C enum ir pazīstams arī kā uzskaitītais veids. Tas ir lietotāja definēts datu tips, kas sastāv no veselu skaitļu vērtībām un nodrošina šīm vērtībām nozīmīgus nosaukumus. Enum izmantošana C valodā padara programmu viegli saprotamu un uzturējamu. Enum tiek definēts, izmantojot enum atslēgvārdu.
Tālāk ir norādīts veids, kā definēt enumu C:
enum flag{integer_const1, integer_const2,.....integter_constN}; Iepriekš minētajā deklarācijā mēs definējam uzskaitījumu, kas nosaukts kā karodziņš, kurā ir “N” vesela skaitļa konstantes. Integer_const1 noklusējuma vērtība ir 0, integer_const2 ir 1 un tā tālāk. Mēs varam arī mainīt veselo skaitļu konstantu noklusējuma vērtību deklarācijas laikā.
Piemēram:
enum fruits{mango, apple, strawberry, papaya}; Mango noklusējuma vērtība ir 0, ābols ir 1, zemeņu ir 2 un papaija ir 3. Ja mēs vēlamies mainīt šīs noklusējuma vērtības, mēs varam rīkoties, kā norādīts tālāk:
enum fruits{ mango=2, apple=1, strawberry=5, papaya=7, }; Uzskaitīta tipa deklarācija
Kā mēs zinām, ka C valodā mums ir jādeklarē iepriekš definēta tipa mainīgais, piemēram, int, float, char utt. Tāpat mēs varam deklarēt lietotāja definēta datu tipa mainīgo, piemēram, enum. Apskatīsim, kā mēs varam deklarēt enum tipa mainīgo.
Pieņemsim, ka mēs izveidojam tipa statusa sarakstu, kā parādīts zemāk:
enum status{false,true}; Tagad mēs izveidojam statusa tipa mainīgo:
enum status s; // creating a variable of the status type.
Iepriekš minētajā paziņojumā esam deklarējuši tipa statusa mainīgo 's'.
Lai izveidotu mainīgo, iepriekš minētos divus paziņojumus var uzrakstīt šādi:
enum status{false,true} s; Šajā gadījumā noklusējuma vērtība false būs vienāda ar 0, un patiesā vērtība būs vienāda ar 1.
Izveidosim vienkāršu enum programmu.
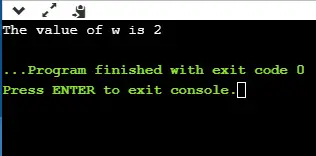
#include enum weekdays{Sunday=1, Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday, Saturday}; int main() { enum weekdays w; // variable declaration of weekdays type w=Monday; // assigning value of Monday to w. printf('The value of w is %d',w); return 0; } Iepriekš minētajā kodā mēs izveidojam enum tipu ar nosaukumu nedēļas dienas, un tajā ir visu septiņu dienu nosaukums. Svētdienai esam piešķīruši 1 vērtību, un visiem pārējiem nosaukumiem tiks piešķirta vērtība kā iepriekšējā vērtība plus viens.
Izvade
Parādīsim vēl vienu piemēru, lai skaidrāk saprastu sarakstu.
#include enum months{jan=1, feb, march, april, may, june, july, august, september, october, november, december}; int main() { // printing the values of months for(int i=jan;i<=december;i++) { printf('%d, ',i); } return 0; < pre> <p>In the above code, we have created a type of enum named as months which consists of all the names of months. We have assigned a '1' value, and all the other months will be given a value as the previous one plus one. Inside the main() method, we have defined a for loop in which we initialize the 'i' variable by jan, and this loop will iterate till December.</p> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/73/enum-c-2.webp" alt="Enum in C"> <h3>Why do we use enum?</h3> <p>The enum is used when we want our variable to have only a set of values. For example, we create a direction variable. As we know that four directions exist (North, South, East, West), so this direction variable will have four possible values. But the variable can hold only one value at a time. If we try to provide some different value to this variable, then it will throw the compilation error.</p> <p>The enum is also used in a switch case statement in which we pass the enum variable in a switch parenthesis. It ensures that the value of the case block should be defined in an enum.</p> <p> <strong>Let's see how we can use an enum in a switch case statement.</strong> </p> <pre> #include enum days{sunday=1, monday, tuesday, wednesday, thursday, friday, saturday}; int main() { enum days d; d=monday; switch(d) { case sunday: printf('Today is sunday'); break; case monday: printf('Today is monday'); break; case tuesday: printf('Today is tuesday'); break; case wednesday: printf('Today is wednesday'); break; case thursday: printf('Today is thursday'); break; case friday: printf('Today is friday'); break; case saturday: printf('Today is saturday'); break; } return 0; } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/73/enum-c-3.webp" alt="Enum in C"> <p> <strong>Some important points related to enum</strong> </p> <ul> <li>The enum names available in an enum type can have the same value. Let's look at the example.</li> </ul> <pre> #include int main(void) { enum fruits{mango = 1, strawberry=0, apple=1}; printf('The value of mango is %d', mango); printf('
The value of apple is %d', apple); return 0; } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/73/enum-c-4.webp" alt="Enum in C"> <ul> <li>If we do not provide any value to the enum names, then the compiler will automatically assign the default values to the enum names starting from 0.</li> <li>We can also provide the values to the enum name in any order, and the unassigned names will get the default value as the previous one plus one.</li> <li>The values assigned to the enum names must be integral constant, i.e., it should not be of other types such string, float, etc.</li> <li>All the enum names must be unique in their scope, i.e., if we define two enum having same scope, then these two enums should have different enum names otherwise compiler will throw an error.</li> </ul> <p> <strong>Let's understand this scenario through an example.</strong> </p> <pre> #include enum status{success, fail}; enum boolen{fail,pass}; int main(void) { printf('The value of success is %d', success); return 0; } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/73/enum-c-5.webp" alt="Enum in C"> <ul> <li>In enumeration, we can define an enumerated data type without the name also.</li> </ul> <pre> #include enum {success, fail} status; int main(void) { status=success; printf('The value of status is %d', status); return 0; } </pre> <p> <strong>Output</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/73/enum-c-6.webp" alt="Enum in C"> <h3>Enum vs. Macro in C</h3> <ul> <li>Macro can also be used to define the name constants, but in case of an enum, all the name constants can be grouped together in a single statement. <br> For example, <br> # define pass 0; <br> # define success 1; <br> The above two statements can be written in a single statement by using the enum type. <br> enum status{pass, success};</li> <li>The enum type follows the scope rules while macro does not follow the scope rules.</li> <li>In Enum, if we do not assign the values to the enum names, then the compiler will automatically assign the default value to the enum names. But, in the case of macro, the values need to be explicitly assigned.</li> <li>The type of enum in C is an integer, but the type of macro can be of any type.</li> </ul> <hr></=december;i++)> Izvade

