Dažreiz mums ir jāpārbauda mainīgā datu tips, lai aprēķinātu datus, jo mēs varam veikt loģisko darbību ar tāda paša veida mainīgajiem. Lai pārbaudītu datu tipu, mēs izmantojam metodi getClass() un getSimpleName(), lai iegūtu attiecīgi klasi un tās nosaukumu. Šajā sadaļā mēs apspriedīsim kā pārbaudīt datu tipu Java?
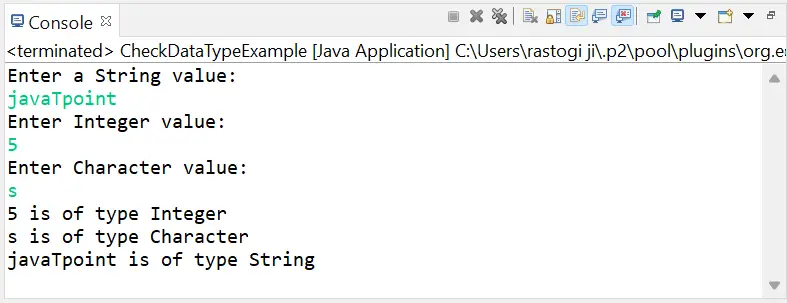
Ieviesīsim kodu mainīgo datu tipu iegūšanai. Vispirms mēs ņemam ievadi no lietotāja un pēc tam atrodam to mainīgo datu tipu, kuros tiks saglabāta lietotāja ievade.
CheckDataTypeExample.java
import java.util.*; // create class CheckDataTypeExample to check the datatype of the variable public class CheckDataTypeExample { // main() method start public static void main(String args[]) { // declare variables int intData; char charData; // create Scanner class object to take input from user Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); // take input from the user to initialize variables System.out.println('Enter a String value:'); String str = sc.nextLine(); System.out.println('Enter Integer value:'); intData = sc.nextInt(); System.out.println('Enter Character value:'); charData = sc.next().charAt(0); // close Scanner class object sc.close(); // show datatypes of variables by using getClass() and getSimpleName() methods System.out.println(intData + ' is of type ' + ((Object)intData).getClass().getSimpleName()); System.out.println(charData + ' is of type ' + ((Object)charData).getClass().getSimpleName()); System.out.println(str + ' is of type ' + str.getClass().getSimpleName()); } } Izvade:
java rakstzīme uz int
Tagad mums ir īpaša metode, t.i., getType() nodrošina java.lang.reflect.Field un Character klases. Izpratīsim abu klašu metodi getType() pa vienai.
Field.getType()
The getType() metode lauks klase tiek izmantota, lai iegūtu lauka veidu, ko nosaka lauks objekts. Atgriešanas vērtība palīdz mums noteikt lauka veidu.
Sintakse:
Sintakse getType() metode ir šāda:
public String getType()
Parametrs: Tas nepieņem argumentus kā parametru.
Atgriež: Tas atgriež klases objektu, kas palīdz mums noteikt lauka veidu.
