Mēs varam izveidot java programmu, lai kārtotu masīva elementus, izmantojot atlases kārtošanu. Atlases kārtošanas algoritmā mēs meklējam zemāko elementu un sakārtojam to pareizajā vietā. Mēs apmainām pašreizējo elementu ar nākamo mazāko skaitli.
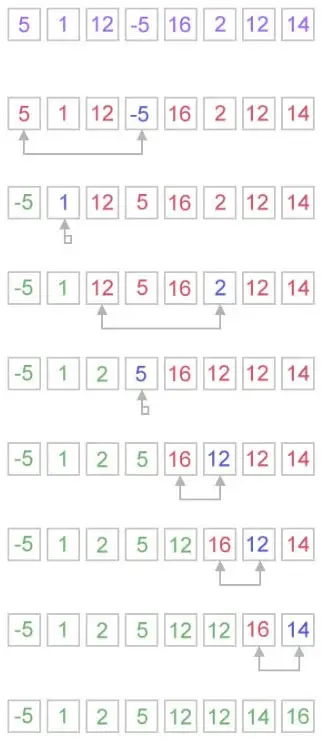
Kā darbojas atlases kārtošana?
Atlases kārtošanas algoritms darbojas ļoti vienkāršā veidā. Tas uztur divus apakšmasīvus dotajam masīvam.
1 miljards uz miljonu
- Apakšbloks jau ir sakārtots.
- Un otrā apakšgrupa ir nešķirota.
Katrā atlases kārtošanas iterācijā elements tiek atlasīts no nešķirotā apakšgrupas un pārvietots uz sakārtoto apakšgrupu.
pelēks kods
arr[] = 25 35 45 12 65 10 // Find the minimum element in arr[0...5] and place it at beginning. 10 25 35 45 12 65 // Find the minimum element in arr[1...5] and place it at beginning of arr[1...5] 10 12 25 35 45 65 // Find the minimum element in arr[2...5] and place it at beginning of arr[2...5] No, you can see that the array is already sorted. 10 12 25 35 45 65
Laika sarežģītība
Labākais: ?(n^2)Vidēji: ?(n^2)
Sliktākais: O(n^2)
Kosmosa sarežģītība
O(1)Atlase Kārtot Java piemērs
public class SelectionSortExample { public static void selectionSort(int[] arr){ for (int i = 0; i <arr.length - 1; i++) { int index="i;" for (int j="i" + < arr.length; j++){ if (arr[j] arr[index]){ lowest } smallernumber="arr[index];" arr[index]="arr[i];" arr[i]="smallerNumber;" public static void main(string a[]){ int[] arr1="{9,14,3,2,43,11,58,22};" system.out.println('before selection sort'); for(int i:arr1){ system.out.print(i+' '); system.out.println(); selectionsort(arr1); sorting array using sort system.out.println('after pre> <p>Output:</p> <pre> Before Selection Sort 9 14 3 2 43 11 58 22 After Selection Sort 2 3 9 11 14 22 43 58 </pre> <h2>Selection Sort in Java (Another way)</h2> <p>You can also use a method where array is not predefined. Here, user has to put the elements as input.</p> <p>In the following Java program, we ask user to enter the array elements or number, now compare the array's element and start swapping with the variable temp. Put the first element in the temp and the second element in the first, and then temp in the second number and continue for the next match to sort the whole array in ascending order.</p> <pre> import java.util.Scanner; public class SelectionSortExample2 { public static void main(String args[]) { int size, i, j, temp; int arr[] = new int[50]; Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print('Enter Array Size : '); size = scan.nextInt(); System.out.print('Enter Array Elements : '); for(i=0; i<size; i++) { arr[i]="scan.nextInt();" } system.out.print('sorting array using selection sort technique..
'); for(i="0;" i<size; for(j="i+1;" j arr[j]) temp="arr[i];" arr[j]="temp;" system.out.print('now the after sorting is :
'); system.out.print(arr[i]+ ' '); < pre> <p>Output:</p> <strong> Use image SelectionSort</strong> </size;></pre></arr.length> Atlases kārtošana Java (cits veids)
Varat arī izmantot metodi, kurā masīvs nav iepriekš definēts. Šeit lietotājam ir jāievieto elementi kā ievade.
Nākamajā Java programmā mēs lūdzam lietotāju ievadīt masīva elementus vai numuru, tagad salīdziniet masīva elementu un sāciet mijmaiņu ar mainīgo temp. Ievietojiet pirmo elementu temp un otro elementu pirmajā, un pēc tam temp otrajā ciparā un turpiniet līdz nākamajai atbilstībai, lai sakārtotu visu masīvu augošā secībā.
import java.util.Scanner; public class SelectionSortExample2 { public static void main(String args[]) { int size, i, j, temp; int arr[] = new int[50]; Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print('Enter Array Size : '); size = scan.nextInt(); System.out.print('Enter Array Elements : '); for(i=0; i<size; i++) { arr[i]="scan.nextInt();" } system.out.print(\'sorting array using selection sort technique..
\'); for(i="0;" i<size; for(j="i+1;" j arr[j]) temp="arr[i];" arr[j]="temp;" system.out.print(\'now the after sorting is :
\'); system.out.print(arr[i]+ \' \'); < pre> <p>Output:</p> <strong> Use image SelectionSort</strong> </size;>