Binārais koks ir koka tipa nelineāra datu struktūra, ko galvenokārt izmanto kārtošanai un meklēšanai, jo tie glabā datus hierarhiskā formā. Šajā sadaļā mēs uzzināsim, binārā koka datu struktūras ieviešana Java . Sniedz arī īsu bināro koku datu struktūras aprakstu.
Binārais koks
Koku, kurā katram mezglam (vecākam) ir ne vairāk kā divi atvasinātie mezgli (kreisais un labais), sauc par bināro koku. Visaugstāko mezglu sauc par saknes mezglu. Binārajā kokā mezgls satur datus un kreisā un labā pakārtotā mezgla rādītāju (adresi).
pārvērst strinu par int
The augstums no binārā koka ir malu skaits starp koka saknēm un tā tālākā (dziļākā) lapa. Ja koks ir tukšs , augstums ir 0 . Mezgla augstums tiek apzīmēts ar h .
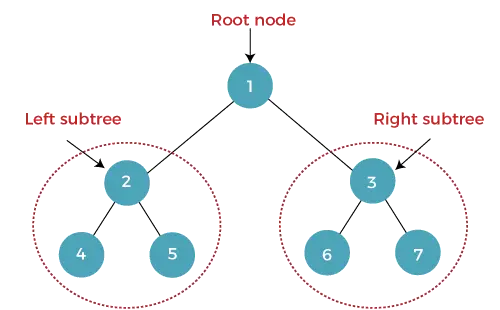
Iepriekš minētā binārā koka augstums ir 2.
Mēs varam aprēķināt lapu skaitu un mezglu, izmantojot šādu formulu.
- Maksimālais lapu mezglu skaits ir binārs koks: 2h
- Maksimālais mezglu skaits ir binārs koks: 2h+1-1
Kur h ir binārā koka augstums.
Binārā koka piemērs

Bināro koku veidi
Datu struktūrā ir šādi bināro koku veidi:
- Pilns/ stingri binārs koks
- Pilnīgs binārais koks
- Ideāls binārais koks
- Līdzsvara binārais koks
- Binārais koks ar saknēm
- Deģenerēts/ patoloģisks binārais koks
- Paplašināts binārais koks
- Šķībs binārais koks
- Pa kreisi šķībs Binārais koks
- Pa labi šķībs Binārais koks
- Vītņots binārais koks
- Viena vītnes binārais koks
- Divu vītņu binārais koks
Binārā koka ieviešana Java
Ir daudz veidu, kā ieviest bināro koku. Šajā sadaļā mēs ieviesīsim bināro koku, izmantojot LinkedList datu struktūru. Līdztekus tam mēs ieviesīsim arī šķērsošanas rīkojumus, meklējot mezglu un ievietojot mezglu binārajā kokā.
Binārā koka ieviešana, izmantojot LinkedList
Algoritms
Definējiet Node klasi, kurā ir trīs atribūti, proti: dati pa kreisi un pa labi. Šeit pa kreisi apzīmē mezgla kreiso atvasi, bet pa labi apzīmē mezgla labo bērnu.
- Kad mezgls ir izveidots, dati tiks pārsūtīti uz mezgla datu atribūtu, un gan pa kreisi, gan pa labi tiks iestatīts uz nulli.
- Definējiet citu klasi, kurai ir atribūta sakne.
- Sakne apzīmē koka saknes mezglu un inicializē to uz nulli.
- Tas pārbauda, vai saknes vērtība ir nulle, kas nozīmē, ka koks ir tukšs. Tas pievienos jauno mezglu kā root.
- Pretējā gadījumā tas rindai pievienos sakni.
- Mainīgais mezgls apzīmē pašreizējo mezglu.
- Pirmkārt, tas pārbauda, vai mezglam ir kreisais un labais bērns. Ja jā, rindai tiks pievienoti abi mezgli.
- Ja kreisais bērns nav klāt, tas pievienos jauno mezglu kā kreiso bērnu.
- Ja ir klāt kreisais, tas pievienos jauno mezglu kā pareizo atvasi.
- Tas šķērso visu koku, pēc tam izdrukā kreiso bērnu, kam seko sakne, pēc tam seko labais bērns.