Ņemsim getType() metodes piemēru un sapratīsim, kā tā darbojas:
GetTypeExample1.java
// import required classes and package if any import java.lang.reflect.Field; // create class GetTypeExample1 to get the type of the Field public class GetTypeExample1 { // main() method start public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { //get the name field object by using getField() method Field nameField = Student.class.getField('name'); // use getTyoe() method of the Field to get the type of name field Class value = nameField.getType(); // print the type of name field System.out.println('The type of the name field is ' + value); //get the totalMarks field object by using getField() method Field marksField = Student.class.getField('totalMarks'); // use getTyoe() method of the Field to get the type of totalMarks field value = marksField.getType(); // print the type of name field System.out.println('The type of the totalMarks field is ' + value); //get the totalFees field object by using getField() method Field feesField = Student.class.getField('totalFees'); // use getTyoe() method of the Field to get the type of name field value = feesField.getType(); // print the type of the totalFees field System.out.println('The type of the totalFees field is ' + value); } } // create a simple student class class Student { // declare and initialize variables public static String name = 'John'; public static double totalMarks = 380; public static float totalFees = 3413.99f; // getter for student name public static String getName() { return name; } // setter for student name public static void setName(String stdName) { name = stdName; } // getter for totalMarks public static double getTotalMarks() { return totalMarks; } // setter for totalMarks public static void setMarks(double marks) { totalMarks = marks; } // getter for totalFees public static float getTotalFees() { return totalFees; } // setter for totalFees public static void setFees(float fees) { totalFees = fees; } } Izvade:
kā palaist skriptu Linux

Izmantojot Field.getType() metodi
The getType() metode Raksturs klase tiek izmantota, lai iegūtu dotās rakstzīmes vispārīgo kategoriju. GetType() metodei ir divas variācijas, kuru pamatā ir parametrs, t.i., Character.getType(char ch) un Character.getType(int codePoint) .
Metode getType(), kas izmanto char kā parametru, nevar apstrādāt papildu rakstzīmes, savukārt metode getType(), kas izmanto int kā parametru, var apstrādāt papildu rakstzīmes.
Sintakse:
The getType() metode Raksturs klasei ir šāda sintakse:
vai abstraktai klasei var būt konstruktors
public static int getType(char ch) public static int getType(int codePoint)
Parametrs: Pirmais getType() metodes variants pieņem tipa parametru char un otrais metodes variants pieņem int tipa parametru, t.i., codePoint.
Atgriež: Abas metodes atgriež vesela skaitļa vērtību, kas norāda rakstzīmju vispārējo kategoriju.
Ņemsim getType() metodes piemēru un sapratīsim, kā tā darbojas:
GetTypeExample2.java
// import required classes and package if any // create class GetTypeExample2 to get the general category of the given character public class GetTypeExample2 { // main() method start public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { // use setter to set ch1, ch2 in CharData CharData.setChar1('C'); CharData.setChar2('%'); // use getter to get char1 and char2 char char1 = CharData.getChar1(); char char2 = CharData.getChar2(); // use getType() method of Character class int val1 = Character.getType(char1); int val2 = Character.getType(char2); // print categories of char1 and char2 System.out.println('The category of ' +char1 + ' is '+ val1); System.out.println('The category of ' +char2 + ' is '+ val2); } } // create a simple CharData class class CharData { // declare variables of type char static char ch1, ch2; // getter for ch1 public static char getChar1() { return ch1; } // setter for ch1 public static void setChar1(char ch) { ch1 = ch; } // getter for ch2 public static char getChar2() { return ch2; } // setter for ch2 public static void setChar2(char ch) { ch2 = ch; } } Izvade:

GetTypeExample3.java
// import required classes and package if any import java.lang.reflect.Field; // create class GetTypeExample3 to get the general category of the given character public class GetTypeExample3 { // main() method start public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { // use setter to set code1, code2 in CodePoint CodePoint.setCodePoint1(0x0037); CodePoint.setCodePoint2(0x016f); // use getter to get code1 and code2 int code1 = CodePoint.getCodePoint1(); int code2 = CodePoint.getCodePoint2(); // use getType() method of Character class int val1 = Character.getType(code1); int val2 = Character.getType(code2); // print categories of char1 and char2 System.out.println('The category of ' +code1+ ' is '+ val1); System.out.println('The category of ' +code2+ ' is '+ val2); } } // create a simple CodePoint class class CodePoint { // declare variables of type int static int codePoint1, codePoint2; // getter for codePoint1 public static int getCodePoint1() { return codePoint1; } // setter for codePoint1 public static void setCodePoint1(int code1) { codePoint1 = code1; } // getter for codePoint2 public static int getCodePoint2() { return codePoint2; } // setter for codePoint2 public static void setCodePoint2(int code2) { codePoint2 = code2; } } Izvade:

