.left curlength root.data + 1 res); longestConsecutiveUtil(root.right curlength root.data + 1 res); } // Driver code public static void main(String args[]) { BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree(); tree.root = new Node(6); tree.root.right = new Node(9); tree.root.right.left = new Node(7); tree.root.right.right = new Node(10); tree.root.right.right.right = new Node(11); System.out.println(tree.longestConsecutive(tree.root)); } } // This code is contributed by shubham96301
# Python3 program to find longest consecutive # sequence in binary tree # A utility class to create a node class newNode: def __init__(self data): self.data = data self.left = self.right = None # Utility method to return length of # longest consecutive sequence of tree def longestConsecutiveUtil(root curLength expected res): if (root == None): return # if root data has one more than its # parent then increase current length if (root.data == expected): curLength += 1 else: curLength = 1 # update the maximum by current length res[0] = max(res[0] curLength) # recursively call left and right subtree # with expected value 1 more than root data longestConsecutiveUtil(root.left curLength root.data + 1 res) longestConsecutiveUtil(root.right curLength root.data + 1 res) # method returns length of longest consecutive # sequence rooted at node root def longestConsecutive(root): if (root == None): return 0 res = [0] # call utility method with current length 0 longestConsecutiveUtil(root 0 root.data res) return res[0] # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': root = newNode(6) root.right = newNode(9) root.right.left = newNode(7) root.right.right = newNode(10) root.right.right.right = newNode(11) print(longestConsecutive(root)) # This code is contributed by PranchalK
// C# program to find longest consecutive // sequence in binary tree using System; class Node { public int data; public Node left right; public Node(int item) { data = item; left = right = null; } } class Result { public int res = 0; } class GFG { Node root; // method returns length of longest consecutive // sequence rooted at node root int longestConsecutive(Node root) { if (root == null) return 0; Result res = new Result(); // call utility method with current length 0 longestConsecutiveUtil(root 0 root.data res); return res.res; } // Utility method to return length of longest // consecutive sequence of tree private void longestConsecutiveUtil(Node root int curlength int expected Result res) { if (root == null) return; // if root data has one more than its parent // then increase current length if (root.data == expected) curlength++; else curlength = 1; // update the maximum by current length res.res = Math.Max(res.res curlength); // recursively call left and right subtree with // expected value 1 more than root data longestConsecutiveUtil(root.left curlength root.data + 1 res); longestConsecutiveUtil(root.right curlength root.data + 1 res); } // Driver code public static void Main(String []args) { GFG tree = new GFG(); tree.root = new Node(6); tree.root.right = new Node(9); tree.root.right.left = new Node(7); tree.root.right.right = new Node(10); tree.root.right.right.right = new Node(11); Console.WriteLine(tree.longestConsecutive(tree.root)); } } // This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
<script> // JavaScript program to find longest consecutive // sequence in binary tree class Node { constructor(item) { this.data=item; this.left = this.right = null; } } let res = 0; let root; function longestConsecutive(root) { if (root == null) return 0; res=[0]; // call utility method with current length 0 longestConsecutiveUtil(root 0 root.data res); return res[0]; } // Utility method to return length of longest // consecutive sequence of tree function longestConsecutiveUtil(rootcurlength expectedres) { if (root == null) return; // if root data has one more than its parent // then increase current length if (root.data == expected) curlength++; else curlength = 1; // update the maximum by current length res[0] = Math.max(res[0] curlength); // recursively call left and right subtree with // expected value 1 more than root data longestConsecutiveUtil(root.left curlength root.data + 1 res); longestConsecutiveUtil(root.right curlength root.data + 1 res); } // Driver code root = new Node(6); root.right = new Node(9); root.right.left = new Node(7); root.right.right = new Node(10); root.right.right.right = new Node(11); document.write(longestConsecutive(root)); // This code is contributed by rag2127 </script>
Izvade
3
Laika sarežģītība: O(N), kur N ir mezglu skaits dotajā binārajā kokā.
Palīgtelpa: O(log(N))
Apspriests arī zemāk esošajā saitē:
Maksimālais secīgais pieaugošā ceļa garums binārajā kokā