BinarySearchTree.java
public class BinarySearchTree { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node{ int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data){ //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public BinarySearchTree(){ root = null; } //factorial() will calculate the factorial of given number public int factorial(int num) { int fact = 1; if(num == 0) return 1; else { while(num > 1) { fact = fact * num; num--; } return fact; } } //numOfBST() will calculate the total number of possible BST by calculating Catalan Number for given key public int numOfBST(int key) { int catalanNumber = factorial(2 * key)/(factorial(key + 1) * factorial(key)); return catalanNumber; } public static void main(String[] args) { BinarySearchTree bt = new BinarySearchTree(); //Display total number of possible binary search tree with key 5 System.out.println('Total number of possible Binary Search Trees with given key: ' + bt.numOfBST(5)); } } Izvade:
Binary tree after insertion 1 Binary tree after insertion 2 1 3 Binary tree after insertion 4 2 5 1 3 Binary tree after insertion 4 2 5 1 6 3 7
Binārā koka operācijas
Ar bināro koku var veikt šādas darbības:
- Ievietošana
- Dzēšana
- Meklēt
- Šķērsošana
Java programma mezgla ievietošanai binārajā kokā
BinaryTreeInsert.java
public class BinaryTreeInsert { public static void main(String[] args) { new BinaryTreeInsert().run(); } static class Node { Node left; Node right; int value; public Node(int value) { this.value = value; } } public void run() { Node rootnode = new Node(25); System.out.println('Building tree with root value ' + rootnode.value); System.out.println('================================='); insert(rootnode, 11); insert(rootnode, 15); insert(rootnode, 16); insert(rootnode, 23); insert(rootnode, 79); } public void insert(Node node, int value) { if (value node.value) { if (node.right != null) { insert(node.right, value); } else { System.out.println(' Inserted ' + value + ' to right of Node ' + node.value); node.right = new Node(value); } } } } Izvade:
Building tree with root value 25 ================================= Inserted 11 to left of Node 25 Inserted 15 to right of Node 11 Inserted 16 to right of Node 15 Inserted 23 to right of Node 16 Inserted 79 to right of Node 25
Java programma Java mezgla dzēšanai
Algoritms
- Sākot ar sakni, atrodiet binārajā kokā dziļāko un vistālāk labējo mezglu un mezglu, kuru vēlamies dzēst.
- Aizstāt dziļākā, galējā labā mezgla datus ar dzēšamo mezglu.
- Pēc tam izdzēsiet dziļāko labo malējo mezglu.
Apsveriet šādu attēlu.

DeleteNode.java
import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; public class DeleteNode { // A binary tree node has key, pointer to // left child and a pointer to right child static class Node { int key; Node left, right; // Constructor Node(int key) { this.key = key; left = null; right = null; } } static Node root; static Node temp = root; // Inorder traversal of a binary tree static void inorder(Node temp) { if (temp == null) return; inorder(temp.left); System.out.print(temp.key + ' '); inorder(temp.right); } // Function to delete deepest // element in binary tree static void deleteDeepest(Node root, Node delNode) { Queue q = new LinkedList(); q.add(root); Node temp = null; // Do level order traversal until last node while (!q.isEmpty()) { temp = q.peek(); q.remove(); if (temp == delNode) { temp = null; return; } if (temp.right!=null) { if (temp.right == delNode) { temp.right = null; return; } else q.add(temp.right); } if (temp.left != null) { if (temp.left == delNode) { temp.left = null; return; } else q.add(temp.left); } } } // Function to delete given element // in binary tree static void delete(Node root, int key) { if (root == null) return; if (root.left == null && root.right == null) { if (root.key == key) { root=null; return; } else return; } Queue q = new LinkedList(); q.add(root); Node temp = null, keyNode = null; // Do level order traversal until // we find key and last node. while (!q.isEmpty()) { temp = q.peek(); q.remove(); if (temp.key == key) keyNode = temp; if (temp.left != null) q.add(temp.left); if (temp.right != null) q.add(temp.right); } if (keyNode != null) { int x = temp.key; deleteDeepest(root, temp); keyNode.key = x; } } // Driver code public static void main(String args[]) { root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(11); root.left.left = new Node(7); root.left.right = new Node(12); root.right = new Node(9); root.right.left = new Node(15); root.right.right = new Node(8); System.out.print('Inorder traversal before deletion: '); inorder(root); //node to delete int key = 7; delete(root, key); System.out.print('
Inorder traversal after deletion: '); inorder(root); } } Izvade:
saulains deols
Inorder traversal before deletion: 7 11 12 10 15 9 8 Inorder traversal after deletion: 8 11 12 10 15 9
Java programma mezgla meklēšanai binārajā kokā
Algoritms
- Definējiet Node klasi, kurai ir trīs atribūti, proti: dati pa kreisi un pa labi. Šeit pa kreisi apzīmē mezgla kreiso atvasi, bet pa labi apzīmē mezgla labo bērnu.
