Ieviešanai tiek izmantota Java TreeMap Kartes interfeiss un NavigableMap kopā ar AbstractMap klasi. Karte tiek sakārtota atbilstoši tās atslēgu dabiskajai secībai vai pēc a Salīdzinātājs tiek nodrošināts kartes izveides laikā, atkarībā no tā, kurš konstruktors tiek izmantots. Tas izrādās efektīvs veids, kā šķirot un saglabāt atslēgu un vērtību pārus. Koka kartes uzturētajai glabāšanas secībai ir jāatbilst vienādām kartēm, tāpat kā jebkurai citai sakārtotai kartei, neatkarīgi no skaidriem salīdzinātājiem. Koka kartes ieviešana nav sinhronizēta tādā nozīmē, ka, ja kartei piekļūst vairāki pavedieni, vienlaikus un vismaz viens no pavedieniem strukturāli modificē karti, tā ir jāsinhronizē ārēji.
TreeMap Java ir konkrēta interfeisa java.util.SortedMap ieviešana. Tas nodrošina sakārtotu atslēgu un vērtību pāru kolekciju, kurā atslēgas tiek sakārtotas, pamatojoties uz to dabisko secību vai pielāgotu salīdzinātāju, kas tiek nodots konstruktoram.
TreeMap tiek ieviests, izmantojot sarkanmelnu koku, kas ir pašbalansējoša binārā meklēšanas koka veids. Tas nodrošina efektīvu veiktspēju parastajām darbībām, piemēram, elementu pievienošanai, noņemšanai un izgūšanai, ar vidējo laika sarežģītību O(log n).
Šeit ir piemērs, kā izmantot TreeMap klasi:
Java
import> java.util.Map;> import> java.util.TreeMap;> public> class> Main {> >public> static> void> main(String[] args) {> >Map treeMap =>new> TreeMap();> >// Adding elements to the tree map> >treeMap.put(>'A'>,>1>);> >treeMap.put(>'C'>,>3>);> >treeMap.put(>'B'>,>2>);> >// Getting values from the tree map> >int> valueA = treeMap.get(>'A'>);> >System.out.println(>'Value of A: '> + valueA);> >// Removing elements from the tree map> >treeMap.remove(>'B'>);> >// Iterating over the elements of the tree map> >for> (String key : treeMap.keySet()) {> >System.out.println(>'Key: '> + key +>', Value: '> + treeMap.get(key));> >}> >}> }> |
>
>Izvade
Value of A: 1 Key: A, Value: 1 Key: C, Value: 3>
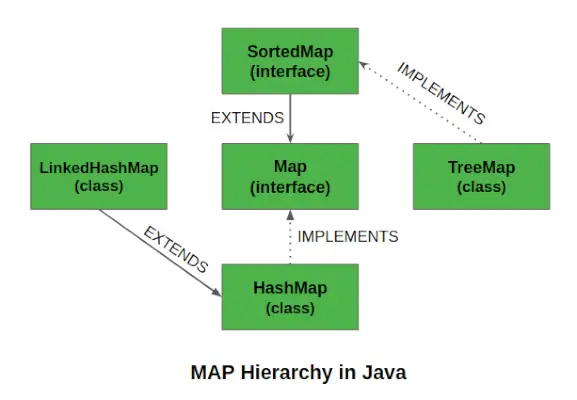
TreeMap funkcijas
Dažas svarīgas koka kartes funkcijas ir šādas:
- Šī klase ir grupas dalībniece Java kolekcijas Ietvars.
- Klase īsteno Kartes saskarnes tostarp NavigableMap , SortedMap un paplašina AbstractMap klasi.
- TreeMap Java neļauj izmantot nulles atslēgas (piemēram, Map), un tādējādi tiek izmests NullPointerException. Tomēr vairākas nulles vērtības var būt saistītas ar dažādām atslēgām.
- Ierakstu pāri, ko atgriež šīs klases metodes, un tās skati atspoguļo kartējumu momentuzņēmumus to izveides laikā. Tie neatbalsta Entry.setValue metodi.
