Masīvs ir vienkāršākā C datu struktūra, kas glabā viendabīgus datus blakus esošās atmiņas vietās. Ja vēlamies izveidot masīvu, mēs deklarējam datu tipu un piešķiram tam elementus:
#include int main() { int i, arr[5] = {1, 2, 4, 2, 4}; for(i = 0; i <5; i++) { printf('%d ', arr[i]); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> 1 2 4 2 4 </pre> <p>In C, a Character and a String are separate data types, unlike other programming languages like Python. A String is a collection of Characters. Hence, to define a String, we use a Character Array:</p> <pre> #include int main() { char str[8]; printf('Enter a String: '); scanf('%s', &str); printf('%s', str); } </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> Enter a String: Hello Hello </pre> <p>Now, we want to create an Array of Strings which means we are trying to create an Array of Character Arrays. We have two ways we can do this:</p> <ol class="points"> <li>Using Two-dimensional Arrays</li> <li>Using Pointers</li> </ol> <h3>Using Two-dimensional Arrays:</h3> <p>Creating a String Array is one of the applications of two-dimensional Arrays. To get a picture of the arrangement, observe the below representation:</p> <p>For suppose we want to create an Array of 3 Strings of size 5:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/46/an-array-strings-c.webp" alt="An Array of Strings in C"> <p>Every String in a String Array must terminate with a null Character. It is the property of a String in C.</p> <p> <strong>Syntax to create a 2D Array:</strong> </p> <pre> Data_type name[rows][columns] = {{values in row 1}, {values in row 2}…}; </pre> <p> <strong>Syntax to create a String Array:</strong> </p> <pre> char Array[rows][columns] = {'String1', 'String2'...}; </pre> <p> <strong>Now, let us create an example String Array:</strong> </p> <ul> <li>Observe that when we assign the number of rows and columns, we need to consider the Null Character to the length.</li> </ul> <pre> #include int main() { int i; char Array[3][6] = {'Black', 'Blame', 'Block'}; printf('String Array:
'); for(i = 0; i <3; i++) { printf('%s
', array[i]); } return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> String Array: Black Blame Block </pre> <ul> <li>char Array[3][6] = {'Black', 'Blame', 'Black'} -> {{'B', 'l', 'a', 'c', 'k', '�'}, {'B', 'l', 'a', 'm', 'e', '�'}, {'B', 'l', 'a', 'c', 'k', '�'}}</li> <li>We cannot directly manipulate the Strings in the Array as a String is an immutable data type. The compiler raises an error:</li> </ul> <pre> char Array[0] = 'Hello'; </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> [Error] assignment to expression with Array type </pre> <ul> <li>We can use the strcpy() function to copy the value by importing the String header file:</li> </ul> <pre> char Array[3][6] = {'Black', 'Blame', 'Block'}; strcpy(Array[0], 'Hello'); for(i = 0; i <3; i++) { printf('%s
', array[i]); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> String Array: Hello Blame Block </pre> <p> <strong>The Disadvantage of using 2D Arrays:</strong> </p> <p>Suppose we want to store 4 Strings in an Array: {'Java', 'T', 'point', 'JavaTpoint'}. We will store the Strings like this:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/46/an-array-strings-c-2.webp" alt="An Array of Strings in C"> <ul> <li>The number of rows will be equal to the number of Strings, but the number of columns will equal the length of the longest String.</li> <li>The memory allocated to all the Strings will be the size of the longest String, causing ' <strong>Memory wastage</strong> '.</li> <li>The orange part in the above representation is the memory wasted.</li> </ul> <h3>Using Pointers:</h3> <p>By using Pointers, we can avoid the Disadvantage of Memory wastage. But how do we do this?</p> <p>We need to create an Array of Pointers pointing to Strings. Hence, we need to create an Array of type ' <strong>char*</strong> '. This way, all the Strings are stored elsewhere in the exactly needed memory, and the Pointers in the Array point to those memory locations causing no memory wastage. More specifically, the Pointers in the Array point to the first Character of the Strings.