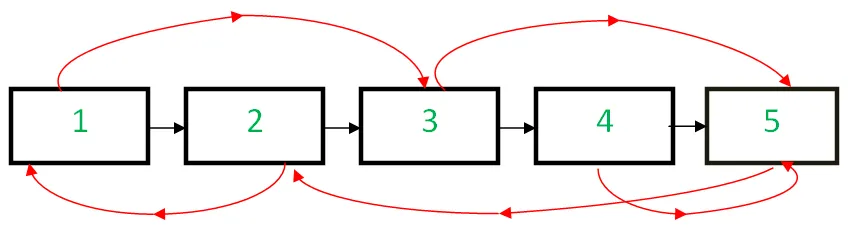
Ņemot vērā a saistītais saraksts izmēra N kur katram mezglam ir divas saites: nākamais rādītājs norādot uz nākamo mezglu un izlases rādītājs uz jebkuru izlases mezglu sarakstā. Uzdevums ir izveidot šī saistītā saraksta klonu O(1) telpā, t.i., bez papildu atstarpes.
Piemēri:
numpy meshgrid
Ievade: Zemāk esošā saraksta vadītājs
Izvade: Jauns saistītais saraksts, kas ir identisks sākotnējam sarakstam.
[Paredzamā pieeja], ievietojot mezglus vietā — O(3n) laiks un O(1) telpa
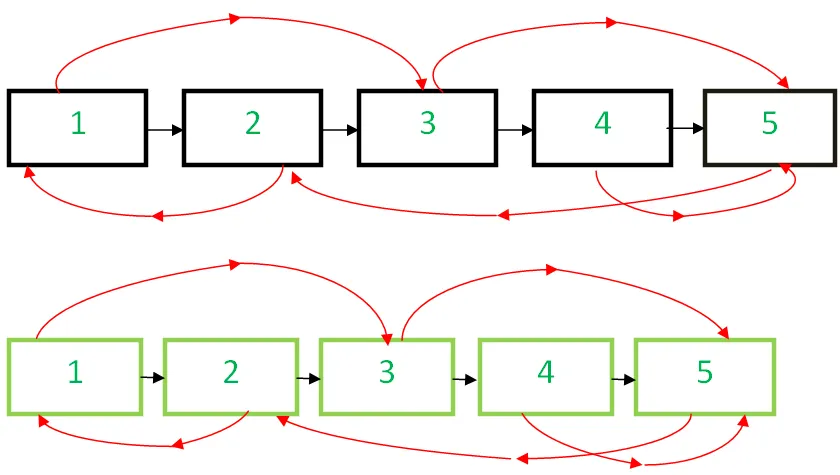
Ideja ir izveidot mezgla dublikātu, un tā vietā, lai saglabātu to atsevišķā hash tabulā, mēs varam ievietot to starp sākotnējo mezglu un nākamo mezglu. Tagad mums būs jauni mezgli alternatīvās pozīcijās. Tagad par a mezgls X tā dublikāts būs X->nākamais un dublikāta izlases rādītājam ir jānorāda uz X->nejauši->nākamais (jo tas ir dublikāts X-> nejauši ). Tāpēc atkārtojiet visu saistīto sarakstu, lai atjauninātu visu klonēto mezglu nejaušo rādītāju, un pēc tam atkārtojiet vēlreiz, lai atdalītu sākotnējo saistīto sarakstu un klonēto saistīto sarakstu.
Lai īstenotu ideju, veiciet tālāk norādītās darbības.
- Izveidojiet kopiju mezgls 1 un ievietojiet to starp mezgls 1 un mezgls 2 sākotnējā saistītajā sarakstā izveidojiet kopiju mezgls 2 un ievietojiet to starp 2 nd un 3 rd mezgls un tā tālāk. Pievienojiet N kopiju aiz Nthmezgls
- Savienojiet klona mezglu, atjauninot nejaušās norādes.
- Atdaliet klonēto saistīto sarakstu no sākotnējā saraksta, atjauninot nākamās norādes.