Tagad virzīsimies uz priekšu un apspriedīsim sinhronizēto koku karti. TreeMap ieviešana nav sinhronizēta. Tas nozīmē, ka, ja vairāki pavedieni vienlaikus piekļūst koka kopai un vismaz viens no pavedieniem pārveido kopu, tas ir jāsinhronizē ārēji. Parasti to panāk, izmantojot metodi Collections.synchronizedSortedMap. To vislabāk var izdarīt izveides laikā, lai novērstu nejaušu nesinhronizētu piekļuvi komplektam. To var izdarīt šādi:
SortedMap m = Collections.synchronizedSortedMap(new TreeMap(...));>
Geeks, tagad jums noteikti jādomā, kā TreeMap darbojas iekšēji?
TreeMap metodes, iegūstot atslēgu kopu un vērtības, atgriež iteratoru, kas pēc būtības ir ātrs. Tādējādi jebkura vienlaicīga modifikācija radīs ConcurrentModificationException . TreeMap pamatā ir sarkanmelna koka datu struktūra.
Katram koka mezglam ir:
- 3 mainīgie ( K taustiņš = atslēga, V vērtība = vērtība, Būla krāsa = krāsa )
- 3 atsauces ( Ieraksts pa kreisi = pa kreisi, ieraksts pa labi = pa labi, ieraksts vecāks = vecāks )
Konstruktori programmā TreeMap
Lai izveidotu TreeMap, mums ir jāizveido TreeMap klases objekts. TreeMap klase sastāv no dažādiem konstruktoriem, kas ļauj izveidot TreeMap. Šajā klasē ir pieejami šādi konstruktori:
- TreeMap ()
- TreeMap (salīdzināšanas komparators)
- TreeMap (M karte)
- TreeMap (SortedMap sm)
Apspriedīsim tos atsevišķi, ieviešot katru konstruktoru šādi:
1. konstruktors: TreeMap ()
Šis konstruktors tiek izmantots, lai izveidotu tukšu koka karti, kas tiks sakārtota, izmantojot dabisko atslēgu secību.
Piemērs
Java
// Java Program to Demonstrate TreeMap> // using the Default Constructor> // Importing required classes> import> java.util.*;> import> java.util.concurrent.*;> // Main class> // TreeMapImplementation> public> class> GFG {> >// Method 1> >// To show TreeMap constructor> >static> void> Example1stConstructor()> >{> >// Creating an empty TreeMap> >TreeMap tree_map> >=>new> TreeMap();> >// Mapping string values to int keys> >// using put() method> >tree_map.put(>10>,>'Geeks'>);> >tree_map.put(>15>,>'4'>);> >tree_map.put(>20>,>'Geeks'>);> >tree_map.put(>25>,>'Welcomes'>);> >tree_map.put(>30>,>'You'>);> >// Printing the elements of TreeMap> >System.out.println(>'TreeMap: '> + tree_map);> >}> >// Method 2> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >System.out.println(>'TreeMap using '> >+>'TreeMap() constructor:
'>);> >// Calling constructor> >Example1stConstructor();> >}> }> |
>
>Izvade
TreeMap using TreeMap() constructor: TreeMap: {10=Geeks, 15=4, 20=Geeks, 25=Welcomes, 30=You}> 2. konstruktors: TreeMap (salīdzināšanas komparators)
Šis konstruktors tiek izmantots, lai izveidotu tukšu TreeMap objektu, kurā elementiem būs nepieciešama šķirošanas secības ārēja specifikācija.