</p> <p> <strong>Syntax to create an Array of Pointers:</strong> </p> <p>Data Type* name[] = {'Value 1', 'Value 2'…};</p> <p> <strong>Syntax to create an Array of String Pointers:</strong> </p> <p>char* Array[] = {'String 1', 'String 2'…};</p> <p> <strong>Representation:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/46/an-array-strings-c-3.webp" alt="An Array of Strings in C"> <p> <strong>Now, let us create an example String Array:</strong> </p> <pre> #include #include int main() { int i; char* Array[] = {'HI', 'UP', 'AT'}; printf('String Array:
'); for(i = 0; i <3; i++) { printf('%s
', array[i]); } return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> String Array: HI UP AT </pre> <h3>Summary:</h3> <p>We cannot create a String Array like a normal one, as a String is an Array of Characters. We have two ways to do this:</p> <p> <strong>1. Using a Two-Dimensional Array:</strong> </p> <p>The Disadvantage of using this way is ' <strong>Memory wastage</strong> ,' as the memory allocated to every String in the Array will be the memory required to store the longest String of the Array.</p> <p> <strong>2. Using Pointers:</strong> </p> <p>Using Pointers, we create a single-dimensional Array of Pointers pointing to Strings. Following this method can eliminate the 'Memory wastage' Disadvantage.</p> <hr></3;></pre></3;></pre></3;></pre></5;> C valodā rakstzīme un virkne ir atsevišķi datu tipi, atšķirībā no citām programmēšanas valodām, piemēram, Python. Virkne ir rakstzīmju kolekcija. Tādējādi, lai definētu virkni, mēs izmantojam rakstzīmju masīvu:
#include int main() { char str[8]; printf('Enter a String: '); scanf('%s', &str); printf('%s', str); } Izvade:
Enter a String: Hello Hello
Tagad mēs vēlamies izveidot virkņu masīvu, kas nozīmē, ka mēs cenšamies izveidot rakstzīmju masīvu masīvu. Mums ir divi veidi, kā to izdarīt:
- Divdimensiju masīvu izmantošana
- Rādītāju izmantošana
Izmantojot divdimensiju masīvus:
Virkņu masīva izveide ir viens no divdimensiju masīvu lietojumiem. Lai iegūtu priekšstatu par izkārtojumu, ievērojiet tālāk redzamo attēlojumu:
Pieņemsim, ka mēs vēlamies izveidot 3 5 izmēra virkņu masīvu:
json json piemērā
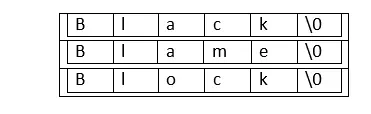
Katrai virknei virkņu masīvā ir jābeidzas ar nulles rakstzīmi. Tas ir virknes īpašums C valodā.
Sintakse 2D masīva izveidei:
Data_type name[rows][columns] = {{values in row 1}, {values in row 2}…}; Sintakse, lai izveidotu virknes masīvu:
char Array[rows][columns] = {'String1', 'String2'...}; Tagad izveidosim virkņu masīva piemēru:
- Ievērojiet, ka, piešķirot rindu un kolonnu skaitu, garumam ir jāņem vērā Null rakstzīme.
#include int main() { int i; char Array[3][6] = {'Black', 'Blame', 'Block'}; printf('String Array:
'); for(i = 0; i <3; i++) { printf(\'%s
\', array[i]); } return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> String Array: Black Blame Block </pre> <ul> <li>char Array[3][6] = {'Black', 'Blame', 'Black'} -> {{'B', 'l', 'a', 'c', 'k', '�'}, {'B', 'l', 'a', 'm', 'e', '�'}, {'B', 'l', 'a', 'c', 'k', '�'}}</li> <li>We cannot directly manipulate the Strings in the Array as a String is an immutable data type. The compiler raises an error:</li> </ul> <pre> char Array[0] = 'Hello'; </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> [Error] assignment to expression with Array type </pre> <ul> <li>We can use the strcpy() function to copy the value by importing the String header file:</li> </ul> <pre> char Array[3][6] = {'Black', 'Blame', 'Block'}; strcpy(Array[0], 'Hello'); for(i = 0; i <3; i++) { printf(\'%s
