Kas ir Hamiltona cikls?
Hamiltona cikls vai ķēde grafikā G ir cikls, kas apmeklē katru virsotni G tieši vienu reizi un atgriežas sākuma virsotnē.
- Ja grafikā ir Hamiltona cikls, to sauc Hamiltona grafiks citādi tā ir ne hamiltonietis .
- Hamiltona cikla atrašana grafikā ir labi zināms NP-pilnīga problēma , kas nozīmē, ka nav zināms efektīvs algoritms, lai to atrisinātu visu veidu grafikiem. Tomēr to var atrisināt maziem vai īpašiem grafiku veidiem.
Hamiltona cikla problēmai ir praktiski pielietojumi dažādās jomās, piemēram loģistika, tīklu projektēšana un datorzinātne .
Kas ir Hamiltona ceļš?
Hamiltona ceļš grafikā G ir ceļš, kas katru G virsotni apmeklē tieši vienreiz un Hamiltona ceļš nav jāatgriežas sākuma virsotnē. Tas ir atvērts ceļš.
- Līdzīgi kā Hamiltona cikls problēma, atrašana a Hamiltona ceļš vispārējā grafikā arī ir NP-pilnīgs un var būt izaicinoši. Tomēr bieži vien tā ir vieglāka problēma nekā Hamiltona cikla atrašana.
- Hamiltona ceļiem ir pielietojums dažādās jomās, piemēram optimālu maršrutu atrašana transporta tīklu, ķēžu projektēšanas un grafu teorijas pētījumos .
Problēmu paziņojums: Ja ir dots nevirzīts grafs, uzdevums ir noteikt, vai grafikā ir vai nav Hamiltona cikls. Ja tas satur, tad izdrukā ceļu.
Piemērs:
Ieteicams: lūdzu, atrisiniet to PRAKSE pirmkārt, pirms pāriet pie risinājuma.Ievade: grafiks[][] = {{0, 1, 0, 1, 0},{1, 0, 1, 1, 1},{0, 1, 0, 0, 1},{1, 1, 0, 0, 1}, {0, 1, 1, 1, 0}}
Ievadiet diagrammu[][]
pārdēvējiet Linux direktorijuIzvade: {0, 1, 2, 4, 3, 0}.
Ievade: grafiks[][] = {{0, 1, 0, 1, 0},{1, 0, 1, 1, 1},{0, 1, 0, 0, 1},{1, 1, 0, 0, 0}, {0, 1, 1, 0, 0}}
Ievadiet diagrammu[][]
Izvade: Risinājums neeksistē
Naivs algoritms : Šo problēmu var atrisināt, izmantojot šādu ideju:
Ģenerējiet visas iespējamās virsotņu konfigurācijas un izdrukājiet konfigurāciju, kas atbilst dotajiem ierobežojumiem. Būs n! (n faktoru) konfigurācijas. Tātad šīs pieejas kopējā laika sarežģītība būs O (N!).
Hamiltona cikla izmantošana Atkāpšanās algoritms :
Izveidojiet tukšu ceļa masīvu un pievienojiet virsotni 0 uz to. Pievienojiet citas virsotnes, sākot no virsotnes 1 . Pirms virsotnes pievienošanas pārbaudiet, vai tā atrodas blakus iepriekš pievienotajai virsotnei un nav jau pievienota. Ja mēs atrodam šādu virsotni, mēs pievienojam virsotni kā daļu no risinājuma. Ja mēs neatrodam virsotni, mēs atgriežamies viltus .
Ilustrācijas:
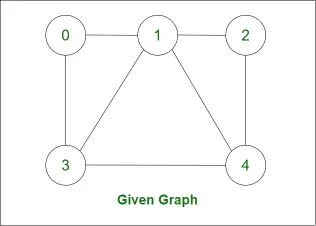
Noskaidrosim Hamiltona ciklu šādam grafikam:
- Sāciet ar mezglu 0.
- Lietojiet DFS, lai atrastu Hamiltona ceļu.
- Kad sasniedz bāzes gadījumu (t.i. kopējais šķērsoto mezglu skaits == V (kopējā virsotne) ):
- Pārbaudiet, vai pašreizējais mezgls ir sākuma mezgla kaimiņš.
- Kā mezgls 2 un mezgls 0 nav viens otram kaimiņi, tāpēc atgriezieties no tā.
