Python ir iepriekš definēts sqrt () funkcija, kas atgriež skaitļa kvadrātsakni. Tas nosaka kvadrātsakni no vērtības, kas reizina sevi, lai iegūtu skaitli. Funkciju sqrt() neizmanto tieši, lai atrastu dotā skaitļa kvadrātsakni, tāpēc mums ir jāizmanto matemātika modulis, lai izsauktu funkciju sqrt (). Python .
Piemēram, 144 kvadrātsakne ir 12.
Tagad apskatīsim kvadrātsaknes funkcijas sintaksi, lai Python atrastu noteikta skaitļa kvadrātsakni:
Sintakse:
math.sqrt(x)
Parametri:
x : Tas ir numurs. kurā skaitlim ir jābūt lielākam par 0 un tas var būt decimālskaitlis vai vesels skaitlis.
Atgriezties:
Izvade ir kvadrātsaknes vērtība.
Piezīme:
- Metodes sqrt () izvade būs peldošā komata vērtība.
- Ja dotā ievade ir negatīvs skaitlis, izvade būs ValueError. Tiek atgriezta ValueError, jo jebkura negatīva skaitļa kvadrātsaknes vērtība netiek uzskatīta par reālu skaitli.
- Ja ievade ir jebkas, izņemot skaitli, funkcija sqrt () atgriež NaN.
Piemērs:
Funkcijas sqrt() izmantošanas piemērs programmā Python.
Kods
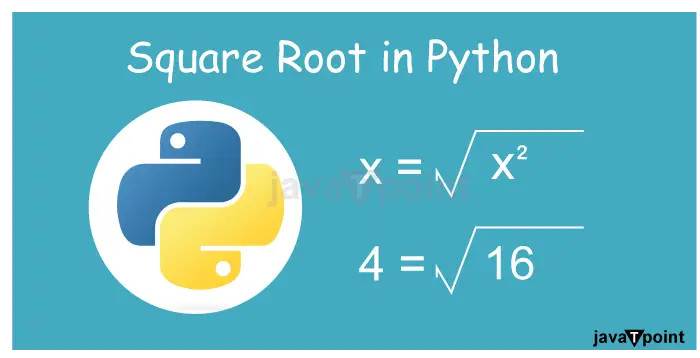
import math x = 16 y = math.sqrt(x) print(y)
Izvade:
4.0
1. Izmantojot math.sqrt() metodi
Funkcija sqrt () ir iebūvēta funkcija, kas atgriež jebkura skaitļa kvadrātsakni. Tālāk ir norādītas darbības, lai atrastu skaitļa kvadrātsakni.
- Sāciet programmu
- Definējiet jebkuru skaitli, kura kvadrātsakne ir jāatrod.
- Izsauciet sqrt () funkciju un nododiet vērtību, ko definējāt 2. darbībā, un saglabājiet rezultātu mainīgajā.
- Izdrukājiet kvadrātsakni.
- Pārtraukt programmu.
Python math.sqrt() metode 1. piemērs
Python piemēra programma, lai atrastu dotā veselā skaitļa kvadrātsakni.
Kods
# import math module import math # define the integer value to the variable num1 num1 = 36 # use math.sqrt() function and pass the variable. result = math.sqrt(num1) # to print the square root of a given number n print(' Square root of number 36 is : ', result) # define the value num2 = 625 result = math.sqrt(num2) print(' Square root of value 625 is : ', result) # define the value num3 = 144 result = math.sqrt(num3) print(' Square root of number 144 is : ', result) # define the value num4 = 64 result = math.sqrt(num4) print(' Square root of number 64 is : ', result)
Izvade:
Square root of number 36 is : 6.0 Square root of number 625 is : 25.0 Square root of number 144 is : 12.0 Square root of number 64 is : 8.0
Python math.sqrt() metode 2. piemērs
Izveidosim python programmu, kas atrod decimālskaitļu kvadrātsakni.