- Kad mezgls ir izveidots, dati tiks pārsūtīti uz mezgla datu atribūtu, un gan pa kreisi, gan pa labi tiks iestatīts uz nulli.
- Definējiet citu klasi, kurai ir divas atribūta saknes un karoga.
- Sakne apzīmē koka saknes mezglu un inicializē to uz nulli.
- Karogs tiks izmantots, lai pārbaudītu, vai konkrētais mezgls atrodas kokā. Sākotnēji tas tiks iestatīts uz nepatiesu.
- Tas pārbauda, vai saknes vērtība ir nulle, kas nozīmē, ka koks ir tukšs.
- Ja koks nav tukšs, tas salīdzinās tempa datus ar vērtību. Ja tie ir vienādi, tas iestatīs karogu uz patiesu un atgriezīsies.
- Pārejiet pa kreiso apakškoku, rekursīvi izsaucot searchNode() un pārbaudiet, vai vērtība atrodas kreisajā apakškokā.
- Pārejiet pa labo apakškoku, rekursīvi izsaucot searchNode() un pārbaudiet, vai vērtība atrodas labajā apakškokā.
SearchBinaryTree.java
public class SearchBinaryTree { //Represent a node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public static boolean flag = false; public SearchBinaryTree() { root = null; } //searchNode() will search for the particular node in the binary tree public void searchNode(Node temp, int value) { //Check whether tree is empty if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); } else { //If value is found in the given binary tree then, set the flag to true if(temp.data == value) { flag = true; return; } //Search in left subtree if(flag == false && temp.left != null) { searchNode(temp.left, value); } //Search in right subtree if(flag == false && temp.right != null) { searchNode(temp.right, value); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { SearchBinaryTree bt = new SearchBinaryTree(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(11); bt.root.left = new Node(8); bt.root.right = new Node(12); bt.root.left.left = new Node(78); bt.root.right.left = new Node(23); bt.root.right.right = new Node(36); //Search for node 5 in the binary tree bt.searchNode(bt.root, 23); if(flag) System.out.println('Element is present in the binary tree.'); else System.out.println('Element is not present in the binary tree.'); } } Izvade:
Element is present in the binary tree.
Binārā koka šķērsošana
| Šķērsošanas pasūtījums | Pirmā vizīte | Otrais apmeklējums | Trešais apmeklējums |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kārtībā | Apmeklējiet kreiso apakškoku secībā | Apmeklējiet saknes mezglu | Apmeklējiet labo apakškoku secībā |
| Iepriekšpasūtījums | Apmeklējiet saknes mezglu | Apmeklējiet kreiso apakškoku priekšpasūtīšanā | Apmeklējiet labo apakškoku priekšpasūtījumā |
| Pasūtījums pa pastu | Apmeklējiet kreiso apakškoku pēc kārtas | Apmeklējiet labo apakškoku pēc kārtas | Apmeklējiet saknes mezglu |
Piezīme. Izņemot iepriekš minētos trīs šķērsošanas veidus, ir vēl viena šķērsošanas secība, ko sauc par robežšķērsošanu.