\', array[i]); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> String Array: Hello Blame Block </pre> <p> <strong>The Disadvantage of using 2D Arrays:</strong> </p> <p>Suppose we want to store 4 Strings in an Array: {'Java', 'T', 'point', 'JavaTpoint'}. We will store the Strings like this:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/46/an-array-strings-c-2.webp" alt="An Array of Strings in C"> <ul> <li>The number of rows will be equal to the number of Strings, but the number of columns will equal the length of the longest String.</li> <li>The memory allocated to all the Strings will be the size of the longest String, causing ' <strong>Memory wastage</strong> '.</li> <li>The orange part in the above representation is the memory wasted.</li> </ul> <h3>Using Pointers:</h3> <p>By using Pointers, we can avoid the Disadvantage of Memory wastage. But how do we do this?</p> <p>We need to create an Array of Pointers pointing to Strings. Hence, we need to create an Array of type ' <strong>char*</strong> '. This way, all the Strings are stored elsewhere in the exactly needed memory, and the Pointers in the Array point to those memory locations causing no memory wastage. More specifically, the Pointers in the Array point to the first Character of the Strings.</p> <p> <strong>Syntax to create an Array of Pointers:</strong> </p> <p>Data Type* name[] = {'Value 1', 'Value 2'…};</p> <p> <strong>Syntax to create an Array of String Pointers:</strong> </p> <p>char* Array[] = {'String 1', 'String 2'…};</p> <p> <strong>Representation:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/46/an-array-strings-c-3.webp" alt="An Array of Strings in C"> <p> <strong>Now, let us create an example String Array:</strong> </p> <pre> #include #include int main() { int i; char* Array[] = {'HI', 'UP', 'AT'}; printf('String Array:
'); for(i = 0; i <3; i++) { printf(\'%s
\', array[i]); } return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> String Array: HI UP AT </pre> <h3>Summary:</h3> <p>We cannot create a String Array like a normal one, as a String is an Array of Characters. We have two ways to do this:</p> <p> <strong>1. Using a Two-Dimensional Array:</strong> </p> <p>The Disadvantage of using this way is ' <strong>Memory wastage</strong> ,' as the memory allocated to every String in the Array will be the memory required to store the longest String of the Array.</p> <p> <strong>2. Using Pointers:</strong> </p> <p>Using Pointers, we create a single-dimensional Array of Pointers pointing to Strings. Following this method can eliminate the 'Memory wastage' Disadvantage.</p> <hr></3;></pre></3;></pre></3;> - char Array[3][6] = {'Melns', 'Blame', 'Melns'} -> {{'B', 'l', 'a', 'c', 'k', '�' }, {'B', 'l', 'a', 'm', 'e', '�'}, {'B', 'l', 'a', 'c', 'k', '�'}}
- Mēs nevaram tieši manipulēt ar virknēm masīvā, jo virkne ir nemainīgs datu tips. Kompilators rada kļūdu:
char Array[0] = 'Hello';
Izvade:
kā izlauzties no brīža cilpas java
[Error] assignment to expression with Array type
- Mēs varam izmantot funkciju strcpy (), lai kopētu vērtību, importējot Virknes galvenes failu:
char Array[3][6] = {'Black', 'Blame', 'Block'}; strcpy(Array[0], 'Hello'); for(i = 0; i <3; i++) { printf(\'%s
\', array[i]); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> String Array: Hello Blame Block </pre> <p> <strong>The Disadvantage of using 2D Arrays:</strong> </p> <p>Suppose we want to store 4 Strings in an Array: {'Java', 'T', 'point', 'JavaTpoint'}. We will store the Strings like this:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/46/an-array-strings-c-2.webp" alt="An Array of Strings in C"> <ul> <li>The number of rows will be equal to the number of Strings, but the number of columns will equal the length of the longest String.</li> <li>The memory allocated to all the Strings will be the size of the longest String, causing ' <strong>Memory wastage</strong> '.</li> <li>The orange part in the above representation is the memory wasted.</li> </ul> <h3>Using Pointers:</h3> <p>By using Pointers, we can avoid the Disadvantage of Memory wastage. But how do we do this?</p> <p>We need to create an Array of Pointers pointing to Strings. Hence, we need to create an Array of type ' <strong>char*</strong> '. This way, all the Strings are stored elsewhere in the exactly needed memory, and the Pointers in the Array point to those memory locations causing no memory wastage. More specifically, the Pointers in the Array point to the first Character of the Strings.