Kods
# Import the math module import math # Calculate the square root of decimal numbers print(' The square root of 4.5 is ', math.sqrt(4.5)) # Pass the decimal number print(' The square root of 627 is ', math.sqrt(627)) # Pass the decimal number print(' The square root of 6.25 is ', math.sqrt(6.25)) # Pass the decimal number # Calculate the square root of 0 print(' The Square root of 0 is ', math.sqrt(0)) # Pass number as 0
Izvade:
The Square root of 4.5 is 2.1213203435596424 The Square root of 627 is 25.039968051096054 The Square root of 6.25 is 2.5 The Square root of 0 is 0.0
Python math.sqrt() metode 3. piemērs
Nākamajā programmā mēs esam izlasījuši skaitli no lietotāja un atraduši kvadrātsakni.
modifikācijas taustiņi
Kods
# import math module import math a = int(input(' Enter a number to get the Square root ')) # Use math.sqrt() function and pass the variable a. result = math.sqrt(a) print(' Square root of the number is ', result)
Izvade:
Enter a number to get the Square root: 25 Square root of the number is: 5.0
1. Funkcijas math.pow() izmantošana
Pow () ir iebūvēta funkcija, kas tiek izmantota Python, lai atgrieztu skaitļa jaudu. Tam ir divi parametri. Pirmais parametrs nosaka skaitli, bet otrais parametrs nosaka jaudas palielinājumu līdz šim skaitlim.
Python math.pow() metode Piemērs
Apskatīsim programmas piemēru funkcijai math.pow():
Kods
# import the math module import math # take an input from the user num = float(input(' Enter the number : ')) # Use the math.pow() function and pass the value and 0.5 (which is equal to ?) as an parameters SquareRoot = math.pow( num, 0.5 ) print(' The Square Root of the given number {0} = {1}' .format( num, SquareRoot )) Izvade:
Enter the number :628 The Square Root of the given number 628.0 = 25.059928172283335
3. Moduļa Numpy izmantošana
NumPy modulis ir arī iespēja python atrast kvadrātsakni.
Python Numpy piemērs
Apskatīsim programmas piemēru, lai atrastu kvadrātsakni noteiktam skaitļu sarakstam masīvā.
Kods
# import NumPy module import numpy as np # define an array of numbers array_nums = np.array([ 1, 4, 9, 16, 25 ]) # use np.sqrt() function and pass the array result = np.sqrt(array_nums) print(' Square roots of the given array are: ', result)
Izvade:
Square roots of the given array are: [ 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. ]
4. Izmantojot ** operatoru
Mēs varam arī izmantot eksponenta operatoru, lai atrastu skaitļa kvadrātsakni. Operatoru var lietot starp diviem operandiem. Piemēram, x**y. Tas nozīmē, ka kreisais operands ir pacelts labās puses pakāpē.
Tālāk ir norādītas darbības, lai atrastu skaitļa kvadrātsakni.
1. darbība. Definējiet funkciju un nododiet vērtību kā argumentu.
2. darbība. Ja definētais skaitlis ir mazāks par 0 vai negatīvs, tas neko neatgriež.
3. darbība. Izmantojiet eksponenciālo zīmi **, lai atrastu skaitļa jaudu.
4. darbība. Paņemiet no lietotāja skaitlisko vērtību.
5. darbība. Izsauciet funkciju un saglabājiet tās izvadi mainīgajā.
6. darbība. Parādiet skaitļa kvadrātsakni Python.
7. darbība. Iziet no programmas.
Python ** Operatora 1. piemērs
Ieviesīsim iepriekš minētās darbības Python programmā un aprēķināsim skaitļa kvadrātsakni.
Kods
# import the math package or module import math # define the sqrt_fun() and pass the num as an argument def sqrt_fun(num): if num <0: 0 # if num is less than or negative, it returns nothing return else: ** 0.5 use the exponent operator (' enter a numeric value: ') ) take an input from user call sqrt_fun() to find result res="sqrt_fun(num)" print square root of variable print(' {0}="{1}" '.format(num, res)) < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> Enter a numeric value: 256 Square Root of the 256 = 16.0 </pre> <p> <strong>Explanation:</strong> </p> <p>As we can see in the above example, first we take an input (number) from the user and then use the exponent ** operator to find out the power of a number. Where 0.5 is equal to √ (root symbol) to raise the power of a given number. At last, the code prints the value of the num and the comparing square root esteem utilizing the format() function. On the off chance that the client inputs a negative number, the capability will not return anything and the result will be clear.</p> <h3>Python ** Operator Example 2</h3> <p>Let's create a Python program that finds the square root of between the specified range. In the following program, we have found the square root of all the number between 0 to 30.