Java programma, lai izietu secībā, priekšpasūtīšanā un pēc pasūtījuma
BinaryTree.java
public class BinaryTree { // first node private Node root; BinaryTree() { root = null; } // Class representing tree nodes static class Node { int value; Node left; Node right; Node(int value) { this.value = value; left = null; right = null; } public void displayData() { System.out.print(value + ' '); } } public void insert(int i) { root = insert(root, i); } //Inserting node - recursive method public Node insert(Node node, int value) { if(node == null){ return new Node(value); } // Move to the left if passed value is // less than the current node if(value node.value) { node.right = insert(node.right, value); } return node; } // Search node in binary search tree public Node find(int searchedValue) { Node current = root; while(current.value != searchedValue) { if(searchedValue = current = current.right; if(current == null) { return null; } } return current; } // For traversing in order public void inOrder(Node node) { if(node != null) { inOrder(node.left); node.displayData(); inOrder(node.right); } } // Preorder traversal public void preOrder(Node node) { if(node != null){ node.displayData(); preOrder(node.left); preOrder(node.right); } } // Postorder traversal public void postOrder(Node node) { if(node != null) { postOrder(node.left); postOrder(node.right); node.displayData(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { BinaryTree bst = new BinaryTree(); bst.insert(34); bst.insert(56); bst.insert(12); bst.insert(89); bst.insert(67); bst.insert(90); System.out.println('Inorder traversal of binary tree'); bst.inOrder(bst.root); System.out.println(); System.out.println('Preorder traversal of binary tree'); bst.preOrder(bst.root); System.out.println(); System.out.println('Postorder traversal of binary tree'); bst.postOrder(bst.root); System.out.println(); } } Izvade:
Inorder traversal of binary tree 12 34 56 67 89 90 Preorder traversal of binary tree 34 12 56 89 67 90 Postorder traversal of binary tree 12 67 90 89 56 34
Papildus iepriekšminētajām darbībām mēs varam veikt arī tādas darbības kā lielais mezgls, mazākais mezgls un visu mezglu summa.
Java programma, lai atrastu lielāko mezglu binārajā kokā
LielākaisNode.java
public class LargestNode { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public LargestNode() { root = null; } //largestElement() will find out the largest node in the binary tree public int largestElement(Node temp) { //Check whether tree is empty if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); return 0; } else { int leftMax, rightMax; //Max will store temp's data int max = temp.data; //It will find largest element in left subtree if(temp.left != null){ leftMax = largestElement(temp.left); //Compare max with leftMax and store greater value into max max = Math.max(max, leftMax); } //It will find largest element in right subtree if(temp.right != null){ rightMax = largestElement(temp.right); //Compare max with rightMax and store greater value into max max = Math.max(max, rightMax); } return max; } } public static void main(String[] args) { LargestNode bt = new LargestNode(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(90); bt.root.left = new Node(99); bt.root.right = new Node(23); bt.root.left.left = new Node(96); bt.root.right.left = new Node(45); bt.root.right.right = new Node(6); bt.root.right.left = new Node(13); bt.root.right.right = new Node(77); //Display largest node in the binary tree System.out.println('Largest element in the binary tree: ' + bt.largestElement(bt.root)); } } Izvade:
Largest element in the binary tree: 99
Java programma, lai atrastu mazāko mezglu binārajā kokā
Algoritms
- Definējiet Node klasi, kurai ir trīs atribūti, proti: dati, pa kreisi un pa labi. Šeit pa kreisi apzīmē mezgla kreiso atvasi, bet pa labi apzīmē mezgla labo bērnu.
- Kad mezgls ir izveidots, dati tiks pārsūtīti uz mezgla datu atribūtu, un gan pa kreisi, gan pa labi tiks iestatīts uz nulli.
- Definējiet citu klasi, kurai ir atribūta sakne.
Sakne attēlo koka saknes mezglu un inicializē to uz nulli.
- Tā pārbauda, vai sakne ir nulle , kas nozīmē, ka koks ir tukšs.
- Ja koks nav tukšs, definējiet mainīgo min, kurā tiks saglabāti temp dati.
- Uzziniet minimālo mezglu kreisajā apakškokā, rekursīvi izsaucot smallestElement(). Saglabājiet šo vērtību leftMin. Salīdziniet min vērtību ar leftMin un saglabājiet minimālo vērtību no diviem līdz min.
- Uzziniet minimālo mezglu labajā apakškokā, rekursīvi izsaucot smallestElement(). Saglabājiet šo vērtību labajā min. Salīdziniet min vērtību ar rightMin un saglabājiet maksimālo vērtību no diviem līdz min.
- Beigās min aizturēs mazāko binārā koka mezglu.