fcfs
Tālāk ir norādīta īstenošana, ja iepriekš aprakstītā pieeja:
C++// C++ code to Clone a linked list with next and random // pointer by Inserting Nodes In-place #include
// Java code to Clone a linked list with next and random // pointer by Inserting Nodes In-place class Node { int data; Node next random; Node(int x) { data = x; next = random = null; } } class GfG { // Function to clone the linked list static Node cloneLinkedList(Node head) { if (head == null) { return null; } // Create new nodes and insert them next to the original nodes Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { Node newNode = new Node(curr.data); newNode.next = curr.next; curr.next = newNode; curr = newNode.next; } // Set the random pointers of the new nodes curr = head; while (curr != null) { if (curr.random != null) { curr.next.random = curr.random.next; } curr = curr.next.next; } // Separate the new nodes from the original nodes curr = head; Node clonedHead = head.next; Node clone = clonedHead; while (clone.next != null) { // Update the next nodes of original node // and cloned node curr.next = curr.next.next; clone.next = clone.next.next; // Move pointers of original and cloned // linked list to their next nodes curr = curr.next; clone = clone.next; } curr.next = null; clone.next = null; return clonedHead; } // Function to print the linked list public static void printList(Node head) { while (head != null) { System.out.print(head.data + '('); if (head.random != null) { System.out.print(head.random.data); } else { System.out.print('null'); } System.out.print(')'); if (head.next != null) { System.out.print(' -> '); } head = head.next; } System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Creating a linked list with random pointer Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); head.random = head.next.next; head.next.random = head; head.next.next.random = head.next.next.next.next; head.next.next.next.random = head.next.next; head.next.next.next.next.random = head.next; // Print the original list System.out.println('Original linked list:'); printList(head); // Function call Node clonedList = cloneLinkedList(head); System.out.println('Cloned linked list:'); printList(clonedList); } }
# Python code to Clone a linked list with next and random # pointer by Inserting Nodes In-place class Node: def __init__(self x): self.data = x self.next = None self.random = None # Function to clone the linked list def clone_linked_list(head): if head is None: return None # Create new nodes and insert them next to # the original nodes curr = head while curr is not None: new_node = Node(curr.data) new_node.next = curr.next curr.next = new_node curr = new_node.next # Set the random pointers of the new nodes curr = head while curr is not None: if curr.random is not None: curr.next.random = curr.random.next curr = curr.next.next # Separate the new nodes from the original nodes curr = head cloned_head = head.next clone = cloned_head while clone.next is not None: # Update the next nodes of original node # and cloned node curr.next = curr.next.next clone.next = clone.next.next # Move pointers of original as well as # cloned linked list to their next nodes curr = curr.next clone = clone.next curr.next = None clone.next = None return cloned_head # Function to print the linked list def print_list(head): while head is not None: print(f'{head.data}(' end='') if head.random: print(f'{head.random.data})' end='') else: print('null)' end='') if head.next is not None: print(' -> ' end='') head = head.next print() if __name__ == '__main__': # Creating a linked list with random pointer head = Node(1) head.next = Node(2) head.next.next = Node(3) head.next.next.next = Node(4) head.next.next.next.next = Node(5) head.random = head.next.next head.next.random = head head.next.next.random = head.next.next.next.next head.next.next.next.random = head.next.next head.next.next.next.next.random = head.next # Print the original list print('Original linked list:') print_list(head) # Function call cloned_list = clone_linked_list(head) print('Cloned linked list:') print_list(cloned_list)
// C# code to Clone a linked list with next and random // pointer by Inserting Nodes In-place using System; using System.Collections.Generic; public class Node { public int Data; public Node next Random; public Node(int x) { Data = x; next = Random = null; } } class GfG { static Node CloneLinkedList(Node head) { if (head == null) return null; // Create new nodes and insert them next to // the original nodes Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { Node newNode = new Node(curr.Data); newNode.next = curr.next; curr.next = newNode; curr = newNode.next; } // Set the random pointers of the new nodes curr = head; while (curr != null) { if (curr.Random != null) curr.next.Random = curr.Random.next; curr = curr.next.next; } // Separate the new nodes from the original nodes curr = head; Node clonedHead = head.next; Node clone = clonedHead; while (clone.next != null) { // Update the next nodes of original node // and cloned node curr.next = curr.next.next; clone.next = clone.next.next; // Move pointers of original as well as // cloned linked list to their next nodes curr = curr.next; clone = clone.next; } curr.next = null; clone.next = null; return clonedHead; } // Function to print the linked list static void PrintList(Node head) { while (head != null) { Console.Write(head.Data + '('); if (head.Random != null) Console.Write(head.Random.Data + ')'); else Console.Write('null)'); if (head.next != null) Console.Write(' -> '); head = head.next; } Console.WriteLine(); } public static void Main() { // Creating a linked list with random pointer Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); head.Random = head.next.next; head.next.Random = head; head.next.next.Random = head.next.next.next.next; head.next.next.next.Random = head.next.next; head.next.next.next.next.Random = head.next; // Print the original list Console.WriteLine('Original linked list:'); PrintList(head); Node clonedList = CloneLinkedList(head); Console.WriteLine('Cloned linked list:'); PrintList(clonedList); } }
// JavaScript code to Clone a linked list with next and random // pointer by Inserting Nodes In-place class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.next = null; this.random = null; } } function cloneLinkedList(head) { if (head === null) { return null; } // Create new nodes and insert them next to the // original nodes let curr = head; while (curr !== null) { let newNode = new Node(curr.data); newNode.next = curr.next; curr.next = newNode; curr = newNode.next; } // Set the random pointers of the new nodes curr = head; while (curr !== null) { if (curr.random !== null) { curr.next.random = curr.random.next; } curr = curr.next.next; } // Separate the new nodes from the original nodes curr = head; let clonedHead = head.next; let clone = clonedHead; while (clone.next !== null) { // Update the next nodes of original node and cloned node curr.next = curr.next.next; clone.next = clone.next.next; // Move pointers of original as well as cloned // linked list to their next nodes curr = curr.next; clone = clone.next; } curr.next = null; clone.next = null; return clonedHead; } // Function to print the linked list function printList(head) { let result = ''; while (head !== null) { result += head.data + '('; result += head.random ? head.random.data : 'null'; result += ')'; if (head.next !== null) { result += ' -> '; } head = head.next; } console.log(result); } // Creating a linked list with random pointer let head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); head.random = head.next.next; head.next.random = head; head.next.next.random = head.next.next.next.next; head.next.next.next.random = head.next.next; head.next.next.next.next.random = head.next; // Print the original list console.log('Original linked list:'); printList(head); let clonedList = cloneLinkedList(head); console.log('Cloned linked list:'); printList(clonedList);
Izvade
Original linked list: 1(3) -> 2(1) -> 3(5) -> 4(3) -> 5(2) Cloned linked list: 1(3) -> 2(1) -> 3(5) -> 4(3) -> 5(2)
Laika sarežģītība: O(3n) jo mēs trīs reizes šķērsojam saistīto sarakstu.
Palīgtelpa: O(1) tā kā mēs glabājam visus klonētos mezglus sākotnējā saistītajā sarakstā, papildu vieta nav nepieciešama.