</p> <p> <strong>Code</strong> </p> <pre> # Import math module import math # Iterate through numbers from 0 to 29 and print their square roots for i in range(30): # Use the format() method to insert the values of i and its square root into the string print(' Square root of a number {0} = {1} '.format( i, math.sqrt(i))) </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> Square root of a number 0 = 0.0 Square root of a number 1 = 1.0 Square root of a number 2 = 1.4142135623730951 Square root of a number 3 = 1.7320508075688772 Square root of a number 4 = 2.0 Square root of a number 5 = 2.23606797749979 Square root of a number 6 = 2.449489742783178 Square root of a number 7 = 2.6457513110645907 Square root of a number 8 = 2.8284271247461903 Square root of a number 9 = 3.0 Square root of a number 10 = 3.1622776601683795 Square root of a number 11 = 3.3166247903554 Square root of a number 12 = 3.4641016151377544 Square root of a number 13 = 3.605551275463989 Square root of a number 14 = 3.7416573867739413 Square root of a number 15 = 3.872983346207417 Square root of a number 16 = 4.0 Square root of a number 17 = 4.123105625617661 Square root of a number 18 = 4.242640687119285 Square root of a number 19 = 4.358898943540674 Square root of a number 20 = 4.47213595499958 Square root of a number 21 = 4.58257569495584 Square root of a number 22 = 4.69041575982343 Square root of a number 23 = 4.795831523312719 Square root of a number 24 = 4.898979485566356 Square root of a number 25 = 5.0 Square root of a number 26 = 5.0990195135927845 Square root of a number 27 = 5.196152422706632 Square root of a number 28 = 5.291502622129181 Square root of a number 29 = 5.385164807134504 Square root of a number 30 = 5.477225575051661 </pre> <h2>Conclusion:</h2> <p>All in all, there are multiple ways of tracking down the square root value of a given number in Python. We can utilize the number related math module, the ** operator, the pow() method, or the NumPy module, contingent upon our prerequisites.</p> <hr></0:> Paskaidrojums:
Kā redzams iepriekš minētajā piemērā, vispirms mēs ņemam ievadi (skaitli) no lietotāja un pēc tam izmantojam eksponenta ** operatoru, lai noskaidrotu skaitļa jaudu. Kur 0,5 ir vienāds ar √ (saknes simbols), lai palielinātu dotā skaitļa jaudu. Visbeidzot, kods izdrukā skaitļa vērtību un salīdzināšanas kvadrātsaknes vērtību, izmantojot format() funkciju. Gadījumā, ja klients ievadīs negatīvu skaitli, iespēja neko neatgriezīs un rezultāts būs skaidrs.
Python ** Operatora 2. piemērs
Izveidosim Python programmu, kas atrod kvadrātsakni starp norādīto diapazonu. Nākamajā programmā mēs esam atraduši kvadrātsakni visiem skaitļiem no 0 līdz 30.
Kods
# Import math module import math # Iterate through numbers from 0 to 29 and print their square roots for i in range(30): # Use the format() method to insert the values of i and its square root into the string print(' Square root of a number {0} = {1} '.format( i, math.sqrt(i))) Izvade:
Square root of a number 0 = 0.0 Square root of a number 1 = 1.0 Square root of a number 2 = 1.4142135623730951 Square root of a number 3 = 1.7320508075688772 Square root of a number 4 = 2.0 Square root of a number 5 = 2.23606797749979 Square root of a number 6 = 2.449489742783178 Square root of a number 7 = 2.6457513110645907 Square root of a number 8 = 2.8284271247461903 Square root of a number 9 = 3.0 Square root of a number 10 = 3.1622776601683795 Square root of a number 11 = 3.3166247903554 Square root of a number 12 = 3.4641016151377544 Square root of a number 13 = 3.605551275463989 Square root of a number 14 = 3.7416573867739413 Square root of a number 15 = 3.872983346207417 Square root of a number 16 = 4.0 Square root of a number 17 = 4.123105625617661 Square root of a number 18 = 4.242640687119285 Square root of a number 19 = 4.358898943540674 Square root of a number 20 = 4.47213595499958 Square root of a number 21 = 4.58257569495584 Square root of a number 22 = 4.69041575982343 Square root of a number 23 = 4.795831523312719 Square root of a number 24 = 4.898979485566356 Square root of a number 25 = 5.0 Square root of a number 26 = 5.0990195135927845 Square root of a number 27 = 5.196152422706632 Square root of a number 28 = 5.291502622129181 Square root of a number 29 = 5.385164807134504 Square root of a number 30 = 5.477225575051661
Secinājums:
Kopumā ir vairāki veidi, kā Python izsekot noteiktā skaitļa kvadrātsaknes vērtību. Mēs varam izmantot ar skaitļiem saistīto matemātikas moduli, operatoru **, metodi pow() vai moduli NumPy atkarībā no mūsu priekšnosacījumiem.