Piemērs
Java
// Java Program to Demonstrate TreeMap> // using Comparator Constructor> // Importing required classes> import> java.util.*;> import> java.util.concurrent.*;> // Class 1> // Helper class representing Student> class> Student {> >// Attributes of a student> >int> rollno;> >String name, address;> >// Constructor> >public> Student(>int> rollno, String name, String address)> >{> >// This keyword refers to current object itself> >this>.rollno = rollno;> >this>.name = name;> >this>.address = address;> >}> >// Method of this class> >// To print student details> >public> String toString()> >{> >return> this>.rollno +>' '> +>this>.name +>' '> >+>this>.address;> >}> }> // Class 2> // Helper class - Comparator implementation> class> Sortbyroll>implements> Comparator {> >// Used for sorting in ascending order of> >// roll number> >public> int> compare(Student a, Student b)> >{> >return> a.rollno - b.rollno;> >}> }> // Class 3> // Main class> public> class> GFG {> >// Calling constructor inside main()> >static> void> Example2ndConstructor()> >{> >// Creating an empty TreeMap> >TreeMap tree_map> >=>new> TreeMap(> >new> Sortbyroll());> >// Mapping string values to int keys> >tree_map.put(>new> Student(>111>,>'bbbb'>,>'london'>),>2>);> >tree_map.put(>new> Student(>131>,>'aaaa'>,>'nyc'>),>3>);> >tree_map.put(>new> Student(>121>,>'cccc'>,>'jaipur'>),>1>);> >// Printing the elements of TreeMap> >System.out.println(>'TreeMap: '> + tree_map);> >}> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >System.out.println(>'TreeMap using '> >+>'TreeMap(Comparator)'> >+>' constructor:
'>);> >Example2ndConstructor();> >}> }> |
>
>Izvade
TreeMap using TreeMap(Comparator) constructor: TreeMap: {111 bbbb london=2, 121 cccc jaipur=1, 131 aaaa nyc=3}> 3. konstruktors: TreeMap (M karte)
Šis konstruktors tiek izmantots, lai inicializētu TreeMap ar ierakstiem no dotās kartes M, kas tiks sakārtoti, izmantojot dabisko taustiņu secību.
Piemērs
Java
// Java Program to Demonstrate TreeMap> // using the Default Constructor> // Importing required classes> import> java.util.*;> import> java.util.concurrent.*;> // Main class> public> class> TreeMapImplementation {> >// Method 1> >// To illustrate constructor> >static> void> Example3rdConstructor()> >{> >// Creating an empty HashMap> >Map hash_map> >=>new> HashMap();> >// Mapping string values to int keys> >// using put() method> >hash_map.put(>10>,>'Geeks'>);> >hash_map.put(>15>,>'4'>);> >hash_map.put(>20>,>'Geeks'>);> >hash_map.put(>25>,>'Welcomes'>);> >hash_map.put(>30>,>'You'>);> >// Creating the TreeMap using the Map> >TreeMap tree_map> >=>new> TreeMap(hash_map);> >// Printing the elements of TreeMap> >System.out.println(>'TreeMap: '> + tree_map);> >}> >// Method 2> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >System.out.println(>'TreeMap using '> >+>'TreeMap(Map)'> >+>' constructor:
'>);> >Example3rdConstructor();> >}> }> |
>
>Izvade
TreeMap using TreeMap(Map) constructor: TreeMap: {10=Geeks, 15=4, 20=Geeks, 25=Welcomes, 30=You}> 4. konstruktors: TreeMap (SortedMap sm)
Šis konstruktors tiek izmantots, lai inicializētu TreeMap ar ierakstiem no dotās sakārtotās kartes, kas tiks saglabāti tādā pašā secībā kā dotā sakārtotā karte.
Piemērs
Java
// Java Program to Demonstrate TreeMap> // using the SortedMap Constructor> // Importing required classes> import> java.util.*;> import> java.util.concurrent.*;> // Main class> // TreeMapImplementation> public> class> GFG {> >// Method> >// To show TreeMap(SortedMap) constructor> >static> void> Example4thConstructor()> >{> >// Creating a SortedMap> >SortedMap sorted_map> >=>new> ConcurrentSkipListMap();> >// Mapping string values to int keys> >// using put() method> >sorted_map.put(>10>,>'Geeks'>);> >sorted_map.put(>15>,>'4'>);> >sorted_map.put(>20>,>'Geeks'>);> >sorted_map.put(>25>,>'Welcomes'>);> >sorted_map.put(>30>,>'You'>);> >// Creating the TreeMap using the SortedMap> >TreeMap tree_map> >=>new> TreeMap(sorted_map);> >// Printing the elements of TreeMap> >System.out.println(>'TreeMap: '> + tree_map);> >}> >// Method 2> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >System.out.println(>'TreeMap using '> >+>'TreeMap(SortedMap)'> >+>' constructor:
'>);> >Example4thConstructor();> >}> }> |
>
>Izvade
TreeMap using TreeMap(SortedMap) constructor: TreeMap: {10=Geeks, 15=4, 20=Geeks, 25=Welcomes, 30=You}> Metodes TreeMap klasē