Daži svarīgi punkti saistībā ar enum
- Uzskaites veida nosaukumiem var būt vienāda vērtība. Apskatīsim piemēru.
#include int main(void) { enum fruits{mango = 1, strawberry=0, apple=1}; printf('The value of mango is %d', mango); printf('
The value of apple is %d', apple); return 0; } Izvade

- Ja enumu nosaukumiem nenorādīsim nekādas vērtības, kompilators enumu nosaukumiem automātiski piešķirs noklusējuma vērtības, sākot no 0.
- Mēs varam arī norādīt vērtības enum nosaukumam jebkurā secībā, un nepiešķirtie nosaukumi saņems noklusējuma vērtību kā iepriekšējais plus viens.
- Uzskaites nosaukumiem piešķirtajām vērtībām jābūt integrālām konstantēm, t.i., tām nevajadzētu būt cita veida, piemēram, virknei, pludiņam utt.
- Visiem enumu nosaukumiem ir jābūt unikāliem savā darbības jomā, t.i., ja mēs definējam divus enum ar vienādu tvērumu, tad šiem diviem enum nosaukumiem jābūt atšķirīgiem, pretējā gadījumā kompilators radīs kļūdu.
Izpratīsim šo scenāriju, izmantojot piemēru.
#include enum status{success, fail}; enum boolen{fail,pass}; int main(void) { printf('The value of success is %d', success); return 0; } Izvade

- Uzskaitē mēs varam definēt uzskaitītu datu tipu arī bez nosaukuma.
#include enum {success, fail} status; int main(void) { status=success; printf('The value of status is %d', status); return 0; } Izvade

Enum pret makro C
- Makro var izmantot arī, lai definētu nosaukuma konstantes, bet enum gadījumā visas nosaukuma konstantes var sagrupēt vienā priekšrakstā.
Piemēram,
# definēt 0;
# definēt panākumus 1;
Iepriekš minētos divus paziņojumus var ierakstīt vienā priekšrakstā, izmantojot enum veidu.
enum statuss {ieskaitīts, veiksme}; - Enum tips ievēro tvēruma noteikumus, savukārt makro neievēro tvēruma noteikumus.
- Enum, ja mēs nepiešķiram vērtības enum nosaukumiem, kompilators automātiski piešķirs noklusējuma vērtību enum nosaukumiem. Bet makro gadījumā vērtības ir skaidri jāpiešķir.
- C enum veids ir vesels skaitlis, bet makro veids var būt jebkura veida.