Sākot no sākuma mezgla 0, kas izsauc DFS
- Tā kā cikls nav atrasts ceļā {0, 3, 1, 4, 2}. Tātad, atgriezieties no 2. mezgla, 4. mezgla.
- Tagad izpētiet citu 1. mezgla (t.i., 2. mezgla) opciju.
- Kad tas atkal sasniedz bāzes stāvokli, pārbaudiet Hamiltona ciklu
- Tā kā 4. mezgls nav mezgla 0 kaimiņš, cikls atkal netiek atrasts, pēc tam atgriezieties.
- Atgriezties no 4. mezgla, 2. mezgla, 1. mezgla.
- Tagad izpētiet citas 3. mezgla iespējas.
Hamiltona cikls
- Hamiltona ceļā 0,3,4,2,1,0} mēs iegūstam ciklu, jo mezgls 1 ir mezgla 0 kaimiņš.
- Tāpēc izdrukājiet šo ciklisko ceļu.
- Šis ir mūsu Hamiltona cikls.
Tālāk ir sniegta Backtracking ieviešana Hamiltona cikla atrašanai:
C++ /* C++ program for solution of Hamiltonian Cycle problem using backtracking */ #include using namespace std; // Number of vertices in the graph #define V 5 void printSolution(int path[]); /* A utility function to check if the vertex v can be added at index 'pos' in the Hamiltonian Cycle constructed so far (stored in 'path[]') */ bool isSafe(int v, bool graph[V][V], int path[], int pos) { /* Check if this vertex is an adjacent vertex of the previously added vertex. */ if (graph [path[pos - 1]][ v ] == 0) return false; /* Check if the vertex has already been included. This step can be optimized by creating an array of size V */ for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++) if (path[i] == v) return false; return true; } /* A recursive utility function to solve hamiltonian cycle problem */ bool hamCycleUtil(bool graph[V][V], int path[], int pos) { /* base case: If all vertices are included in Hamiltonian Cycle */ if (pos == V) { // And if there is an edge from the // last included vertex to the first vertex if (graph[path[pos - 1]][path[0]] == 1) return true; else return false; } // Try different vertices as a next candidate // in Hamiltonian Cycle. We don't try for 0 as // we included 0 as starting point in hamCycle() for (int v = 1; v < V; v++) { /* Check if this vertex can be added // to Hamiltonian Cycle */ if (isSafe(v, graph, path, pos)) { path[pos] = v; /* recur to construct rest of the path */ if (hamCycleUtil (graph, path, pos + 1) == true) return true; /* If adding vertex v doesn't lead to a solution, then remove it */ path[pos] = -1; } } /* If no vertex can be added to Hamiltonian Cycle constructed so far, then return false */ return false; } /* This function solves the Hamiltonian Cycle problem using Backtracking. It mainly uses hamCycleUtil() to solve the problem. It returns false if there is no Hamiltonian Cycle possible, otherwise return true and prints the path. Please note that there may be more than one solutions, this function prints one of the feasible solutions. */ bool hamCycle(bool graph[V][V]) { int *path = new int[V]; for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) path[i] = -1; /* Let us put vertex 0 as the first vertex in the path. If there is a Hamiltonian Cycle, then the path can be started from any point of the cycle as the graph is undirected */ path[0] = 0; if (hamCycleUtil(graph, path, 1) == false ) { cout << '
Solution does not exist'; return false; } printSolution(path); return true; } /* A utility function to print solution */ void printSolution(int path[]) { cout << 'Solution Exists:' ' Following is one Hamiltonian Cycle
'; for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) cout << path[i] << ' '; // Let us print the first vertex again // to show the complete cycle cout << path[0] << ' '; cout << endl; } // Driver Code int main() { /* Let us create the following graph (0)--(1)--(2) | / | | / | | / | (3)-------(4) */ bool graph1[V][V] = {{0, 1, 0, 1, 0}, {1, 0, 1, 1, 1}, {0, 1, 0, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 0, 0, 1}, {0, 1, 1, 1, 0}}; // Print the solution hamCycle(graph1); /* Let us create the following graph (0)--(1)--(2) | / | | / | | / | (3) (4) */ bool graph2[V][V] = {{0, 1, 0, 1, 0}, {1, 0, 1, 1, 1}, {0, 1, 0, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 0, 0, 0}, {0, 1, 1, 0, 0}}; // Print the solution hamCycle(graph2); return 0; } // This is code is contributed by rathbhupendra> C++ #include using namespace std; int main() { cout << 'GFG!'; return 0; }> C /* C program for solution of Hamiltonian Cycle problem using backtracking */ #include // Number of vertices in the