| Metode | Darbība veikta |
|---|---|
| skaidrs () | Šī metode noņem visus kartējumus no šīs TreeMap un notīra karti. |
| klons () | Metode atgriež seklu šīs TreeMap kopiju. |
| includeKey (objekta atslēga) | Atgriež vērtību True, ja šajā kartē ir norādītās atslēgas kartējums. |
| includeValue (objekta vērtība) | Atgriež vērtību True, ja šī karte kartē vienu vai vairākas atslēgas uz norādīto vērtību. |
| ierakstsSet() | Atgriež šajā kartē ietverto kartējumu kopskatu. |
| firstKey() | Atgriež pirmo (zemāko) atslēgu pašlaik šajā sakārtotajā kartē. |
| iegūt (objekta atslēga) | Atgriež vērtību, ar kuru šī karte kartē norādīto atslēgu. |
| headMap (objekta atslēgas_vērtība) | Metode atgriež kartes daļas skatu, kas ir mazāks par parametru atslēgas_vērtība. |
| keySet() | Metode atgriež koka kartē ietverto atslēgu kopas skatu. |
| pēdējā atslēga() | Atgriež pēdējo (augstāko) atslēgu pašlaik šajā sakārtotajā kartē. |
| likt (objekta atslēga, objekta vērtība) | Šo metodi izmanto, lai kartē ievietotu kartējumu. |
| ievietot visu (kartes karte) | Kopē visus kartējumus no norādītās kartes uz šo karti. |
| noņemt (objekta atslēga) | Noņem šīs atslēgas kartējumu no šīs TreeMap, ja tāda ir. |
| Izmērs() | Atgriež atslēgu vērtību kartējumu skaitu šajā kartē. |
| apakškarte ((K startKey, K endKey) | Metode atgriež šīs kartes daļu, kuras atslēgas ir no startKey, ieskaitot, līdz endKey, ekskluzīvai. |
| vērtības () | Atgriež šajā kartē ietverto vērtību kolekcijas skatu. |
Īstenošana: Tālāk norādītās programmas labāk parādīs, kā izveidot, ievietot un pārvietoties pa TreeMap.
Ilustrācija:
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Operations in TreeMap> // Such as Creation, insertion> // searching, and traversal> // Importing required classes> import> java.util.*;> import> java.util.concurrent.*;> // Main class> // Implementation of TreeMap> public> class> GFG {> >// Declaring a TreeMap> >static> TreeMap tree_map;> >// Method 1> >// To create TreeMap> >static> void> create()> >{> >// Creating an empty TreeMap> >tree_map =>new> TreeMap();> >// Display message only> >System.out.println(>'TreeMap successfully'> >+>' created'>);> >}> >// Method 2> >// To Insert values in the TreeMap> >static> void> insert()> >{> >// Mapping string values to int keys> >// using put() method> >tree_map.put(>10>,>'Geeks'>);> >tree_map.put(>15>,>'4'>);> >tree_map.put(>20>,>'Geeks'>);> >tree_map.put(>25>,>'Welcomes'>);> >tree_map.put(>30>,>'You'>);> >// Display message only> >System.out.println(>'
Elements successfully'> >+>' inserted in the TreeMap'>);> >}> >// Method 3> >// To search a key in TreeMap> >static> void> search(>int> key)> >{> >// Checking for the key> >System.out.println(>'
Is key ''> + key> >+>'' present? '> >+ tree_map.containsKey(key));> >}> >// Method 4> >// To search a value in TreeMap> >static> void> search(String value)> >{> >// Checking for the value> >System.out.println(>'
Is value ''> + value> >+>'' present? '> >+ tree_map.containsValue(value));> >}> >// Method 5> >// To display the elements in TreeMap> >static> void> display()> >{> >// Displaying the TreeMap> >System.out.println(>'
Displaying the TreeMap:'>);> >System.out.println(>'TreeMap: '> + tree_map);> >}> >// Method 6> >// To traverse TreeMap> >static> void> traverse()> >{> >// Display message only> >System.out.println(>'
Traversing the TreeMap:'>);> >for> (Map.Entry e :> >tree_map.entrySet())> >System.out.println(e.getKey() +>' '> >+ e.getValue());> >}> >// Method 6> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String[] args)> >{> >// Calling above defined methods inside main()> >// Creating a TreeMap> >create();> >// Inserting the values in the TreeMap> >insert();> >// Search key '50' in the TreeMap> >search(>50>);> >// Search value 'Geeks' in the TreeMap> >search(>'Geeks'>);> >// Display the elements in TreeMap> >display();> >// Traversing the TreeMap> >traverse();> >}> }> |
>
>Izvade
TreeMap successfully created Elements successfully inserted in the TreeMap Is key '50' present? false Is value 'Geeks' present? true Displaying the TreeMap: TreeMap: {10=Geeks, 15=4, 20=Geeks, 25=Welcomes, 30=You} Traversing the TreeMap: 10 Geeks 15 4 20 Geeks 25 Welcomes 30 You> Dažādu darbību veikšana ar TreeMap
Pēc Generics ieviešanas Java 1.5 versijā ir iespējams ierobežot TreeMap glabājamo objektu veidu. Tagad apskatīsim, kā TreeMap veikt dažas bieži lietotas darbības.