</p> <p> <strong>Syntax to create an Array of Pointers:</strong> </p> <p>Data Type* name[] = {'Value 1', 'Value 2'…};</p> <p> <strong>Syntax to create an Array of String Pointers:</strong> </p> <p>char* Array[] = {'String 1', 'String 2'…};</p> <p> <strong>Representation:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/46/an-array-strings-c-3.webp" alt="An Array of Strings in C"> <p> <strong>Now, let us create an example String Array:</strong> </p> <pre> #include #include int main() { int i; char* Array[] = {'HI', 'UP', 'AT'}; printf('String Array:
'); for(i = 0; i <3; i++) { printf(\'%s
\', array[i]); } return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> String Array: HI UP AT </pre> <h3>Summary:</h3> <p>We cannot create a String Array like a normal one, as a String is an Array of Characters. We have two ways to do this:</p> <p> <strong>1. Using a Two-Dimensional Array:</strong> </p> <p>The Disadvantage of using this way is ' <strong>Memory wastage</strong> ,' as the memory allocated to every String in the Array will be the memory required to store the longest String of the Array.</p> <p> <strong>2. Using Pointers:</strong> </p> <p>Using Pointers, we create a single-dimensional Array of Pointers pointing to Strings. Following this method can eliminate the 'Memory wastage' Disadvantage.</p> <hr></3;></pre></3;> 2D masīvu izmantošanas trūkums:
Pieņemsim, ka mēs vēlamies saglabāt 4 virknes masīvā: {'Java', 'T', 'point', 'JavaTpoint'}. Mēs saglabāsim virknes šādi:

- Rindu skaits būs vienāds ar virkņu skaitu, bet kolonnu skaits būs vienāds ar garākās virknes garumu.
- Visām virknēm atvēlētā atmiņa būs garākās virknes lielumā, izraisot ' Atmiņas izšķērdēšana '.
- Oranžā daļa iepriekš minētajā attēlojumā ir izniekota atmiņa.
Izmantojot rādītājus:
Izmantojot norādes, mēs varam izvairīties no atmiņas izšķērdēšanas trūkuma. Bet kā mēs to darām?
Mums ir jāizveido rādītāju masīvs, kas norāda uz virknēm. Tāpēc mums ir jāizveido masīvs ar tipu ' char* '. Tādā veidā visas virknes tiek glabātas citur tieši vajadzīgajā atmiņā, un rādītāji masīvā norāda uz šīm atmiņas vietām, neizraisot atmiņas zudumu. Konkrētāk, norādes masīvā norāda uz pirmo virkņu rakstzīmi.
Sintakse, lai izveidotu rādītāju masīvu:
Datu tips* name[] = {'Vērtība 1', 'Vērtība 2'…};
Sintakse, lai izveidotu virknes rādītāju masīvu:
char* Array[] = {'1. virkne', '2. virkne'...};
Pārstāvība:

Tagad izveidosim virkņu masīva piemēru:
#include #include int main() { int i; char* Array[] = {'HI', 'UP', 'AT'}; printf('String Array:
'); for(i = 0; i <3; i++) { printf(\'%s
\', array[i]); } return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> String Array: HI UP AT </pre> <h3>Summary:</h3> <p>We cannot create a String Array like a normal one, as a String is an Array of Characters. We have two ways to do this:</p> <p> <strong>1. Using a Two-Dimensional Array:</strong> </p> <p>The Disadvantage of using this way is ' <strong>Memory wastage</strong> ,' as the memory allocated to every String in the Array will be the memory required to store the longest String of the Array.</p> <p> <strong>2. Using Pointers:</strong> </p> <p>Using Pointers, we create a single-dimensional Array of Pointers pointing to Strings. Following this method can eliminate the 'Memory wastage' Disadvantage.</p> <hr></3;> Kopsavilkums:
Mēs nevaram izveidot virkņu masīvu kā parastu, jo virkne ir rakstzīmju masīvs. Mums ir divi veidi, kā to izdarīt:
1. Divdimensiju masīva izmantošana:
Šāda veida izmantošanas trūkums ir ' Atmiņas izšķērdēšana ”, jo katrai masīva virknei atvēlētā atmiņa būs atmiņa, kas nepieciešama, lai saglabātu garāko masīva virkni.
1 miljards uz miljonu
2. Rādītāju izmantošana:
Izmantojot rādītājus, mēs izveidojam viendimensionālu rādītāju masīvu, kas norāda uz virknēm. Šīs metodes ievērošana var novērst 'atmiņas izšķērdēšanas' trūkumu.
