Dots taisnstūrveida papīrs ar izmēriem a x b . Uzdevums ir sagriezt visu papīru minimums skaits kvadrāts gabaliem. Mēs varam izvēlēties jebkura izmēra kvadrātveida gabalus, bet tie ir jāsagriež nepārklājoties un neatstājot papildu vietu .
Piemēri:
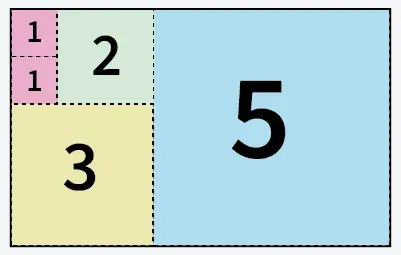
Ievade: a = 5 b = 8
fibonači sērija gadsimtā5 kvadrāti, kas izgriezti no 5 x 8 izmēra papīra
Izvade: 5
Paskaidrojums: Mēs varam sagriezt papīru 5 kvadrātos: 1 kvadrāts ar izmēru 5x5 1 kvadrāts ar izmēru 3x3 1 kvadrāts ar izmēru 2x2 un 2 kvadrāti ar izmēru 1x1.Ievade: a = 13 b = 11
6 kvadrāti, kas izgriezti no papīra ar izmēru 13 x 11
Izvade: 6
Paskaidrojums: Mēs varam sagriezt papīru 6 kvadrātos: 1 kvadrāts ar izmēru 7x7 1 kvadrāts ar izmēru 6x6 1 kvadrāts ar izmēru 5x5 2 kvadrāts ar izmēru 4x4 un 1 kvadrāts ar izmēru 1x1.Ievade: a = 6 b = 7
5 kvadrāti, kas izgriezti no 6 x 7 izmēra papīra
Izvade: 5
Paskaidrojums: Mēs varam sagriezt papīru 5 kvadrātos: 1 kvadrāts ar izmēru 4x4, 2 kvadrāti ar izmēru 3x3 un 2 kvadrāti ar izmēru 3x3.
Satura rādītājs
- [Nepareiza pieeja 1] Mantkārīgas tehnikas izmantošana
- [Nepareiza pieeja 2] Dinamiskās programmēšanas izmantošana
- [Pareizā pieeja] Izmantojot DFS un dinamisko programmēšanu
[Nepareiza pieeja 1] Mantkārīgas tehnikas izmantošana
No pirmā acu uzmetiena varētu šķist, ka problēmu var viegli atrisināt, vispirms izgriežot lielāko iespējamo kvadrātu no papīra, pēc tam izgriežot lielāko kvadrātu no atlikušā papīra un tā tālāk, līdz esam izgriezuši visu papīru. Bet šis risinājums ir nepareizs.
Kāpēc mantkārīgā pieeja nedarbosies?
Apsveriet papīra izmēru 6x7 tad, ja mēģināsim alkatīgi griezt papīru, mēs saņemsim 7 kvadrāti: 1 izmēra kvadrāts 6x6 un 6 kvadrātu izmērs 1x1 tā kā pareizais risinājums ir: 5. Tāpēc mantkārīga pieeja nedarbosies.
pievienojot virkni java
[Nepareiza pieeja 2] Dinamiskās programmēšanas izmantošana
Dinamiskā programmēšana ar vertikāliem vai horizontāliem griezumiem: Vēl viens risinājums, kas varētu šķist pareizs, ir izmantošana Dinamiskā programmēšana . Mēs varam uzturēt dp[][] tabulu tā, lai dp[i][j] = minimālais kvadrātu skaits, ko var izgriezt no izmēra papīra i x j . Tad par papīra izmēru axb
- Mēs varam mēģināt to sagriezt katrā rindā: dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] 1 + dp[i - k][j] + dp[k][j]) kur k var būt diapazonā [1 i - 1].
- Mēs varam mēģināt to izgriezt pa katru kolonnu: dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] 1 + dp[i][j - k] + dp[i][k]) kur k var būt diapazonā [1 j - 1].
Beidzot visu samazinājumu minimums būs atbilde. Bet arī šis risinājums ir nepareizs.
Kāpēc griešana vertikāli vai horizontāli, izmantojot dinamiskās programmēšanas pieeju, nedarbosies?
Tas nedarbosies, jo mēs pieņemam, ka vertikāls vai horizontāls griezums vienmēr sadalīs taisnstūri divās daļās. Apsveriet papīra izmēru 13x11 tad, ja mēs mēģināsim izgriezt papīru, izmantojot DP pieeju, mēs iegūsim 8 kvadrātus, bet pareizā atbilde (kā parādīts piemēros) ir 6. Tādējādi dinamiskā programmēšana nedarbosies.