graph #define V 5 void printSolution(int path[]); /* A utility function to check if the vertex v can be added at index 'pos' in the Hamiltonian Cycle constructed so far (stored in 'path[]') */ int isSafe(int v, int graph[V][V], int path[], int pos) { /* Check if this vertex is an adjacent vertex of the previously added vertex. */ if (graph [ path[pos-1] ][ v ] == 0) return 0; /* Check if the vertex has already been included. This step can be optimized by creating an array of size V */ for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++) if (path[i] == v) return 0; return 1; } /* A recursive utility function to solve hamiltonian cycle problem */ int hamCycleUtil(int graph[V][V], int path[], int pos) { /* base case: If all vertices are included in Hamiltonian Cycle */ if (pos == V) { // And if there is an edge from the last included vertex to the // first vertex if ( graph[ path[pos-1] ][ path[0] ] == 1 ) return 1; else return 0; } // Try different vertices as a next candidate in Hamiltonian Cycle. // We don't try for 0 as we included 0 as starting point in hamCycle() for (int v = 1; v < V; v++) { /* Check if this vertex can be added to Hamiltonian Cycle */ if (isSafe(v, graph, path, pos)) { path[pos] = v; /* recur to construct rest of the path */ if (hamCycleUtil (graph, path, pos+1) == 1) return 1; /* If adding vertex v doesn't lead to a solution, then remove it */ path[pos] = -1; } } /* If no vertex can be added to Hamiltonian Cycle constructed so far, then return false */ return 0; } /* This function solves the Hamiltonian Cycle problem using Backtracking. It mainly uses hamCycleUtil() to solve the problem. It returns false if there is no Hamiltonian Cycle possible, otherwise return true and prints the path. Please note that there may be more than one solutions, this function prints one of the feasible solutions. */ int hamCycle(int graph[V][V]) { int path[V]; for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) path[i] = -1; /* Let us put vertex 0 as the first vertex in the path. If there is a Hamiltonian Cycle, then the path can be started from any point of the cycle as the graph is undirected */ path[0] = 0; if ( hamCycleUtil(graph, path, 1) == 0 ) { printf('
Solution does not exist'); return 0; } printSolution(path); return 1; } /* A utility function to print solution */ void printSolution(int path[]) { printf ('Solution Exists:' ' Following is one Hamiltonian Cycle
'); for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) printf(' %d ', path[i]); // Let us print the first vertex again to show the complete cycle printf(' %d ', path[0]); printf('
'); } // driver program to test above function int main() { /* Let us create the following graph (0)--(1)--(2) | / | | / | | / | (3)-------(4) */ int graph1[V][V] = {{0, 1, 0, 1, 0}, {1, 0, 1, 1, 1}, {0, 1, 0, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 0, 0, 1}, {0, 1, 1, 1, 0}, }; // Print the solution hamCycle(graph1); /* Let us create the following graph (0)--(1)--(2) | / | | / | | / | (3) (4) */ int graph2[V][V] = {{0, 1, 0, 1, 0}, {1, 0, 1, 1, 1}, {0, 1, 0, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 0, 0, 0}, {0, 1, 1, 0, 0}, }; // Print the solution hamCycle(graph2); return 0; }> Java /* Java program for solution of Hamiltonian Cycle problem using backtracking */ class HamiltonianCycle { final int V = 5; int path[]; /* A utility function to check if the vertex v can be added at index 'pos'in the Hamiltonian Cycle constructed so far (stored in 'path[]') */ boolean isSafe(int v, int graph[][], int path[], int pos) { /* Check if this vertex is an adjacent vertex of the previously added vertex. */ if (graph[path[pos - 1]][v] == 0) return false; /* Check if the vertex has already been included. This step can be optimized by creating an array of size V */ for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++) if (path[i] == v) return false; return true; } /* A recursive utility function to solve hamiltonian cycle problem */ boolean hamCycleUtil(int graph[][], int path[], int pos) { /* base case: If all vertices are included in Hamiltonian Cycle */ if (pos == V) { // And if there is an edge from the last included // vertex to the first vertex if (graph[path[pos - 1]][path[0]] == 1) return true; else return false; } // Try different vertices as a next candidate