1. darbība: Elementu pievienošana
Lai TreeMap pievienotu elementu, mēs varam izmantot metodi put() . Tomēr ievietošanas secība netiek saglabāta TreeMap. Iekšēji katram elementam atslēgas tiek salīdzinātas un sakārtotas augošā secībā.
Piemērs
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Addition of Elements> // in TreeMap using put() Method> // Importing required classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String args[])> >{> >// Default Initialization of a TreeMap> >TreeMap tm1 =>new> TreeMap();> >// Inserting the elements in TreeMap> >// using put() method> >tm1.put(>3>,>'Geeks'>);> >tm1.put(>2>,>'For'>);> >tm1.put(>1>,>'Geeks'>);> >// Initialization of a TreeMap using Generics> >TreeMap tm2> >=>new> TreeMap();> >// Inserting the elements in TreeMap> >// again using put() method> >tm2.put(>new> Integer(>3>),>'Geeks'>);> >tm2.put(>new> Integer(>2>),>'For'>);> >tm2.put(>new> Integer(>1>),>'Geeks'>);> >// Printing the elements of both TreeMaps> >// Map 1> >System.out.println(tm1);> >// Map 2> >System.out.println(tm2);> >}> }> |
>
>Izvade
{1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks} {1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}> 2. darbība: elementu maiņa
Pēc elementu pievienošanas, ja vēlamies elementu mainīt, to var izdarīt, vēlreiz pievienojot elementu ar metodi put() . Tā kā koka kartes elementi tiek indeksēti, izmantojot taustiņus, atslēgas vērtību var mainīt, vienkārši ievietojot atjaunināto vērtību atslēgai, kuru mēs vēlamies mainīt.
Piemērs
Java
// Java program to Illustrate Updation of Elements> // in TreeMap using put() Method> // Importing required classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String args[])> >{> >// Initialization of a TreeMap> >// using Generics> >TreeMap tm> >=>new> TreeMap();> >// Inserting the elements in Map> >// using put() method> >tm.put(>3>,>'Geeks'>);> >tm.put(>2>,>'Geeks'>);> >tm.put(>1>,>'Geeks'>);> >// Print all current elements in map> >System.out.println(tm);> >// Inserting the element at specified> >// corresponding to specified key> >tm.put(>2>,>'For'>);> >// Printing the updated elements of Map> >System.out.println(tm);> >}> }> |
>
>Izvade
{1=Geeks, 2=Geeks, 3=Geeks} {1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}> 3. darbība: Elementa noņemšana
Lai noņemtu elementu no TreeMap, mēs varam izmantot metodi remove() . Šī metode ņem atslēgas vērtību un noņem atslēgas kartējumu no šīs koka kartes, ja tā ir kartē.