[Pareizā pieeja] Izmantojot DFS un dinamisko programmēšanu
C++The ideja ir izgriezt visu papīru, izmantojot DFS iekšā no apakšas uz augšu veidā. Katrā solī atrodiet papīra zemāko kreiso stūri un mēģiniet no šī stūra izgriezt visu iespējamo izmēru kvadrātus. Pēc kvadrāta izgriešanas vēlreiz atrodiet atlikušā papīra zemāko kreiso stūri, lai izgrieztu visu iespējamo izmēru kvadrātus un tā tālāk. Bet, ja mēs izmēģinātu visus iespējamos griezumus no katra iespējamā papīra izmēra apakšējā kreisā stūra, tas būtu diezgan neefektīvi. Mēs varam to optimizēt, izmantojot Dinamiskā programmēšana lai saglabātu minimālos izgriezumus katram iespējamajam papīra izmēram.
Lai unikāli identificētu jebkuru papīra izmēru, mēs varam uzturēt remSq[] masīvu tā, lai remSq[i] saglabātu atlikušo kvadrātu skaitu ar izmēru 1x1 papīra i-tajā kolonnā. Tātad papīram ar izmēru 6x7 remSq[] = {6 6 6 6 6 6 6}. Arī, lai atrastu zemāko kreiso stūri, mēs atradīsim pirmo indeksu ar maksimālo atlikušo kvadrātu skaitu. Tātad mēs varam sajaukt remSq[] masīva vērtību, lai atrastu unikālu atslēgu visām iespējamajām remSq[] masīva vērtībām.
// C++ Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb #include
// Java Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb import java.util.*; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey(int[] remSq int b) { int base = 1; int key = 0; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * base); base = base * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil(int[] remSq int a int b Map<Integer Integer> memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey(remSq b); if (memo.containsKey(key)) return memo.get(key); int maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq == 0) return 0; end = start; int[] newRemSq = Arrays.copyOf(remSq b); int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo.put(key ans); return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut(int a int b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a == b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int[] remSq = new int[b]; Arrays.fill(remSq a); Map<Integer Integer> memo = new HashMap<>(); return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Sample Input int a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb System.out.println(minCut(a b)); } }
# Python Program to find minimum number of squares to cut # from a paper of size axb # function to get the hash key for remSq array def getKey(remSq b): base = 1 key = 0 for i in range(b): key += remSq[i] * base base = base * (b + 1) return key # Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts # for a given remSq array def minCutUtil(remSq a b memo): # pointers to mark the start and end of range # with maximum remaining squares start = 0 # Check if we have previously calculated the answer # for the same state key = getKey(remSq b) if key in memo: return memo[key] maxRemSq = 0 # Find the starting point of min height for i in range(b): if remSq[i] > maxRemSq: maxRemSq = remSq[i] start = i # If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already # cut the entire paper if maxRemSq == 0: return 0 end = start newRemSq = remSq[:] ans = float('inf') # Find the ending point of min height while end < b: # length of edge of square from start till current end squareEdge = end - start + 1 # If the current column does not have maximum remaining # squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of # size squareEdge then break out of the loop if newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq or newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0: break # If we can cut a square of size squareEdge # update the remainingSquares for i in range(start end + 1): newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge # Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)) end += 1 memo[key] = ans return ans # Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut # using paper of size a X b def minCut(a b): # if the given rectangle is a square if a == b: return 1 # Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns remSq = [a] * b memo = {} return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo) if __name__ == '__main__': # Sample Input a = 13 b = 11 # Function call to get minimum number # of squares for axb print(minCut(a b))
// C# Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey(int[] remSq int b) { int baseVal = 1; int key = 0; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * baseVal); baseVal = baseVal * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil(int[] remSq int a int b Dictionary<int int> memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey(remSq b); if (memo.ContainsKey(key)) return memo[key]; int maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq == 0) return 0; end = start; int[] newRemSq = (int[])remSq.Clone(); int ans = int.MaxValue; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.Min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo[key] = ans; return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut(int a int b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a == b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int[] remSq = new int[b]; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) remSq[i] = a; Dictionary<int int> memo = new Dictionary<int int>(); return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } static void Main() { int a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb Console.WriteLine(minCut(a b)); } }
// JavaScript Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb // function to get the hash key for remSq array function getKey(remSq b) { let base = 1; let key = 0; for (let i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * base); base = base * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array function minCutUtil(remSq a b memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares let start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state let key = getKey(remSq b); if (key in memo) return memo[key]; let maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (let i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq === 0) return 0; end = start; let newRemSq = remSq.slice(); let ans = Infinity; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end let squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] !== maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (let i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo[key] = ans; return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b function minCut(a b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a === b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns let remSq = new Array(b).fill(a); let memo = {}; return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } // Driver Code let a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb console.log(minCut(a b));
Izvade
6
Laika sarežģītība: O(a^b) katrai no b kolonnām var būt kvadrāts.
Palīgtelpa: O(a^b) memoizācijas dēļ, saglabājot katru unikālo stāvokli.

 5 kvadrāti, kas izgriezti no 5 x 8 izmēra papīra
5 kvadrāti, kas izgriezti no 5 x 8 izmēra papīra 6 kvadrāti, kas izgriezti no papīra ar izmēru 13 x 11
6 kvadrāti, kas izgriezti no papīra ar izmēru 13 x 11 5 kvadrāti, kas izgriezti no 6 x 7 izmēra papīra
5 kvadrāti, kas izgriezti no 6 x 7 izmēra papīra