in // Hamiltonian Cycle. We don't try for 0 as we // included 0 as starting point in hamCycle() for (int v = 1; v < V; v++) { /* Check if this vertex can be added to Hamiltonian Cycle */ if (isSafe(v, graph, path, pos)) { path[pos] = v; /* recur to construct rest of the path */ if (hamCycleUtil(graph, path, pos + 1) == true) return true; /* If adding vertex v doesn't lead to a solution, then remove it */ path[pos] = -1; } } /* If no vertex can be added to Hamiltonian Cycle constructed so far, then return false */ return false; } /* This function solves the Hamiltonian Cycle problem using Backtracking. It mainly uses hamCycleUtil() to solve the problem. It returns false if there is no Hamiltonian Cycle possible, otherwise return true and prints the path. Please note that there may be more than one solutions, this function prints one of the feasible solutions. */ int hamCycle(int graph[][]) { path = new int[V]; for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) path[i] = -1; /* Let us put vertex 0 as the first vertex in the path. If there is a Hamiltonian Cycle, then the path can be started from any point of the cycle as the graph is undirected */ path[0] = 0; if (hamCycleUtil(graph, path, 1) == false) { System.out.println('
Solution does not exist'); return 0; } printSolution(path); return 1; } /* A utility function to print solution */ void printSolution(int path[]) { System.out.println('Solution Exists: Following' + ' is one Hamiltonian Cycle'); for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) System.out.print(' ' + path[i] + ' '); // Let us print the first vertex again to show the // complete cycle System.out.println(' ' + path[0] + ' '); } // driver program to test above function public static void main(String args[]) { HamiltonianCycle hamiltonian = new HamiltonianCycle(); /* Let us create the following graph (0)--(1)--(2) | / | | / | | / | (3)-------(4) */ int graph1[][] = {{0, 1, 0, 1, 0}, {1, 0, 1, 1, 1}, {0, 1, 0, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 0, 0, 1}, {0, 1, 1, 1, 0}, }; // Print the solution hamiltonian.hamCycle(graph1); /* Let us create the following graph (0)--(1)--(2) | / | | / | | / | (3) (4) */ int graph2[][] = {{0, 1, 0, 1, 0}, {1, 0, 1, 1, 1}, {0, 1, 0, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 0, 0, 0}, {0, 1, 1, 0, 0}, }; // Print the solution hamiltonian.hamCycle(graph2); } } // This code is contributed by Abhishek Shankhadhar> Python # Python program for solution of # hamiltonian cycle problem class Graph(): def __init__(self, vertices): self.graph = [[0 for column in range(vertices)] for row in range(vertices)] self.V = vertices ''' Check if this vertex is an adjacent vertex of the previously added vertex and is not included in the path earlier ''' def isSafe(self, v, pos, path): # Check if current vertex and last vertex # in path are adjacent if self.graph[ path[pos-1] ][v] == 0: return False # Check if current vertex not already in path for vertex in path: if vertex == v: return False return True # A recursive utility function to solve # hamiltonian cycle problem def hamCycleUtil(self, path, pos): # base case: if all vertices are # included in the path if pos == self.V: # Last vertex must be adjacent to the # first vertex in path to make a cycle if self.graph[ path[pos-1] ][ path[0] ] == 1: return True else: return False # Try different vertices as a next candidate # in Hamiltonian Cycle. We don't try for 0 as # we included 0 as starting point in hamCycle() for v in range(1,self.V): if self.isSafe(v, pos, path) == True: path[pos] = v if self.hamCycleUtil(path, pos+1) == True: return True # Remove current vertex if it doesn't # lead to a solution path[pos] = -1 return False def hamCycle(self): path = [-1] * self.V ''' Let us put vertex 0 as the first vertex in the path. If there is a Hamiltonian Cycle, then the path can be started from any point of the cycle as the graph is undirected ''' path[0] = 0 if self.hamCycleUtil(path,1) == False: print ('Solution does not exist