MazākaisNode.java
public class SmallestNode { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public SmallestNode() { root = null; } //smallestElement() will find out the smallest node in the binary tree public int smallestElement(Node temp) { //Check whether tree is empty if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); return 0; } else { int leftMin, rightMin; //Min will store temp's data int min = temp.data; //It will find smallest element in left subtree if(temp.left != null) { leftMin = smallestElement(temp.left); //If min is greater than leftMin then store the value of leftMin into min min = Math.min(min, leftMin); } //It will find smallest element in right subtree if(temp.right != null) { rightMin = smallestElement(temp.right); //If min is greater than rightMin then store the value of rightMin into min min = Math.min(min, rightMin); } return min; } } public static void main(String[] args) { SmallestNode bt = new SmallestNode(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(9); bt.root.left = new Node(5); bt.root.right = new Node(7); bt.root.left.left = new Node(1); bt.root.right.left = new Node(2); bt.root.right.right = new Node(8); bt.root.right.left = new Node(4); bt.root.right.right = new Node(3); //Display smallest node in the binary tree System.out.println('Smallest element in the binary tree: ' + bt.smallestElement(bt.root)); } } Izvade:
Smallest element in the binary tree: 1
Java programma, lai atrastu maksimālo binārā koka platumu
Algoritms
- Definējiet Node klasi, kurai ir trīs atribūti, proti: dati pa kreisi un pa labi. Šeit pa kreisi apzīmē mezgla kreiso atvasi, bet pa labi apzīmē mezgla labo bērnu.
- Kad mezgls ir izveidots, dati tiks pārsūtīti uz mezgla datu atribūtu, un gan pa kreisi, gan pa labi tiks iestatīts uz nulli.
- Definējiet citu klasi, kurai ir atribūta sakne.
Sakne apzīmē koka saknes mezglu un inicializē to uz nulli.
- Mainīgais maxWidth saglabās maksimālo mezglu skaitu jebkurā līmenī.
- Rinda tiek izmantota binārā koka šķērsošanai līmenī.
- Tas pārbauda, vai saknes vērtība ir nulle, kas nozīmē, ka koks ir tukšs.
- Ja nē, pievienojiet saknes mezglu rindai. Mainīgais nodesInLevel seko mezglu skaitam katrā līmenī.
- Ja nodesInLevel > 0, noņemiet mezglu no rindas priekšpuses un pievienojiet rindai tā kreiso un labo pakārtoto daļu. Pirmajā iterācijā mezgls 1 tiks noņemts, un rindai tiks pievienoti tā atvasinātie mezgli 2 un 3. Otrajā iterācijā mezgls 2 tiks noņemts, tā bērni 4 un 5 tiks pievienoti rindai un tā tālāk.
- MaxWidth saglabās max(maksimālais platums, nodesInLevel). Tātad jebkurā konkrētā brīdī tas attēlo maksimālo mezglu skaitu.
- Tas turpināsies, līdz tiks šķērsoti visi koka līmeņi.
BinaryTree.java
import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; public class BinaryTree { //Represent the node of binary tree public static class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; public Node(int data) { //Assign data to the new node, set left and right children to null this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } //Represent the root of binary tree public Node root; public BinaryTree() { root = null; } //findMaximumWidth() will find out the maximum width of the given binary tree public int findMaximumWidth() { int maxWidth = 0; //Variable nodesInLevel keep tracks of number of nodes in each level int nodesInLevel = 0; //queue will be used to keep track of nodes of tree level-wise Queue queue = new LinkedList(); //Check if root is null, then width will be 0 if(root == null) { System.out.println('Tree is empty'); return 0; } else { //Add root node to queue as it represents the first level queue.add(root); while(queue.size() != 0) { //Variable nodesInLevel will hold the size of queue i.e. number of elements in queue nodesInLevel = queue.size(); //maxWidth will hold maximum width. //If nodesInLevel is greater than maxWidth then, maxWidth will hold the value of nodesInLevel maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, nodesInLevel); //If variable nodesInLevel contains more than one node //then, for each node, we'll add left and right child of the node to the queue while(nodesInLevel > 0) { Node current = queue.remove(); if(current.left != null) queue.add(current.left); if(current.right != null) queue.add(current.right); nodesInLevel--; } } } return maxWidth; } public static void main(String[] args) { BinaryTree bt = new BinaryTree(); //Add nodes to the binary tree bt.root = new Node(1); bt.root.left = new Node(2); bt.root.right = new Node(3); bt.root.left.left = new Node(4); bt.root.left.right = new Node(5); bt.root.right.left = new Node(6); bt.root.right.right = new Node(7); bt.root.left.left.left = new Node(8); //Display the maximum width of given tree System.out.println('Maximum width of the binary tree: ' + bt.findMaximumWidth()); } } Izvade:
Maximum width of the binary tree: 4