Piemērs
Java
topoloģijas
// Java program to Illustrate Removal of Elements> // in TreeMap using remove() Method> // Importing required classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String args[])> >{> >// Initialization of a TreeMap> >// using Generics> >TreeMap tm> >=>new> TreeMap();> >// Inserting the elements> >// using put() method> >tm.put(>3>,>'Geeks'>);> >tm.put(>2>,>'Geeks'>);> >tm.put(>1>,>'Geeks'>);> >tm.put(>4>,>'For'>);> >// Printing all elements of Map> >System.out.println(tm);> >// Removing the element corresponding to key> >tm.remove(>4>);> >// Printing updated TreeMap> >System.out.println(tm);> >}> }> |
>
>Izvade
{1=Geeks, 2=Geeks, 3=Geeks, 4=For} {1=Geeks, 2=Geeks, 3=Geeks}> 4. darbība: Atkārtošana, izmantojot TreeMap
Ir vairāki veidi, kā atkārtot karti. Slavenākais veids ir izmantot a katrai cilpai un paņem atslēgas. Atslēgas vērtība tiek atrasta, izmantojot metodi getValue(). .
Piemērs
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Iterating over TreeMap> // using> // Importing required classes> import> java.util.*;> // Main class> class> GFG {> >// Main driver method> >public> static> void> main(String args[])> >{> >// Initialization of a TreeMap> >// using Generics> >TreeMap tm> >=>new> TreeMap();> >// Inserting the elements> >// using put() method> >tm.put(>3>,>'Geeks'>);> >tm.put(>2>,>'For'>);> >tm.put(>1>,>'Geeks'>);> >// For-each loop for traversal over Map> >// via entrySet() Method> >for> (Map.Entry mapElement : tm.entrySet()) {> >int> key = (>int>)mapElement.getKey();> >// Finding the value> >String value = (String)mapElement.getValue();> >// Printing the key and value> >System.out.println(key +>' : '> + value);> >}> >}> }> |
>
>Izvade
1 : Geeks 2 : For 3 : Geeks>
TreeMap priekšrocības:
- Kārtotā secība: TreeMap nodrošina elementu sakārtotu secību, pamatojoties uz atslēgu dabisko secību vai pielāgotu salīdzinātāju, kas nodots konstruktoram. Tas padara to noderīgu situācijās, kad elementi ir jāizgūst noteiktā secībā.
- Paredzamā iterācijas secība: tā kā TreeMap elementi tiek glabāti sakārtotā secībā, varat paredzēt secību, kādā tie tiks atgriezti iterācijas laikā, tādējādi atvieglojot algoritmu rakstīšanu, kas apstrādā elementus noteiktā secībā.
- Meklēšanas veiktspēja: TreeMap nodrošina efektīvu kartes saskarnes ieviešanu, ļaujot izgūt elementus logaritmiskā laikā, padarot to noderīgu meklēšanas algoritmos, kur elementi ir jāizgūst ātri.
- Pašbalansēšana: TreeMap tiek ieviests, izmantojot sarkanmelno koku, kas ir pašbalansējoša binārā meklēšanas koka veids. Tas nodrošina efektīvu elementu pievienošanas, noņemšanas un izgūšanas veiktspēju, kā arī elementu sakārtotības saglabāšanu.
TreeMap trūkumi:
- Lēns elementu ievietošanai: elementu ievietošana TreeMap var būt lēnāka nekā elementu ievietošana parastajā kartē, jo TreeMap ir jāsaglabā elementu sakārtotā secība.
- Taustiņu ierobežojums: TreeMap taustiņiem ir jāievieš interfeiss java.lang.Comparable, vai arī ir jānodrošina pielāgots Comparator. Tas var būt ierobežojums, ja jums ir jāizmanto pielāgotas atslēgas, kas neīsteno šo saskarni.
Uzziņu grāmatas:
Morisa Naftalina un Filipa Veidlera Java kolekcijas. Šī grāmata sniedz visaptverošu pārskatu par Java kolekciju sistēmu, tostarp TreeMap.
Deivids Flanagans Java īsumā. Šajā grāmatā ir sniegta ātra uzziņa par Java galvenajām funkcijām, tostarp TreeMap.
Morisa Naftalina un Filipa Veidlera Java vispārīgie materiāli un kolekcijas. Šajā grāmatā ir sniegts visaptverošs ceļvedis par vispārīgajām zālēm un kolekcijām Java, tostarp TreeMap.