') return False self.printSolution(path) return True def printSolution(self, path): print ('Solution Exists: Following', 'is one Hamiltonian Cycle') for vertex in path: print (vertex ) # Driver Code ''' Let us create the following graph (0)--(1)--(2) | / | | / | | / | (3)-------(4) ''' g1 = Graph(5) g1.graph = [ [0, 1, 0, 1, 0], [1, 0, 1, 1, 1], [0, 1, 0, 0, 1,],[1, 1, 0, 0, 1], [0, 1, 1, 1, 0], ] # Print the solution g1.hamCycle(); ''' Let us create the following graph (0)--(1)--(2) | / | | / | | / | (3) (4) ''' g2 = Graph(5) g2.graph = [ [0, 1, 0, 1, 0], [1, 0, 1, 1, 1], [0, 1, 0, 0, 1,], [1, 1, 0, 0, 0], [0, 1, 1, 0, 0], ] # Print the solution g2.hamCycle(); # This code is contributed by Divyanshu Mehta> C# // C# program for solution of Hamiltonian // Cycle problem using backtracking using System; public class HamiltonianCycle { readonly int V = 5; int []path; /* A utility function to check if the vertex v can be added at index 'pos'in the Hamiltonian Cycle constructed so far (stored in 'path[]') */ bool isSafe(int v, int [,]graph, int []path, int pos) { /* Check if this vertex is an adjacent vertex of the previously added vertex. */ if (graph[path[pos - 1], v] == 0) return false; /* Check if the vertex has already been included. This step can be optimized by creating an array of size V */ for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++) if (path[i] == v) return false; return true; } /* A recursive utility function to solve hamiltonian cycle problem */ bool hamCycleUtil(int [,]graph, int []path, int pos) { /* base case: If all vertices are included in Hamiltonian Cycle */ if (pos == V) { // And if there is an edge from the last included // vertex to the first vertex if (graph[path[pos - 1],path[0]] == 1) return true; else return false; } // Try different vertices as a next candidate in // Hamiltonian Cycle. We don't try for 0 as we // included 0 as starting point in hamCycle() for (int v = 1; v < V; v++) { /* Check if this vertex can be added to Hamiltonian Cycle */ if (isSafe(v, graph, path, pos)) { path[pos] = v; /* recur to construct rest of the path */ if (hamCycleUtil(graph, path, pos + 1) == true) return true; /* If adding vertex v doesn't lead to a solution, then remove it */ path[pos] = -1; } } /* If no vertex can be added to Hamiltonian Cycle constructed so far, then return false */ return false; } /* This function solves the Hamiltonian Cycle problem using Backtracking. It mainly uses hamCycleUtil() to solve the problem. It returns false if there is no Hamiltonian Cycle possible, otherwise return true and prints the path. Please note that there may be more than one solutions, this function prints one of the feasible solutions. */ int hamCycle(int [,]graph) { path = new int[V]; for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) path[i] = -1; /* Let us put vertex 0 as the first vertex in the path. If there is a Hamiltonian Cycle, then the path can be started from any point of the cycle as the graph is undirected */ path[0] = 0; if (hamCycleUtil(graph, path, 1) == false) { Console.WriteLine('
Solution does not exist'); return 0; } printSolution(path); return 1; } /* A utility function to print solution */ void printSolution(int []path) { Console.WriteLine('Solution Exists: Following' + ' is one Hamiltonian Cycle'); for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) Console.Write(' ' + path[i] + ' '); // Let us print the first vertex again // to show the complete cycle Console.WriteLine(' ' + path[0] + ' '); } // Driver code public static void Main(String []args) { HamiltonianCycle hamiltonian = new HamiltonianCycle(); /* Let us create the following graph (0)--(1)--(2) | / | | / | | / | (3)-------(4) */ int [,]graph1= {{0, 1, 0, 1, 0}, {1, 0, 1, 1, 1}, {0, 1, 0, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 0, 0, 1}, {0, 1, 1, 1, 0}, }; // Print the solution hamiltonian.hamCycle(graph1); /* Let us create the following graph (0)--(1)--(2) | / | | / | | / | (3) (4) */ int [,]graph2 = {{0, 1, 0, 1, 0}, {1, 0, 1, 1, 1}, {0, 1, 0, 0, 1}, {1, 1, 0, 0, 0}, {0, 1, 1, 0, 0}, }; // Print the solution hamiltonian.hamCycle(graph2); } } // This code contributed by Rajput-Ji> Javascript >>PHP>>
Izvade Laika sarežģītība: O(N!), kur N ir virsotņu skaits.
Palīgtelpa: O(1), jo nav izmantota papildu vieta. Piezīme: Iepriekš minētais kods vienmēr izdrukā ciklu, sākot no 0 . Sākumpunktam nav nozīmes, jo ciklu var sākt no jebkura punkta. Ja vēlaties mainīt sākuma punktu, iepriekš minētajā kodā ir jāveic divas izmaiņas.
Mainīt ceļu[0] = 0; uz ceļš[0] = s ; kur s ir tavs jaunais sākumpunkts . Mainiet arī cilpu uz (int v = 1; v